Detailed Descriptions
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Equatorial Region
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing the Equatorial Region. This area is characterized by dense forests and receives year-round rainfall. Who can tell me where we can find the Equatorial Region?

It's in areas like the Amazon Basin and the Congo Basin!

That's correct! Also, it’s found in Indonesia. Now, what do you think is a significant environmental impact of the heavy rainfall in this region?

Maybe it makes the soil poor due to leaching?

Exactly! The heavy rains wash away essential nutrients from the soil. Remember this with the mnemonic 'E.R.LAZY' - Equatorial Rain means Leaching Affects Yield.

What types of wildlife thrive there?

Good question! Many species thrive, thanks to the diverse vegetation. Let’s summarize: the Equatorial Region is located in tropical parts of the world, experiences high rainfall, and has rich biodiversity but poor soil. Got it?

Yes, it’s a key area for biodiversity.
Tropical Grasslands (Savannas)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's move on to Tropical Grasslands, also known as savannas. Where are these regions typically found?

They are in parts of Central Africa and Brazil!

Correct! They have tall grasses and scattered trees. What do large herbivores, like elephants, rely on in these areas?

They depend on the grasses for food!

Exactly! And this region has diverse wildlife. Remember 'G.R.E.A.T.' - Grasslands are rich in Elephants and Antelopes, Tall grasses. Great job!

Why do you think preservation of this biome is essential?

Because they support large populations of wildlife and are crucial for local communities. Let's summarize: The Tropical Grasslands host important ecosystems teeming with large herbivores and characteristic vegetation.
Hot Deserts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next up, we have hot deserts, like the Sahara and Arabian Deserts. What do you think makes these areas unique?

They have extreme temperature variations!

Absolutely! Sand dunes and xerophytic plants, like cacti, are also key features. Let’s create a mnemonic here: 'H.E.A.T.' - Hot deserts have Extreme And Thirsty environments!

How do animals survive in such conditions?

Great question! Animals adapt through behaviors like being nocturnal to avoid the heat. We can summarize that hot deserts have distinct climatic conditions with adaptations exhibited by local fauna.
Mediterranean Region
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss the Mediterranean Region, known for its unique climate. Where is it located?

Around the Mediterranean Sea and in places like California!

Right on target! It experiences winter rainfall and summer drought. What types of crops do you think thrive here?

Maybe citrus fruits and grapes?

Exactly! Remember: 'M.E.D.B.' - Mediterranean has Evergreen, Drought-resistant crops. To summarize, the region is characterized by seasonal rainfall beneficial for specific types of agriculture.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section elaborates on various natural regions, including features such as climate, soil, vegetation, and locations. It highlights distinct characteristics of each region, establishing their ecological significance and biodiversity.
Detailed
Detailed Descriptions
This section explores major natural regions that showcase variations in climate, vegetation, and wildlife across the globe. Each region is characterized by unique features that influence human lifestyles, economy, and environmental interactions.
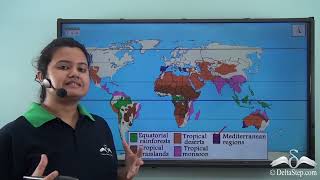
- Equatorial Region: Found in the Amazon Basin, Congo Basin, and Indonesia, this region is known for its dense forests, year-round rainfall, and poor soil due to leaching, making it a crucial biodiversity hotspot.
- Tropical Grasslands (Savannas): Occupying areas in Central Africa, parts of Brazil, and Australia, this region features tall grasses and scattered trees, sustaining large herbivores and carnivores, which contribute to its complex ecosystem.
- Hot Deserts: Comprising regions such as the Sahara, Thar, Arabian, and Australian Deserts, this area experiences extreme temperature variations and is characterized by sand dunes and xerophytic vegetation, adapted to arid conditions.
- Mediterranean Region: Located around the Mediterranean Sea, California, and South Australia, this region enjoys winter rainfall and summer drought, allowing the growth of citrus fruits and grapes.
- Temperate Grasslands: Found in North America's prairies, Eurasia's steppes, and South America's Pampas, these regions have fertile soils ideal for wheat and maize cultivation, supporting significant agricultural activities.
- Temperate Deciduous Forests: Present in the Eastern USA, Europe, and China, this region features trees that shed leaves in autumn, fostering rich biodiversity and settled agriculture.
- Taiga (Coniferous Forests): Spanning Canada, Scandinavia, and Siberia, the taiga is known for its long, cold winters and softwood trees, which are vital for the paper and furniture industries.
- Tundra: Occupying the Arctic shores, Greenland, and northern Canada and Russia, this region is characterized by permafrost, short summers, and a lack of trees, supporting a unique array of flora and fauna.
- Mountain or Highland Regions: Including ranges like the Himalayas, Andes, Rockies, and Alps, these regions exhibit varied climates and vegetation based on altitude, featuring forests at lower elevations and grasslands and snow at peaks.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Equatorial Region
Chapter 1 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Equatorial Region
- Location: Amazon Basin, Congo Basin, Indonesia.
- Features: Dense forests, year-round rainfall, poor soil due to leaching.
Detailed Explanation
The Equatorial Region is located in areas like the Amazon Basin, Congo Basin, and Indonesia. This region is characterized by dense forests, which means you'll find a lot of trees and rich vegetation. It experiences year-round rainfall, meaning it rains throughout the year without a distinct dry season. However, the soil in this region is generally poor because of a process called leaching, where heavy rainfall washes away essential nutrients from the soil.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a garden that gets watered every day but doesn't get enough nutrients because the water washes away the nutrients in the soil. This is similar to the Equatorial Region, where the constant rain results in lush forests but not very fertile soil.
Tropical Grasslands (Savannas)
Chapter 2 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Tropical Grasslands (Savannas)
- Location: Central Africa, parts of Brazil, Australia.
- Features: Tall grasses, scattered trees, home to large herbivores and carnivores.
Detailed Explanation
Tropical Grasslands, also known as Savannas, are found in areas like Central Africa, parts of Brazil, and Australia. In these regions, you will see tall grasses and scattered trees. This environment supports a variety of wildlife, including many large herbivores like elephants and giraffes, as well as carnivores like lions and cheetahs, which hunt these herbivores.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a vast, open field with a few trees here and there, where animals like zebras and lions roam freely. That's what a Savanna looks like—a beautiful balance of grass and trees where many animals thrive.
Hot Deserts
Chapter 3 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Hot Deserts
- Location: Sahara, Thar, Arabian, Australian Deserts.
- Features: Sand dunes, extreme temperature variation, xerophytic vegetation.
Detailed Explanation
Hot Deserts, such as the Sahara, Thar, Arabian, and Australian Deserts, are regions characterized by sand dunes and extreme variations in temperature, with very hot days and cooler nights. This area supports xerophytic vegetation, meaning plants adapted to survive with very little water, like cacti and thorny bushes.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine being in a large sandy area during a sunny day; it’s scorching hot with little shade, but when it gets dark, it becomes surprisingly cool. This fluctuation is typical of hot deserts, where plants have learned to conserve water to survive the harsh conditions.
Mediterranean Region
Chapter 4 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Mediterranean Region
- Location: Around the Mediterranean Sea, California, South Australia.
- Features: Winter rainfall, summer drought, citrus fruits and grapes grown.
Detailed Explanation
The Mediterranean Region can be found around the Mediterranean Sea and in places like California and South Australia. This region experiences winter rainfall followed by summer drought, which means it rains mostly in the winter and stays dry during the summer months. This type of climate is ideal for growing citrus fruits and grapes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a garden where you plant oranges and grapes. If the rain comes mostly in the winter, your plants will thrive during their growing season in the spring and early summer, but you must be careful during the hot, dry summer months, just like farmers in the Mediterranean Region.
Temperate Grasslands
Chapter 5 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Temperate Grasslands
- Location: Prairies (N. America), Steppes (Eurasia), Pampas (S. America).
- Features: Fertile soil, ideal for wheat and maize cultivation.
Detailed Explanation
Temperate Grasslands are found in regions such as the Prairies of North America, the Steppes of Eurasia, and the Pampas of South America. They are known for their fertile soil, which makes them ideal for cultivating crops like wheat and maize because these crops thrive in this type of environment.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a field ripe with golden wheat ready for harvest—this is what temperate grasslands provide. Farmers love this land because the soil is rich and perfect for growing food, just like in the Midwest of the United States.
Temperate Deciduous Forests
Chapter 6 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Temperate Deciduous Forests
- Location: Eastern USA, Europe, China.
- Features: Trees shed leaves in autumn, rich biodiversity, settled agriculture.
Detailed Explanation
Temperate Deciduous Forests are located in places like the eastern USA, Europe, and China. The key feature of these forests is that the trees shed their leaves in the autumn, which means they go through seasonal changes. These forests have rich biodiversity, supporting a wide variety of plants and animals, and are also areas where settled agriculture occurs.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine walking through a forest in autumn, seeing vibrant leaves falling to the ground. This forest is alive with various animals and plants all thriving together, and nearby, you might find farms where people grow crops, just as you would in a temperate deciduous forest area.
Taiga (Coniferous Forests)
Chapter 7 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Taiga (Coniferous Forests)
- Location: Canada, Scandinavia, Siberia.
- Features: Long, cold winters, softwood trees (used in paper and furniture).
Detailed Explanation
The Taiga, or Coniferous Forests, are found in regions like Canada, Scandinavia, and Siberia. This area is characterized by long, cold winters and is dominated by softwood trees, like pines and spruces. These trees are important as they are often used to make paper and furniture.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a snowy landscape filled with tall pine trees that stay green year-round. These trees are essential for producing materials we use every day, just like the wood you might see used for a wooden chair or your favorite book.
Tundra
Chapter 8 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Tundra
- Location: Arctic shores, Greenland, northern Canada and Russia.
- Features: Permafrost, short summers, no trees.
Detailed Explanation
The Tundra is primarily found in Arctic shores, Greenland, and northern regions of Canada and Russia. It is characterized by permafrost—a layer of permanently frozen soil—and has very short summers where temperatures hardly rise. This region has little to no trees, primarily supporting mosses and lichens.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a landscape that’s frozen for most of the year, with only a few plants like moss and lichen that can survive the extreme cold. This reflects the Tundra, a harsh but fascinating environment where life adapts to survive despite the conditions.
Mountain or Highland Regions
Chapter 9 of 9
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Mountain or Highland Regions
- Location: Himalayas, Andes, Rockies, Alps.
- Features: Varied climate and vegetation with altitude – forests at base, grasslands and snow at peaks.
Detailed Explanation
Mountain or Highland Regions, such as the Himalayas, Andes, Rockies, and Alps, exhibit varied climates and types of vegetation depending on the altitude. You'll find forests at lower altitudes, grasslands as you go higher up, and snow at the peaks. This variation is due to changes in temperature and pressure as you ascend.
Examples & Analogies
Think about climbing a mountain. At the bottom, you see lush forests filled with animals, but as you climb higher, it gets colder and you encounter grassy slopes, eventually reaching snow at the top. This highlights how different parts of a mountain can have completely different environments.
Key Concepts
-
Equatorial Region: Dense forests, high rainfall, poor soil.
-
Tropical Grasslands: Tall grasses, scattered trees, diverse wildlife.
-
Hot Deserts: Extreme temperatures, sandy terrain, xerophytic plants.
-
Mediterranean Region: Mild winters, dry summers, specific crops.
-
Temperate Grasslands: Fertile soils suited for agriculture.
-
Deciduous Forests: Seasonal leaf shedding, rich biodiversity.
-
Taiga: Cold climate, dominated by coniferous trees.
-
Tundra: Cold, treeless environment with permafrost.
-
Mountain Regions: Varied climatic zones based on altitude.
Examples & Applications
The Amazon Basin as an example of the Equatorial Region.
Savannas in Africa hosting animals like lions and elephants.
The Sahara Desert showcasing the hot desert climate.
California as an illustrative location of the Mediterranean Region.
Prairies in North America as a representation of Temperate Grasslands.
Eastern US as a locus for Temperate Deciduous Forests.
The Taiga in Canada as a representation of boreal forests.
The tundra regions in northern Canada and Russia.
Mountains like the Himalayas displaying diverse altitudinal climates.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
If you seek the Equator's might, Rainforests dense, a wondrous sight.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a land of tall grasses and roaming elephants, the savannah thrived with life, where the sun painted the earth gold, nourishing all that called it home.
Memory Tools
For the Mediterranean, remember 'M.D.R.' - Mild winter, Dry summer, Rich harvest.
Acronyms
E.D.C. - Equatorial, Deserts, Cold climates showcase the diversity of Earth’s natural regions.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Equatorial Region
A geographical area characterized by dense forests and year-round rainfall, often found in tropical areas.
- Savanna
A grassland ecosystem characterized by tall grasses, scattered trees, and a diverse variety of herbivores and carnivores.
- Hot Desert
An arid region with extreme temperatures, characterized by sand dunes and xerophytic vegetation.
- Mediterranean Region
A climatic region with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers known for specific agriculture like citrus and grapes.
- Temperate Grasslands
Grasslands found in temperate zones that are often fertile and suitable for agriculture.
- Deciduous Forests
Forests characterized by trees that shed their leaves seasonally, supporting rich biodiversity.
- Taiga
A biome characterized by long, cold winters and dominated by coniferous forests.
- Tundra
A cold, treeless region where the ground is often covered with ice or permafrost.
- Mountain Regions
High-altitude environments that display varied climates and ecosystems based on their elevation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
