Combined Gas Law
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Combined Gas Law
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll discuss the Combined Gas Law, which helps us understand how pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas are connected.

What is it based on, Teacher?

Great question! It combines Boyle's Law, which relates pressure and volume, with Charles's Law, which relates volume and temperature.

How do we write this law mathematically?

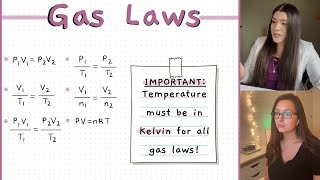
We express it as PV/T = constant, where P is pressure, V is volume, and T is temperature in Kelvin.
Understanding the Equation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's see how we can apply this formula. When we have initial and final conditions, we use: P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2.

So, if I change one of the variables, can I find the others?

Exactly! By rearranging the equation, we can solve for any of the variables. Just remember, all temperatures must be in Kelvin!

What happens to the gas if we increase the temperature?

Good observation! Increasing the temperature, while keeping pressure constant, will increase the volume. This follows Charles's Law.
Applications of Combined Gas Law
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The Combined Gas Law is not just theoretical; it has real applications! Can anyone think of where this might be used?

In weather balloons?

Exactly! As the balloon rises, the pressure and temperature change, affecting the volume of the gas inside.

What about scuba diving?

Great point! Divers must understand how gas behaves under pressure to avoid problems like decompression sickness.
Practical Example of Combined Gas Law
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's consider a gas in a sealed container. If we start with initial values of P1, V1, and T1, and double the temperature, what do you think will happen to the pressure if the volume remains constant?

The pressure will double too!

That’s correct! By using the equation, you can see how changing one variable directly affects the others.

So it's all linked together!

Exactly! Remember, all these changes are interdependent, and this is the beauty of the Combined Gas Law.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Combined Gas Law allows us to analyze the behavior of a fixed amount of gas when the temperature, pressure, and volume change simultaneously. It is expressed as PV/T = constant and is useful in various scientific applications.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of the Combined Gas Law
The Combined Gas Law is a fundamental equation in gas physics that combines two of the most essential gas laws: Boyle's Law and Charles's Law. It mathematically expresses how pressure (P), volume (V), and temperature (T) of a gas are interrelated. This law is represented by the equation:
$$\frac{PV}{T} = \text{constant}$$
When considering the initial and final states of a gas, the relationship is articulated as:
$$P_1V_1/T_1 = P_2V_2/T_2$$
This equation is crucial in conditions where a gas undergoes changes in these three parameters simultaneously, thus allowing predictions and calculations pertaining to real-world scenarios involving gases. The significance of the Combined Gas Law lies in its application across various scientific fields, including meteorology, chemistry, and engineering, where understanding gas behaviors is fundamental.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to the Combined Gas Law
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Combines Boyle’s and Charles’s Laws:
P\[\frac{PV}{T} = \text{constant}\]
Detailed Explanation
The Combined Gas Law is a single formula that integrates the principles of Boyle’s and Charles’s Laws. It states that the ratio of the product of pressure (P) and volume (V) of a gas to its temperature (T) remains constant, as long as the amount of gas is held steady. This means that if one of these variables changes, at least one of the other variables must change to maintain this balance.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a balloon. When you pinch the neck of a balloon (decreasing the volume), the pressure inside increases. If you then warm the balloon by holding it in your hands (increasing the temperature), the pressure change in the balloon can be observed. The Combined Gas Law helps to understand the relationship between these changes.
Using the Combined Gas Law for Initial and Final Conditions
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
For initial and final conditions:
P1V1T1 = P2V2T2
\[\frac{P_1V_1}{T_1} = \frac{P_2V_2}{T_2}\]
Detailed Explanation
The equation for the Combined Gas Law allows us to compare the initial and final states of a gas under changing conditions. P1, V1, and T1 represent the initial pressure, volume, and temperature, respectively, while P2, V2, and T2 denote the final conditions. This relationship enables us to calculate unknown values when the initial and final states of a gas are provided.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're baking bread. If you increase the oven's temperature (T2) while the dough expands (V2), you may need to adjust the pressure of steam inside the oven (P2). The Combined Gas Law helps bakers understand how changes in temperature will impact the volume and pressure of gases, which is essential for baking the perfect loaf.
Key Concepts
-
Combined Gas Law: PV/T = constant, combining the principles of Boyle's and Charles's Laws.
-
Pressure (P): Force exerted by gas molecules per unit area.
-
Volume (V): The space occupied by gas.
-
Temperature (T): Must be measured in Kelvin for gas law calculations.
Examples & Applications
When a balloon rises in the atmosphere, its volume increases as the pressure decreases, which can be explained using the Combined Gas Law.
In a sealed container, if you heat the gas and keep the volume constant, the pressure will increase, demonstrating the relationship dictated by the Combined Gas Law.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Gas laws combined, not far behind, pressure and volume intertwined!
Stories
Imagine a balloon rising high into the sky, as the air pressure drops, it expands, oh my! Temperature warms up as the sun begins to shine, the Combined Gas Law helps us see, everything align!
Memory Tools
Remember PVT: Pressure, Volume, Temperature – PV over T keeps them forever together!
Acronyms
PVT helps you recall
Pressure
Volume
Temperature – a gas's call!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Combined Gas Law
An equation that combines Boyle's and Charles's Law, expressed as PV/T = constant.
- Pressure (P)
The force exerted by gas molecules per unit area.
- Volume (V)
The space occupied by the gas.
- Temperature (T)
The measure of thermal energy, must be in Kelvin for gas law calculations.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
