Natural Regions of the World
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Equatorial Region
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start by exploring the Equatorial Region. Can anyone tell me where this region is typically found?

Is it in the Amazon and Congo Basins?

Yes, that's right! This region is known for hot climates, with temperatures averaging between 25 and 30 degrees Celsius and heavy rainfall exceeding 2000 mm annually. What kind of vegetation do you think thrives in such conditions?

I think there would be a lot of forests, like rainforests?

Correct! We see dense tropical rainforests here. It's interesting to note that while the rainfall seems beneficial, the soil quality is poor due to leaching. Can anyone explain what leaching means?

I think it means that nutrients are washed away from the soil.

Exactly! Great job, everyone. To summarize, the Equatorial Region is warm and wet, supporting rich biodiversity but with nutrient-poor soils.
Hot Deserts
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s shift our focus to Hot Deserts. Where do we commonly find these types of regions?

Are they found in places like the Sahara and the Arabian Desert?

Absolutely! Hot deserts experience extreme temperatures that can soar up to 50 degrees Celsius, and they receive very little rainfall, often less than 250 mm. What kind of plants do you think are suited for such harsh conditions?

Probably plants like cacti or thorny bushes?

Great observation! Cacti and xerophytic plants are adapted to conserve water. These adaptations are crucial for survival in such environments. Can you think of any animals that might live in these deserts?

Maybe scorpions or camels?

Correct! Animals like camels, which can go for long periods without water, are perfectly suited to desert life. In summary, Hot Deserts are characterized by extreme conditions and specialized flora and fauna.
Temperate Deciduous Forests
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's talk about Temperate Deciduous Forests. Can anyone list some locations where we find these forests?

They are found in places like Europe and the eastern United States?

Exactly! These forests enjoy mild summers and cold winters, which is perfect for a variety of tree species like oaks and maples. What happens to the trees in autumn?

They shed their leaves, right?

Correct! This process helps conserve water and energy during the winter months. Why do you think biodiversity is crucial in these forests?

Biodiversity supports various ecosystems and helps with things like pollination!

Great point! To recap, Temperate Deciduous Forests support rich biodiversity and are characterized by the seasonal shedding of leaves.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
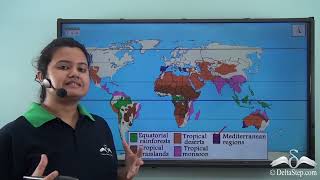
Natural regions are categorized based on climate, rainfall, and vegetation types, encompassing various global environments like deserts, forests, and grasslands. Understanding these regions aids in the sustainable management of resources and enhances geographical awareness.
Detailed
Natural Regions of the World
Natural regions represent extensive geographical areas defined by common characteristics in climate, vegetation, wildlife, and human activities. These regions are classified primarily based on climatic factors, including temperature and rainfall, as well as the prevalent types of natural vegetation. This section delves into the major natural regions of the world, exploring their distinct climates and features.
- Equatorial Region: Known for hot temperatures and heavy rainfall, housing dense tropical rainforests.
- Tropical Grasslands: Characterized by a warm climate and tall grasses.
- Hot Deserts: Features extreme heat and minimal rainfall, with xerophytic vegetation like cacti.
- Mediterranean Region: Noted for its warm, dry summers and moderate winter rainfall.
- Temperate Grasslands: Found in regions with fertile soil, ideal for agriculture.
- Temperate Deciduous Forests: Home to diverse deciduous trees, shedding leaves in the autumn.
- Taiga or Boreal Forest: Cold climate with coniferous trees.
- Tundra: Characterized by extreme cold and a lack of trees.
- Mountain Regions: Varied climates based on altitude, featuring diverse vegetation.
Studying these regions is crucial for understanding the world’s climate diversity and supports sustainable resource use, aiding agriculture, forestry, and human habitation planning.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Natural Regions
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Natural regions are large geographical areas that have similar climate, vegetation, wildlife, and human lifestyle. They are classified based on factors like temperature, rainfall, and types of natural vegetation.
Detailed Explanation
Natural regions are broad areas on Earth that share common characteristics such as climate and the types of plants and animals that live there. For example, areas that are warm and wet throughout the year will have different plants and animals compared to areas that are dry or cold. To classify these regions, scientists look at factors like how hot or cold it is, how much it rains, and what kinds of plants grow in the area.
Examples & Analogies
Think of natural regions like different neighborhoods in a city. Each neighborhood has its own style of houses, parks, and activities, similar to how each natural region has its own climate and wildlife.
Major Natural Regions Overview
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Natural regions are classified based on climate type, temperature, rainfall, and natural vegetation. Here is a brief overview of major natural regions:
- Equatorial Region: Hot (25–30°C), Heavy rainfall (2000+ mm), Dense tropical rainforests.
- Tropical Grasslands: Wet & Warm (20–30°C), Moderate rainfall (500–1500 mm), Tall grasses (savannas).
- Tropical Deserts: Very hot (up to 50°C), Very low rainfall (<250 mm), Cacti, thorny bushes.
- Mediterranean Region: Warm, dry summers (~500–900 mm), Evergreen shrubs, olive trees.
- Temperate Grasslands: Cold winters, hot summers (300–600 mm), Short grasses.
- Temperate Deciduous Forests: Mild summers, cold winters (750–1500 mm), Deciduous trees (oak, maple).
- Taiga or Boreal Forest: Cold (−10 to 15°C), Low to moderate rainfall, Coniferous trees.
- Tundra: Very cold (<0°C), Very low rainfall (<250 mm), Mosses, lichens.
- Mountain or Highland Regions: Varies with altitude, Mixed forest, grass, snow.
Detailed Explanation
There are several major natural regions across the globe, each with specific weather patterns and types of vegetation. For instance, the Equatorial Region is characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall, which leads to dense tropical forests. In contrast, Tropical Deserts receive very little rainfall and have extremely high temperatures, resulting in sparse plant life like cacti. Each region's climate impacts what plants and animals thrive there and how humans adapt their lifestyles.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine each natural region as a different costume party, where each group of people represents a unique region. The Equatorial Region would be dressed in lush green outfits, reflecting its rich forests, while those at the Tropical Desert party might wear light, sandy colors with accessories like hats to shield themselves from the sun.
Detailed Descriptions of Natural Regions
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Equatorial Region: Amazon Basin, Congo Basin, Indonesia. Features: Dense forests, year-round rainfall, poor soil due to leaching.
- Tropical Grasslands (Savannas): Central Africa, parts of Brazil, Australia. Features: Tall grasses, scattered trees, home to large herbivores and carnivores.
- Hot Deserts: Sahara, Thar, Arabian, Australian Deserts. Features: Sand dunes, extreme temperature variation, xerophytic vegetation.
- Mediterranean Region: Around the Mediterranean Sea, California, South Australia. Features: Winter rainfall, summer drought, citrus fruits and grapes grown.
- Temperate Grasslands: Prairies (N. America), Steppes (Eurasia), Pampas (S. America). Features: Fertile soil, ideal for wheat and maize cultivation.
- Temperate Deciduous Forests: Eastern USA, Europe, China. Features: Trees shed leaves in autumn, rich biodiversity, settled agriculture.
- Taiga (Coniferous Forests): Canada, Scandinavia, Siberia. Features: Long, cold winters, softwood trees (used in paper and furniture).
- Tundra: Arctic shores, Greenland, northern Canada and Russia. Features: Permafrost, short summers, no trees.
- Mountain or Highland Regions: Himalayas, Andes, Rockies, Alps. Features: Varied climate and vegetation with altitude – forests at base, grasslands and snow at peaks.
Detailed Explanation
Each natural region has unique characteristics based on its geographical location. For example, the Equatorial Region is known for its dense forests and consistent rainfall, which supports a rich ecosystem. In contrast, the Tundra is characterized by cold temperatures and limited vegetation due to permafrost. Different regions have adapted their agriculture and lifestyles to align with their environmental conditions, like growing citrus fruits in the Mediterranean Region where winters are wet.
Examples & Analogies
Consider natural regions as a global menu in a restaurant. Just like different cuisines have their own dishes based on available ingredients, each natural region serves up unique ecosystems and agricultural opportunities. The Equatorial Region might offer a tropical fruit salad, while the Taiga provides something hearty made of coniferous trees.
Importance of Studying Natural Regions
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Helps understand global climatic diversity.
• Aids in sustainable use of natural resources.
• Supports planning for agriculture, forestry, and human settlements.
• Enhances geographical awareness and environmental conservation.
Detailed Explanation
Studying natural regions is essential for several reasons. First, it helps us understand the wide variety of climates existing on Earth. This is critical for managing natural resources sustainably, ensuring we do not overuse our environment. Additionally, knowledge of these regions assists in effective planning for agriculture and human settlements, allowing people to live in harmony with nature. Lastly, understanding these regions fosters greater awareness of environmental issues and conservation efforts.
Examples & Analogies
Think of studying natural regions like learning to read a treasure map. Each natural region reveals clues about how to protect our planet and use its resources wisely. Just as a treasure map helps you find hidden jewels, studying these regions helps uncover methods to treasure and conserve our natural environment.
Key Concepts
-
Natural Regions: Defined by climate, vegetation, and lifestyle.
-
Equatorial Region: Characterized by heavy rainfall and tropical forests.
-
Hot Deserts: Presence of extreme heat with minimal rainfall.
-
Mediterranean Region: Known for warm, dry summers.
-
Temperate Deciduous Forests: Characterized by seasonal leaf shedding.
Examples & Applications
The Amazon Basin is a notable example of the Equatorial Region.
The Sahara Desert represents a classic Hot Desert environment.
Temperate regions in the USA exhibit significant areas of Deciduous Forests.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the desert where the cactus grows, Heat extremes and little rain flows.
Stories
Once there was a wise owl who nestled in a deciduous forest. Every autumn, he would watch as trees prepared for the cold by shedding their colorful leaves.
Memory Tools
Remember 'CETT' for Climatic Regions: Cold = Taiga, Equatorial = Rainforests, Tropical Grasslands = Tall grasses, Temperate = Deciduous Trees.
Acronyms
D.E.S.E.R.T. - Dry, Extreme, Sandy, Evaporating, Rarely, Trees.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Natural Region
A large geographical area characterized by similar climate, vegetation, wildlife, and human lifestyle.
- Equatorial Region
A geographical area near the equator, characterized by hot temperatures and heavy rainfall.
- Tropical Grasslands
Regions characterized by tall grasses and scattered trees, typically found in warmer climates.
- Hot Desert
A dry region with very high temperatures and minimal rainfall, hosting specialized plant and animal life.
- Mediterranean Region
A climate and geographic area marked by warm summers and moderate winters, often supporting a unique type of vegetation.
- Taiga
A subarctic forest dominated by coniferous trees, characterized by cold winters.
- Tundra
A cold, treeless area characterized by permafrost and limited vegetation.
- Temperate Deciduous Forests
Forests in temperate regions where trees shed leaves seasonally.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
