Mechanical Advantage (M.A.), Velocity Ratio (V.R.), Efficiency
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Mechanical Advantage
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing Mechanical Advantage or M.A. Can anyone tell me what it means?

Is it how much force a machine can multiply?

Exactly! M.A. indicates how many times a machine can amplify your input effort. The formula is M.A. = Load / Effort. Can anyone explain why this is important?

It helps us understand how much easier a task can be with a machine.

Correct! The higher the M.A., the less effort you will have to exert to lift a load. Remember this with the acronym 'M.A. = Load over Effort!'
Velocity Ratio
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's discuss Velocity Ratio or V.R. What do you think it represents?

Is it about how far the effort moves compared to the load?

Exactly! V.R. is expressed as Distance moved by Effort over Distance moved by Load. It shows the relationship between how far you move the input force versus what you lift.

So, if I lift a load up 1 meter, and I pull the effort rope 2 meters, the V.R. is 2?

Correct! V.R. of 2 means for every meter lifted, you have to pull 2 meters. Remember, V.R. gives an idea of the trade-off between distance and force.
Efficiency
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s talk about Efficiency! What does Efficiency tell us?

It measures how well a machine works, right?

That's right! Efficiency is calculated as (M.A. / V.R.) × 100%. It helps determine how much of the input work translates into useful output work.

So if there's a lot of friction, the efficiency would be lower?

Exactly! More friction means more energy loss, so the efficiency drops. A higher percentage means better performance. Remember this using: 'More efficiency equals less wasted energy!'
Application of M.A., V.R., and Efficiency
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, how do we use M.A., V.R., and Efficiency in real life? Can anyone give examples?

Like using a pulley to lift heavy boxes?

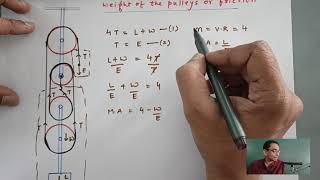
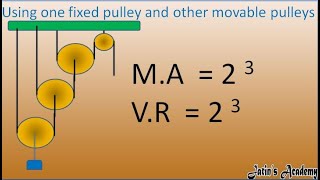
Great example! Pulleys can increase M.A., reduce effort, and are commonly used. When we know the M.A. and V.R., we can also calculate how efficient the pulley system is.

And in a car? It would have M.A. related to the gears, right?

Exactly! Different gears provide different M.A.s, and knowing their efficiencies helps understand fuel consumption. Always think 'Easy and efficient means well designed!'
Review and Conclusion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s summarize what we’ve learned! What is Mechanical Advantage?

It’s the ratio of Load to Effort!

Correct! And what does V.R. represent?

The distance moved by the effort compared to the load.

Spot on! And finally, what is the formula for Efficiency?

Efficiency equals (M.A. / V.R.) times 100%!

Excellent recap! Remember these concepts as they are vital for understanding how machines work and improve our lives.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Mechanical Advantage (M.A.) and Velocity Ratio (V.R.) are crucial concepts in understanding how simple machines work. M.A. measures the amplification of force, V.R. relates to the distance moved by load and effort, and Efficiency indicates how effectively a machine converts input work to output work, expressed in percentage form. Each plays a vital role in evaluating the performance of machines.
Detailed
Mechanical Advantage (M.A.), Velocity Ratio (V.R.), Efficiency
This section focuses on three key concepts crucial to understanding the performance of simple machines:
Mechanical Advantage (M.A.)
- Definition: Mechanical Advantage (M.A.) quantifies the factor by which a machine multiplies the effort force applied to it.
- Formula: M.A. = Load / Effort
- Here, 'Load' is the output force and 'Effort' is the input force.
Velocity Ratio (V.R.)
- Definition: Velocity Ratio (V.R.) compares the distance moved by the effort to the distance moved by the load.
- Formula: V.R. = Distance moved by Effort / Distance moved by Load
Efficiency
- Definition: Efficiency measures how well a machine converts the input work (effort) into output work (load).
- Formula: Efficiency = (M.A. / V.R.) × 100%
- This indicates the percentage effectiveness of the machine; a higher efficiency signifies lesser energy loss due to friction and other factors.
Understanding these terms is essential for analyzing the function and usefulness of various mechanical systems, enabling better design and application in practical scenarios.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Mechanical Advantage (M.A.)
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Mechanical Advantage:
M.A. = Load / Effort
Detailed Explanation
Mechanical Advantage (M.A.) is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device, or machine. It is calculated as the ratio of the load (the weight or resistance being moved) to the effort required to move that load. A higher M.A. indicates a greater advantage in how much easier it is to move the load. For example, if you lift a load of 100 N with an effort of 20 N, the M.A. would be 100 N / 20 N = 5. This means the effort you apply is five times less than the load you are lifting.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine using a lever to lift a heavy rock. If the lever allows you to lift a 100 kg rock using only 20 kg of force, the M.A. shows just how effective the lever is in helping you perform this task. It's like using a long crowbar to lift a heavy object; the longer the crowbar, the less force you need to apply.
Velocity Ratio (V.R.)
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Velocity Ratio:
V.R. = Distance moved by effort / Distance moved by load
Detailed Explanation
Velocity Ratio (V.R.) describes the relationship between the distance moved by the effort applied and the distance moved by the load being lifted or moved. It tells us how much the output motion (movement of the load) differs from the input motion (movement of the effort). For instance, if you move the effort through 4 meters, but the load only rises 1 meter, the V.R. would be 4. This indicates that for every 4 meters you move the effort, the load moves only 1 meter.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a bicycle: when you pedal, you may move the pedals (effort) a certain distance, while the bike (load) moves a different, usually shorter distance due to the gears. The V.R. helps understand how gear ratios work; it shows how effectively your pedaling translates into riding distance.
Efficiency
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Efficiency:
Efficiency = (M.A. / V.R.) × 100%
Detailed Explanation
Efficiency is a measure of how effectively a machine converts input work (effort) into output work (load). It is expressed as a percentage and calculated using the formula: Efficiency = (M.A. / V.R.) × 100%. A higher efficiency means that less energy is wasted and that a greater proportion of the effort goes into moving the load rather than being lost to friction or other forces. For example, if a machine has an M.A. of 4 and a V.R. of 5, its efficiency would be (4/5) × 100% = 80%. This means 80% of the effort goes into lifting the load, while 20% is lost.
Examples & Analogies
Consider an elevator system: If it takes the same amount of energy to move the elevator a short distance as it does to move it a long distance, a more efficient elevator would do a better job of moving quickly and using less energy. It's like using an energy-efficient light bulb that gives off the same brightness but uses less electricity.
Key Concepts
-
Mechanical Advantage: The ratio of Load to Effort, providing a measure of how much a machine can amplify input force.
-
Velocity Ratio: The comparison of distances moved by effort versus load, showcasing the trade-off in movement and effort.
-
Efficiency: A percentage that indicates the effectiveness of a machine in transforming input work to useful output work.
Examples & Applications
Using a wheelbarrow where the load (the heavy soil) is lifted with less effort due to the Mechanical Advantage provided by the wheel.
Using a pulley system to lift a weight, allowing the user to lift a heavy load with reduced effort due to its Mechanical Advantage.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To find M.A., just remember this play, 'Load over Effort' will save your day!
Stories
Imagine a friend helping you lift a heavy box. With their help, you lift more - that’s M.A. being your newfound strength!
Memory Tools
Remember 'M.E.V.': M.A. = Load/Effort, E = (M.A./V.R.) x 100%, V.R. = Distance Effort/Distance Load.
Acronyms
M.A. is 'Maximized Assistance', V.R. is 'Variable Ratio', and E for 'Efficiency' - track all three!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Mechanical Advantage
A measure of the amplification of force achieved by using a machine.
- Velocity Ratio
The ratio of the distance moved by the effort to the distance moved by the load.
- Efficiency
The ratio of the useful output work to the total input work expressed as a percentage.
- Load
The force exerted by the machine, or the weight it lifts.
- Effort
The force applied to a machine to perform work.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
