Introduction
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Natural Regions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's delve into the concept of natural regions. Can anyone tell me what they think defines a natural region?

I think it's about areas that have similar climates and plants.

Excellent point! Natural regions do indeed share similarities in climate, vegetation, wildlife, and even human lifestyles. We can think of them like large ecosystems that are influenced by local climate conditions. Remember the acronym CLVHW for Climate, Land, Vegetation, Habitat, and Wildlife.

How do they classify different natural regions, then?

Great question! Natural regions are classified based on temperature, rainfall, and types of vegetation. These factors are crucial because they determine the characteristic flora and fauna of each region.
Importance of Viewing Natural Regions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think it’s important to study natural regions?

So we can understand different environments?

That's right! Studying natural regions helps us understand global climatic diversity and plays a vital role in the sustainable management of our natural resources. It enhances geographical awareness and aids in conservation efforts. Remember, understanding where we live helps us better protect it.

Can it also help in planning where to build farms or cities?

Absolutely! Knowledge of natural regions aids in planning for agriculture and human settlements based on the specific climate and environmental factors.
Classification Based on Climate
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into how we classify these regions. Who can recap the main factors?

Temperature and rainfall are two of the main factors.

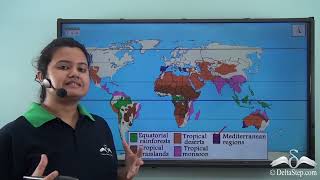
Correct! For instance, the equatorial region is characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall, leading to dense rainforests. Can anyone think of how these climates impact the types of vegetation?

In wet climates, there are more trees, while in dry climates, there are probably more deserts or grasslands.

Exactly! Remember this relationship: wetter climates generally support diverse and dense vegetation, while drier climates lead to more drought-resistant plants like cacti.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Natural regions encompass vast geographical areas sharing similar climatic conditions, vegetation types, wildlife, and human lifestyles. These regions are strategically classified based on climatic factors like temperature and rainfall, which play a significant role in determining the characteristics of each region.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Natural regions refer to extensive geographical areas that exhibit similarities in climate, vegetation, wildlife, and human activity. The classification of these regions is primarily based on climatic factors including temperature, rainfall, and the types of natural vegetation found within them. Understanding these regions is crucial as it allows us to grasp the diversity of global climates and how they affect biodiversity and human life. This section serves as a gateway to exploring the major natural regions of the world and emphasizes the importance of studying these geographical classifications for effective resource management and environmental awareness.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What are Natural Regions?
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Natural regions are large geographical areas that have similar climate, vegetation, wildlife, and human lifestyle.
Detailed Explanation
Natural regions refer to extensive areas on Earth that share common features in terms of climate, vegetation, wildlife, and the way people live. This can mean that specific areas experience similar weather patterns, types of plants and animals, and even have populations that adapt to their environment in similar ways.
Examples & Analogies
Think of natural regions like different neighborhoods in a city where each neighborhood has its own characteristics. Just like a neighborhood may have a particular type of architecture, parks, and types of people that live there, a natural region has its own climate, plants, and animals that thrive in that environment.
Classification Factors for Natural Regions
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
They are classified based on factors like temperature, rainfall, and types of natural vegetation.
Detailed Explanation
Natural regions are categorized by specific characteristics that affect the environment. Three primary factors are temperature, rainfall, and the types of vegetation that grow there. For instance, regions with high temperatures and heavy rainfall will have distinct tropical rainforests, while areas with low rainfall and extreme heat will be classified as deserts.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine wearing different clothes depending on the weather. In the summer, you might wear shorts and a t-shirt because it's warm, while in winter, you'd wear a coat and boots to keep warm. Just like how you adapt your clothing to the weather, different regions are shaped by their weather conditions, which defines what plants and animals can thrive.
Key Concepts
-
Natural Regions: Large geographical areas characterized by similar climates and ecosystems.
-
Climatic Factors: Elements that influence the classification of natural regions, including temperature and rainfall.
Examples & Applications
Equatorial regions are known for their dense tropical rainforests due to high rainfall and warm temperatures.
Deserts like the Sahara exhibit extreme water scarcity and unique vegetation adapted to harsh conditions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Regions vary with climate and flora, from dry deserts to rainforest euphoria.
Stories
Once upon a time, a curious child traveled around the world, discovering lush forests where it rained all year, and dry deserts with hardly any water, each region telling a story of its own.
Memory Tools
CLVHW: Climate, Land, Vegetation, Habitat, Wildlife - remember these when thinking about natural regions.
Acronyms
RAVEN
Regions Are Varied Even Naturally - to remember the diversity of natural regions.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Natural Region
A large geographical area characterized by similar climate, vegetation, wildlife, and human lifestyle.
- Climatic Factors
Elements such as temperature and rainfall that determine the characteristics of a region.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
