Important Terms
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Pressure and Its Importance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the term 'Pressure'. Who can tell me what pressure means in the context of gases?

I think it's how hard the gas is pushing against something.

Exactly! Pressure (P) is the force exerted by gas molecules over a unit area. It’s measured in atm or Pa. Can anyone tell me why understanding pressure is important?

Because it affects how gases behave, like for example when you inflate a balloon?

Right! The behavior of gases changes with pressure, which we'll see more in Boyle's Law later! Let's remember: 'Pressure is crucial, it’s how gases push and move!'

Is there a formula for pressure?

Good question! Pressure can also be involved in calculations with volume and temperature. Let’s keep that in mind as we move on!
Understanding Volume
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss 'Volume'. Can anyone explain what volume refers to when talking about gases?

It’s the space that the gas takes up!

Correct! Volume (V) is the space occupied by gas, measured in liters or cubic centimeters. How do you think volume changes in a sealed container as pressure increases?

If you increase pressure, the volume should decrease?

Yes! That’s exactly Boyle’s Law. Remember that it’s all interconnected: more pressure leads to less volume.
Temperature Measurement in Gas Laws
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s look at 'Temperature'. Why do we have to measure temperature in Kelvin for gas laws?

Because absolute temperature is essential for calculations, right?

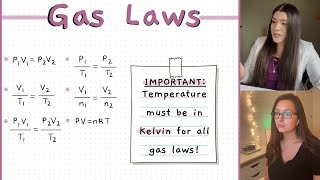
Exactly! Temperature (T) in gas law calculations must be in Kelvin (K). The conversion from Celsius is K = °C + 273. Can anyone provide an example?

If it’s 25°C, then in Kelvin it would be 298 K?

Spot on! It’s important when we calculate gas behaviors to always use Kelvin. Let’s create a memory phrase: 'Temperature in Kelvin, gas work is heaven!'
Understanding STP
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's discuss Standard Temperature and Pressure, or STP. What are the values for STP?

It’s 0°C and 1 atm, right?

You got it! STP simplifies experiments by providing a reference. Why do we define it like that?

To have consistency when doing gas-related calculations?

Exactly! Let’s remember the STP values using: 'Zero and One, for experiments, it’s fun!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section defines essential terms like pressure, volume, temperature, and standard temperature and pressure (STP), foundational for understanding gas behavior. It also emphasizes the importance of absolute temperature in calculations.
Detailed
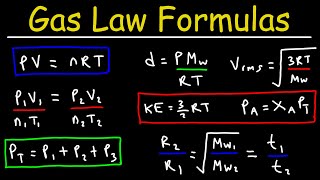
In gas laws, several important terms must be understood to grasp how gases behave under different conditions. Pressure (P) is defined as the force exerted by gas molecules per unit area, measured in atmospheres (atm), Pascals (Pa), or millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Volume (V) refers to the space occupied by the gas, with units such as cm³, dm³, or liters (L). It’s crucial that Temperature (T) is measured in Kelvin (K) for all calculations related to gas laws, with a conversion formula: K = °C + 273. Additionally, we introduce the concept of Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP), which provides a reference point for scientific measurements, defined as 0°C (or 273 K) and 1 atm (or 760 mmHg). Understanding these terms lays a foundation for further study of gas laws and their applications.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Pressure (P)
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Pressure (P): Force exerted by gas molecules per unit area.
Unit: atmosphere (atm), Pascal (Pa), mmHg
Detailed Explanation
Pressure is defined as the force applied by gas molecules over a certain area. Since gases are composed of particles that constantly move and collide, they exert pressure on the walls of their container. It can be measured in different units such as atmosphere (atm), Pascal (Pa), or millimeters of mercury (mmHg). This measurement is crucial when working with gas laws, as it helps us understand how gases behave under different conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine blowing air into a balloon. As you blow air into it, the gas molecules inside the balloon push against the inner walls of the balloon. The more air you blow in, the higher the pressure inside the balloon becomes, causing it to expand.
Volume (V)
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Volume (V): Space occupied by the gas.
Unit: cm³, dm³, or L
Detailed Explanation
Volume refers to the amount of space that a gas occupies. Unlike solids and liquids, gases can change their volume based on the pressure they are under and the temperature of their surroundings. Volume can be measured in cubic centimeters (cm³), cubic decimeters (dm³), or liters (L). Understanding the volume of gas is essential in predicting how it will respond to changes in pressure and temperature according to gas laws.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a balloon again; when you fill it with air, the space that the air takes up inside the balloon is its volume. If you press on the balloon (applying pressure), the volume may decrease, illustrating how gases can compress.
Temperature (T)
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Temperature (T): Must always be measured in Kelvin (K) for gas law calculations.
Conversion:
K=°C+273
K = °C + 273
Detailed Explanation
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. When it comes to gas laws, it's essential to use the Kelvin scale, as it begins at absolute zero, the point where all molecular motion stops. To convert from degrees Celsius (°C) to Kelvin (K), simply add 273 to the Celsius temperature. This ensures that the temperature is always a positive value, which is necessary for calculations involving gases.
Examples & Analogies
Think of temperature as the 'mood' of gas particles. At higher temperatures, the particles are 'excited' and move around quickly, while at lower temperatures, they are 'calm' and move slowly. Using the Kelvin scale ensures we are always measuring this energy correctly.
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP):
○ Temperature: 0°C or 273 K
○ Pressure: 1 atm or 760 mmHg
Detailed Explanation
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) are reference points used for gas calculations. STP is defined as a temperature of 0 degrees Celsius (or 273 Kelvin) and a pressure of 1 atmosphere (or 760 mmHg). These conditions allow scientists to compare gas measurements consistently. Gas volumes can change widely depending on temperature and pressure, so STP provides a common ground for these comparisons.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how you might want to measure soda in a bottle. If you want to compare its volume to other bottles or brands, measuring it at the same temperature and pressure (STP) helps ensure that you're comparing apples to apples, rather than different conditions which could change the volume.
Key Concepts
-
Pressure (P): A force exerted by gas molecules on the surfaces they collide with.
-
Volume (V): The three-dimensional space occupied by a gas.
-
Temperature (T): A measure of the average kinetic energy of gas molecules, required to be in Kelvin for calculations.
-
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP): Reference conditions used for gas law calculations.
Examples & Applications
The pressure in a soda can increases when shaken due to gas bubbles being forced into a smaller volume.
When a balloon is taken outside on a cold day, it shrinks due to lower kinetic energy and reduced volume.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Pressure, volume, temperature too; know them well and you’ll get through!
Stories
Imagine a balloon in your hand. As you squeeze, the pressure inside increases, causing the volume to decrease and reminding you of how gas laws work.
Memory Tools
For STP, remember 'Zero and One' — it's scientific fun!
Acronyms
PVT for Pressure, Volume, Temperature.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Pressure (P)
The force exerted by gas molecules per unit area.
- Volume (V)
The space occupied by the gas, measured in cm³, dm³, or liters.
- Temperature (T)
Must always be measured in Kelvin (K) for gas law calculations.
- Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)
Defined as 0°C (273 K) and 1 atm (760 mmHg).
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
