Nuclear Fission
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Nuclear Fission
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we are discussing nuclear fission, which is when a heavy nucleus, like uranium, splits into two lighter nuclei. Why do you think this process is important?

Is it because it can release a lot of energy?

Exactly! When fission occurs, a significant amount of energy is released. This energy can be harnessed for various applications, such as electricity generation in nuclear power plants.

But isn’t it also used in bombs?

Correct! In atomic bombs, fission happens uncontrolled, leading to a huge explosion. Remember, 'Fission for energy, fusion for fury' can help you differentiate their applications.
How Nuclear Fission Works
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Nuclear fission occurs when a heavy nucleus absorbs a neutron and becomes unstable, resulting in its split. What do you think happens next?

Does it release more neutrons?

Right! It releases additional neutrons that can initiate further fission in nearby nuclei, creating a chain reaction.

So, could this chain reaction continue indefinitely?

It can, but control is crucial in reactors to prevent an uncontrolled explosion. Think of it as a delicate balance! If the reaction isn’t monitored, it could lead to catastrophic results.
Applications of Nuclear Fission
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone name some common applications of nuclear fission?

Nuclear power plants for generating electricity?

And atomic bombs, right?

Absolutely! Fission is the heart of nuclear energy and weaponry. It's crucial to understand these applications for both technological advancement and safety.

Is there a way to make it safer?

Yes, using modern reactor designs and safety protocols significantly reduces risks. Always remember: knowledge is power, but safety must come first!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Nuclear fission involves the splitting of a heavy nucleus into lighter nuclei, accompanied by a release of energy. This process is crucial for both nuclear reactors, where it is harnessed for energy production, and in atomic bombs, where it leads to explosive reactions.
Detailed
Nuclear Fission
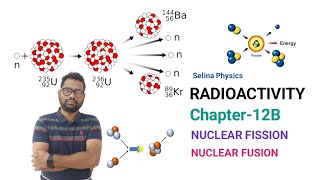
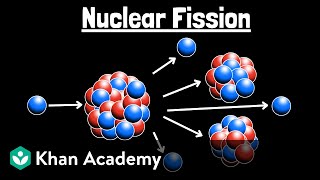
Nuclear fission refers to the process where a heavy atomic nucleus, such as uranium-235 or plutonium-239, splits into two lighter nuclei. Alongside the production of these lighter nuclei, a substantial amount of energy is released, primarily in the form of kinetic energy of the fragments and electromagnetic radiation. This energy release occurs due to the conversion of a small amount of mass into energy, as described by Einstein’s equation, E=mc².
Fission is a critical reaction utilized in nuclear reactors, where controlled fission processes generate heat that is then transformed into electricity. Conversely, in the context of atomic weapons, fission occurs in an uncontrolled manner, resulting in massive explosions. Fission reactions also generate neutrons, which can induce further fissions, leading to a chain reaction, which is a key principle behind both nuclear power generation and nuclear weaponry.
Significance
Understanding nuclear fission is vital because it not only poses potential dangers due to its association with atomic bombs, but it also offers opportunities for generating clean energy through controlled nuclear reactions.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Nuclear Fission
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● A heavy nucleus splits into two lighter nuclei, releasing energy.
Detailed Explanation
Nuclear fission is a process where a large atomic nucleus breaks apart into two smaller nuclei. This splitting occurs due to the instability of the heavy nucleus, which cannot hold itself together any longer. As it splits, it releases a significant amount of energy, which is a fundamental aspect of how nuclear reactors and atomic bombs function.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a large balloon filled with air. If you poke it with a sharp object, it pops loudly and breaks into smaller pieces, releasing the air rapidly. Similarly, when a heavy atomic nucleus breaks apart, it releases energy just like the popping balloon.
Applications of Nuclear Fission
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Used in nuclear reactors and atomic bombs.
Detailed Explanation
Nuclear fission is harnessed in various applications. In nuclear reactors, the energy released from fission reactions is used to heat water, producing steam that drives turbines to generate electricity. Conversely, in atomic bombs, the uncontrolled fission process leads to a massive explosion due to the rapid release of energy.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a controlled fire in a fireplace, which gives warmth to your home. This is like using nuclear fission in a reactor. Now, picture a fire raging out of control, causing destruction. This is similar to the fission reaction in an atomic bomb.
Key Concepts
-
Nuclear Fission: A nuclear reaction where a heavy nucleus splits into lighter nuclei and releases energy.
-
Chain Reaction: A process where released neutrons from fission can trigger additional fission events.
-
Energy Release: The significant energy produced from fission, used in both power generation and weapons.
Examples & Applications
An example of nuclear fission occurs in nuclear reactors where uranium-235 absorbs a neutron and splits, producing heat for electricity generation.
In atomic bombs, the uncontrolled chain reaction of fission leads to an explosive release of energy.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When heavy atoms split in two, energy comes dancing into view.
Stories
Imagine a giant balloon. When you poke it (the neutron), it pops (fission) into smaller pieces, releasing air (energy) all around.
Memory Tools
Fission is Fun! (Think of how splitting brings energy.)
Acronyms
HEN - Heavy nucleus Emits Neutrons.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Nuclear Fission
The process of splitting a heavy atomic nucleus into two lighter nuclei, accompanied by the release of energy.
- Chain Reaction
A series of fission reactions where released neutrons from one fission event induce further fissions in nearby nuclei.
- Uranium235
A specific isotope of uranium that is commonly used as fuel for nuclear fission.
- Plutonium239
A man-made isotope used in nuclear weapons and reactors, created from uranium in fission reactors.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
