Reduce Frequency (f)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Frequency Reduction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into how reducing frequency can help us manage power consumption in integrated circuits. Can anyone tell me how frequency relates to power usage?

I think higher frequencies mean higher power consumption because of more switching events.

Exactly! Power increases with frequency. Now, how might we go about reducing that frequency?

Maybe by using clock gating?

Right! Clock gating helps save power by disabling the clock to sections that aren't active. Can you recall what dynamic frequency scaling does?

It adjusts the frequency based on workload!

Well done! So, reducing frequency can help significantly in low power designs. Let's summarize: clock gating disables inactive sections, and dynamic frequency scaling adjusts according to workload.
Deep Dive into Clock Gating
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s take a closer look at clock gating. Does anyone know how this technique is implemented in practical scenarios?

I think it disables the clock at certain parts of the circuit when they’re not needed.

Correct! This drastically reduces the dynamic power consumed. What do you think happens if we don’t implement clock gating?

The circuits will consume more power and possibly overheat?

Exactly! Keeping functionalities on like that wastes energy, leading to inefficiencies. So, effective clock gating can really help maintain system reliability. Any questions on how to implement it?

What tools can we use for clock gating implementation?

Great question! Certain EDA tools provide functionalities to analyze and implement clock gating. Remember, efficiency here supports better power management overall.
Dynamic Frequency Scaling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s shift our focus to dynamic frequency scaling. Can anyone explain why it’s beneficial for low power design?

It allows the processor to operate faster when needed and slow down during less intensive tasks, saving power!

Exactly, well said! Dynamic scaling adjusts the operating frequency based on workload. What might be a potential downside?

There could be latency when changing frequency?

Yes, that’s right! This trade-off is essential to consider: performance versus power savings. Remember, incorporating both techniques allows for a more effective design.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
By employing strategies such as clock gating and dynamic frequency scaling, engineers can effectively lower power consumption in integrated circuits while ensuring performance remains optimized. This balance is critical in modern low power designs.
Detailed
Reduce Frequency (f)
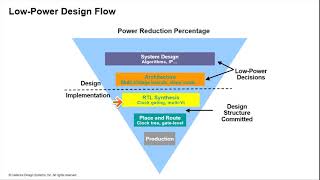
In the quest to minimize power consumption in integrated circuits, reducing the frequency of operations has emerged as a key technique. Frequency reduction plays a pivotal role in managing dynamic power, particularly in CMOS and FinFET technologies, where power consumption is significantly influenced by the operating frequency. This section outlines essential strategies for frequency reduction in integrated circuits.
Key Techniques
-
Clock Gating:
This technique disables the clock signal to portions of the circuit that are not in use, effectively reducing dynamic power consumption. By shutting off the clock, circuits don’t switch, thus conserving energy. -
Dynamic Frequency Scaling:
This approach allows systems to adjust their operating frequency in real time according to workload demands. Lowering frequency during less demanding tasks directly decreases power consumption while maintaining necessary performance for higher demands. -
Trade-offs:
Reducing frequency may lead to an increase in delay and potentially impact system throughput. However, integrating frequency reduction strategies can yield a holistic approach to power management in complex systems-on-chip (SoCs).
These methods align well within a comprehensive low power design strategy, balancing the need for performance with the imperative for lower power consumption in modern integrated circuits.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Frequency Reduction
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Employ clock gating and dynamic frequency scaling.
Detailed Explanation
Reducing the frequency of a circuit can significantly lower its power consumption. This reduction is essential in digital circuits where the power consumed is directly related to the frequency of operation. The techniques mentioned are clock gating and dynamic frequency scaling. Clock gating prevents the clock signal from reaching parts of a circuit that are unused, effectively reducing their power consumption. Dynamic frequency scaling allows the system to change the operating frequency according to workload demands, optimizing power without sacrificing performance.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a car that only goes as fast as needed. If you're stuck in traffic, it's wasteful to speed. By 'scaling' the frequency of operation, like a car adjusting speed based on traffic, the circuit only uses the power it needs, minimizing waste without losing the ability to accelerate quickly when needed.
Clock Gating Explained
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Employ clock gating.
Detailed Explanation
Clock gating is a technique used to reduce power consumption by turning off the clock signal to certain components of a circuit when they are not active. Since digital circuits consume power mainly during switching events driven by clock signals, by stopping the clock, those sections of the circuit can prevent switching, thereby conserving energy. Clock gating can be seen as a switch that ensures that power is only supplied to the components when they are needed, actively reducing unnecessary power usage.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a light bulb that automatically turns off when you leave the room. Instead of keeping it lit when you're not around (which wastes energy), it saves power by 'gating' the electricity, allowing it only when you enter. Similarly, clock gating ensures components are powered only when in use.
Dynamic Frequency Scaling Overview
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
○ Employ dynamic frequency scaling.
Detailed Explanation
Dynamic frequency scaling (DFS) adjusts the clock frequency of a processor dynamically based on the current workload. When the workload is light, the frequency is reduced, thereby lowering the power consumption. Conversely, when more processing power is needed, the frequency increases to meet that demand. This adaptation allows systems to operate more efficiently, balancing performance with power saving, and is particularly useful in mobile devices that run on battery power.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a smartphone that can 'slow down' when you're merely browsing the internet but can 'speed up' if you're playing a demanding game. A similar concept runs in dynamic frequency scaling. The phone adjusts its operational pace based on your current needs, helping to preserve battery life when full power is unnecessary.
Key Concepts
-
Clock Gating: A method to disable the clock to inactive circuit parts to reduce power.
-
Dynamic Frequency Scaling: Adjusting frequency in response to workload to save power.
Examples & Applications
Using clock gating in microcontrollers to disable parts of the circuit not in use, such as the display during low-power modes.
Dynamic frequency scaling in smartphones, where CPU frequency increases during gaming and decreases when idle.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When circuits do not need to play, turn the clock off. It's a power-saving way.
Stories
Imagine a knight who only draws his sword during battle; similarly, clock gating turns off the clock until needed.
Memory Tools
C for Clock Gating, D for Dynamic Scaling. Both save energy - that's the main thing!
Acronyms
DFS for Dynamic Frequency Scaling
Designing Frequency Smartly.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Dynamic Frequency Scaling
A technique that adjusts the operating frequency of a circuit in real time based on workload to conserve power.
- Clock Gating
A power-saving technique that disables the clock signal to inactive parts of a circuit to reduce dynamic power consumption.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
