Measuring Distance, Area, and Gradient
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Measuring Distance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

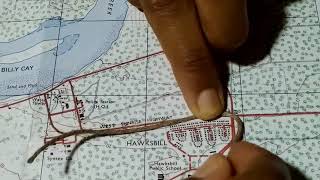
Let's start our discussion by understanding how we can measure distances on a topographical map. We can use tools like dividers, scales, or even a piece of string to measure straight and curved paths.

How do we use dividers exactly?

Good question! You open the divider to the distance you want to measure on the map, then transfer that distance to the scale at the bottom to get the actual distance on the ground.

Does it work on curved paths too?

Absolutely! For curves, you can use a piece of string to follow the path, then measure that length with the scale.

Can you give us a mnemonic to remember the steps?

Certainly! Think of the acronym 'DSS' - Divider, String, Scale! That can help you remember the tools you will use for measuring distances.

What if I have to measure a really long distance?

You could break it into segments using your divider or string for more accuracy, and then add the segments together!

To recap, we can measure distances using dividers for straight lines, strings for curves, and always check our scale for ground distances.
Measuring Area
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about measuring area. How can we accurately estimate the area shown on our maps?

Do we count squares?

Exactly! We count both full and half grid squares. Remember, each square represents 1 km².

What if I have a shape that doesn’t fit nicely into the squares?

Great observation! When the shape doesn't fit neatly, add up the full squares and estimate the half squares as needed.

Could you give me a mnemonic for area measurement?

Sure! Think of 'FHA' - Full, Half, Area. This can help remind you of what to count to estimate area!

What if we're looking at a very complex map?

Break it down into smaller segments! For complicated areas, calculating section by section can lead to a more accurate total.

To summarize, count full squares and half squares, and use the acronym 'FHA' to guide your calculations!
Measuring Gradient
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s examine how to measure gradient. This tells us how steep the terrain is!

I know we use the vertical interval and horizontal distance, but how?

Excellent! You can calculate it using the formula: Gradient = Vertical Interval / Horizontal Distance.

What does this tell us exactly?

The gradient shows how steep the slope is. A larger number indicates a steeper incline!

Can we use a mnemonic for this too?

Of course! Think of 'V Never H' - Vertical over Horizontal, which will help you remember the gradient formula!

What would be a real-world application of this calculation?

Great question! Engineers use gradient measurements in construction and urban planning to ensure safe building on inclines.

To wrap up, remember the formula for gradient and the helpful mnemonic 'V Never H' for ease of remembrance!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, students will learn how to accurately measure distance using dividers and scales, calculate area by counting grid squares, and determine gradient using the formula for vertical interval and horizontal distance. These skills are critical for interpreting topographical maps effectively.
Detailed
Measuring Distance, Area, and Gradient
This section delves into important techniques for evaluating topographical maps. Understanding how to measure distance accurately is essential for interpreting geographical information. Using a divider, scale, or string can help in covering curved paths. The area can be estimated by counting complete and half grid squares on the map, knowing that each square represents 1 km².
Furthermore, learning how to calculate gradient is crucial to comprehend the steepness of the terrain. The gradient is computed using the formula:
\[ Gradient = \frac{Vertical\ Interval}{Horizontal\ Distance} \]
This metric gives valuable insight into how sloped or flat an area is, which assists in planning in areas such as construction, agriculture, and navigation. Mastering these measurement techniques lays the foundation for more applied geographic understanding.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Measuring Distance
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Distance: Use divider and scale or string for curves.
Detailed Explanation
Measuring distance on a topographical map is crucial for understanding the space between different points of interest. You can use tools like a divider, which helps measure straight distances, or a string to measure longer, curved paths. Here’s how it works:
1. Place the divider point on one location on the map and the other point on the destination.
2. Read the measurement on the scale provided on the map.
3. For curves, you can use a string to follow along the contour of the path, then measure the string against the map's scale.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are walking to a friend's house, but the route isn't a straight line. If you use a piece of string to measure your walk and then compare it to a map scale, you can calculate how far you traveled much like measuring the twisted path of a river.
Measuring Area
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Area: Count full and half grid squares (1 sq = 1 km²).
Detailed Explanation
To measure area on a topographical map, you look at the grid squares that cover the terrain. Each full grid square on the map represents 1 square kilometer. If the area includes parts of multiple squares, you count any full squares and half squares to estimate the total area. For instance, if you have three full squares and one that is half-filled, you would estimate the area to be 3.5 km².
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a pizza cut into squares. If each square represents one slice, and you have three whole slices plus one half slice left, you can easily figure out how much pizza (or area) is left to share.
Understanding Gradient
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Gradient: Gradient=Vertical IntervalHorizontal Distance\text{Gradient} = \frac{\text{Vertical Interval}}{\text{Horizontal Distance}} Indicates how steep the terrain is.
Detailed Explanation
The concept of gradient helps you understand how steep a terrain is by comparing the vertical rise to the horizontal distance. To calculate it, you find the vertical interval (the elevation change) and divide it by the horizontal distance (the actual distance on the ground). This tells you how much the elevation changes for a certain distance along the ground. A steeper gradient means a more abrupt rise or fall in terrain, such as hills or cliffs.
Examples & Analogies
Consider riding a bike up a hill. If the hill rises sharply over a short distance, it’s harder to pedal and feels steeper. If it rises gradually, it’s easier to ride. The steeper the hill, the higher the gradient. Using the gradient formula helps you quantify this steepness just like measuring the incline of your bike ride.
Key Concepts
-
Distance measurement: Tools such as dividers, scales, and strings are essential.
-
Area calculation: Count full and half grid squares.
-
Gradient: Calculated through the ratio of vertical interval to horizontal distance.
Examples & Applications
To measure a distance of 2 km on a map with a scale of 1:50,000, use a divider to find this distance on the map and then refer to the scale for the actual distance.
If a terrain's vertical interval between two elevations is 100 meters and the horizontal distance is 500 meters, then the gradient is 0.2 or 1:5, indicating a moderate slope.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To find distance, use a divider, to find the area just get wider; count full squares and halves the same, that’s how topography is the name of the game.
Stories
Imagine you are a treasure hunter with a map! You need to measure distances to find treasures, so you pull out your dividers, and for tricky routes, you use a string. Mark areas with squares, counting full ones like steps and half ones like half-steps to get to your treasure!
Memory Tools
To remember area measurements, use 'FHA' for Full, Half, Area!
Acronyms
Remember 'V Never H' to recall how to calculate gradient
Vertical over Horizontal!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Divider
A tool used to measure distances on a map by transferring distances to a scale.
- Gradient
The measure of steepness of a slope, calculated as the vertical interval divided by the horizontal distance.
- Grid Square
A 1-km² square unit on a topographical map used for area calculations.
- Vertical Interval
The difference in elevation between two points on a topographical map.
- Horizontal Distance
The straight-line distance measured on the map between two points.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
