Land Transport
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Road Transportation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore road transport in India. It is the most commonly used mode of transport in our country. Can anyone tell me the different types of roads we have?

Yes! There are National Highways, State Highways, and Rural Roads!

Exactly! National Highways connect major cities, while State Highways connect important towns within a state. Can you name one example of a National Highway?

NH-44?

That's right! NH-44 is a major route. Now, can someone explain what the Golden Quadrilateral is?

It's a highway network that connects Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata!

Great job! The Golden Quadrilateral is crucial for trade and connectivity. Remember, it's important to stay aware of how these roads contribute to our economy!

Got it! It connects the busiest cities.

Exactly! So, to wrap up, these roads form the backbone of land transport and are vital for economic growth.
Railway Transportation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's turn to railways, which form one of the largest railway networks in the world. Can anyone tell me who operates these railways in India?

Indian Railways?

Exactly! It’s a government undertaking. What are some of the zones of Indian Railways?

There are Northern, Southern, Eastern, and Western zones.

Correct! These zones help in the effective management of the railway network. Why do you think railways are important for our economy?

They carry bulk goods and passengers over long distances.

Yes! They significantly contribute to economic growth. However, what challenges do you think the railway system faces?

Maybe overcrowding and old infrastructure?

Spot on! Overcrowding and outdated infrastructure are major challenges we must address to improve our railways. Keep these points in mind!
Significance of Land Transport
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s summarize why land transport is so critical. Can anyone give a few reasons on its importance?

It facilitates economic development and trade!

Absolutely! It promotes mobility and connectivity. What else?

It helps in disaster relief and national defense.

Good point! These systems play a crucial role during emergencies. Any other thoughts?

It encourages tourism and cultural exchange.

Exactly! So, to sum up, land transport plays a vital role in the economic and social fabric of India.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The land transport system in India includes an extensive network of roadways comprising National Highways, State Highways, and rural roads, along with one of the world's largest railway networks, managed by Indian Railways. These systems not only provide mobility for goods and people but also contribute significantly to economic development, although they face challenges that necessitate modernization and investment.
Detailed
Land Transport
Overview
Land transport serves as a vital infrastructure in India, accommodating the movement of goods and people across the country. This section will explore the two primary facets of land transport: roadways and railways.
11.2.1 Roadways
- Most Commonly Used Mode: Roadways are the predominant means of transport in India.
- Types of Roads:
- National Highways (NH): Major highways connecting big cities; for instance, NH-44 and NH-27 are critical routes.
- State Highways: Connect districts and significant towns.
- District and Rural Roads: Facilitate access to villages and smaller localities.
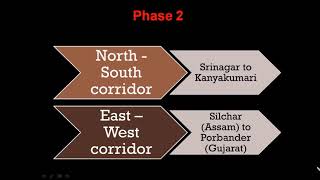
- Golden Quadrilateral: A key highway network that links Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata, enhancing connectivity and trade.
11.2.2 Railways
- Extensive Network: India boasts one of the largest railway systems globally, governed by Indian Railways.
- Division into Zones: The railway is organized into geographical zones such as Northern, Southern, and Eastern, which improves management and efficiency.
- Significance:
- Essential for transporting goods in bulk and passengers over long distances,
- Plays a pivotal role in driving economic growth and trade within the nation.
- Challenges: The railway network faces issues like overcrowding, aging infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance, which require attention for improvement.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Land Transport
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Land transport refers to the ways in which people and goods are moved over land. In India, this is predominantly achieved through roadways and railways.
Detailed Explanation
Land transport is crucial for daily life as it facilitates the movement of people and goods across various distances. It is the most commonly used mode of transport in India, supporting both urban and rural areas. Clear road and rail networks enable effective transport solutions for economic activities, daily commuting, and large-scale logistics.
Examples & Analogies
Think of land transport like the highways and streets in a city that connect homes, businesses, and markets. Just like how a busy road shows vehicles moving about, land transport is essential for keeping a community connected.
Roadways
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Most commonly used mode of transport in India.
● Types:
○ National Highways (NH): Connect major cities (e.g., NH-44, NH-27).
○ State Highways: Connect districts and important towns within a state.
○ District and Rural Roads: Connect villages and small towns.
● Golden Quadrilateral: High-speed highway network connecting Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata.
Detailed Explanation
Roadways are the primary mode of transport for a large proportion of the population in India. They are categorized into three main types: National Highways, which connect major cities; State Highways, which connect various districts and towns within states; and District and Rural Roads, which link small villages. The Golden Quadrilateral is a significant project that enhances connectivity between major metropolitan areas by providing a fast roadway network.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine planning a road trip across India. National highways would be the main routes you take to get to important cities quickly, while state and rural roads allow you to explore smaller towns and scenery along the way.
Railways
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● One of the largest railway networks in the world.
● Operated by Indian Railways (a government undertaking).
● Divided into zones: Northern, Southern, Eastern, Western, etc.
● Importance:
○ Carries bulk goods and long-distance passengers.
○ Boosts economic growth and trade.
● Challenges:
○ Overcrowding, outdated infrastructure, and maintenance issues.
Detailed Explanation
Indian Railways is a significant mode of land transport, boasting one of the largest railway networks globally. It is structured into various zones for effective management. The railways are vital for transporting both people and goods across long distances, which is essential for economic activities. However, challenges such as overcrowding and outdated infrastructure also exist, impacting efficiency and the travel experience.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the railways as a vast web connecting cities and towns, much like a spider's web where each strand leads to a different location. While it helps many travel easily, some strands (or trains) get overcrowded, making travel less comfortable.
Key Concepts
-
Roadways: Fundamental for intra-state and inter-state connectivity.
-
Railways: Vital for bulk transportation and passenger movement.
-
Economic Impact: Both roadways and railways significantly contribute to India’s economy.
Examples & Applications
Example of NH-44 connecting Kashmir to Kanyakumari.
Example of how Indian Railways connects remote areas.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Roads and rails, oh what a ride, Connecting us all, with pride!
Stories
Imagine a train leaving Mumbai, carrying goods and passengers. It travels through the vast landscapes, eventually reaching Delhi, showing how railways bridge the gaps in distances.
Memory Tools
R for Roads, R for Railways, E for Economy. Remember these 'RRE' to emphasize their importance.
Acronyms
GRE (Golden Quadrilateral, Railways, Economic Growth) to connect the essential aspects of land transport.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- National Highways (NH)
Major roads connecting significant cities across India.
- State Highways
Roads that connect districts and important towns within a state.
- Golden Quadrilateral
A network of highways connecting Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata.
- Indian Railways
The state-owned national railway system of India.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
