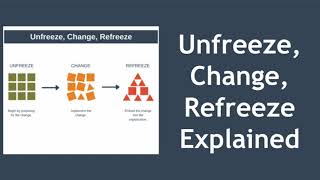
Refreezing
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Refreezing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with understanding refreezing. Refreezing signifies the process of solidifying new changes within an organization. Who can tell me why this phase is essential?

Is it because it helps in making the changes permanent?

Exactly! By focusing on institutionalizing the changes, organizations set themselves up for long-term success and sustainability.

What are some ways organizations can ensure changes are refrozen?

Great question! It can involve modifying policies, providing ongoing support, and aligning organizational rewards with new behaviors. Remember the acronym 'CPRS' - Communication, Policies, Rewards, Support.

How do you measure if a change has been successfully refrozen?

We can measure it through feedback mechanisms, performance metrics, and observing the new behaviors in action. Regular assessments help ensure the changes stick.

So, if I understand correctly, refreezing is about embedding changes into the organization's culture?

Precisely! Refreezing ensures changes are not just adopted but are part of who we are as an organization.

To summarize, refreezing is crucial for making changes sustainable, through strategic actions like communication, policy adjustments, and establishing supportive environments.
Challenges in Refreezing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's move on to the challenges that organizations might face during refreezing. Can anyone think of some common obstacles?

Resistance from employees who might want to revert to old ways?

Exactly! Employee resistance can significantly hinder the refreezing process. How can we effectively manage that?

Maybe through additional training or reinforcement of the benefits of the new changes?

Correct! Training and highlighting benefits are key strategies. Other strategies include celebrating small wins, which can create a sense of ownership and commitment.

Are there organizational structures that can help support refreezing?

Certainly! Structures that promote teamwork and open communication can facilitate a smoother refreezing process. Remember 'TCO' - Teamwork, Communication, Ownership.

So, ultimately it's about creating an environment where new changes can thrive?

Exactly, and to conclude, overcoming resistance and fostering an environment of support and communication are vital for successful refreezing.
Role of Leaders in Refreezing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about the role of leadership during the refreezing phase. Why do you think leaders play a crucial role?

Because they set the vision and culture for the organization?

Exactly! Leaders are instrumental in embodying the changes and helping to motivate employees to adopt them. Can anyone give an example of how a leader can reinforce changes?

By recognizing and rewarding employees who demonstrate the new behaviors?

Yes, acknowledging efforts reinforces desired behaviors. This is where aligning rewards with new norms becomes crucial.

So, is the role of feedback also important?

Definitely! Feedback helps gauge the acceptance of changes and facilitates ongoing improvement. Any final thoughts on leadership's role?

I think leaders should also be approachable for discussing challenges with the new changes.

Absolutely! Building trust helps create a culture of openness, which is beneficial for refreezing. To wrap up, leaders play a crucial role in embodying, communicating, and reinforcing new practices.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The refreezing stage reinforces and institutionalizes the changes implemented during the 'Changing' phase. It involves embedding the new norms into the organization's culture, policies, and rewards to maintain momentum and prevent regression to old practices.
Detailed
Refreezing
Refreezing is the third and final stage in Kurt Lewin's Three-Stage Model of change management, representing the consolidation of new behaviors, practices, and processes within an organization. After implementing changes during the changing phase, refreezing aims to ensure that these changes are durable and integrated into the organizational culture. This process entails a strategic approach to embed new behaviors in daily operations and can include adjusting policies, creating incentives that align with the new goals, and actively promoting the new standards throughout the organization. The significance of refreezing cannot be understated, as it prevents organizations from slipping back into their old methods, thus maintaining the momentum for continued growth and adaptation.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Purpose of Refreezing
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Reinforcing and institutionalizing new changes.
• Embedding changes in organizational culture, policies, and rewards.
Detailed Explanation
The purpose of refreezing is to ensure that the changes made during the transition phase of the change process are not only adopted but also sustained over time. This involves two key actions: first, reinforcing the new behaviors or practices to create a sense of stability; and second, embedding these changes into the organizational culture, which includes updating relevant policies and aligning rewards and recognition systems to support the new ways of working.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you’ve recently adopted a new healthy eating habit after attending a nutrition workshop. At first, it’s challenging, and you might revert to your old habits. To ensure you stick with it (refreezing), you start incorporating healthier food options into your meals (reinforcing the change), remove junk food from your pantry, and perhaps reward yourself when you hit a certain milestone (embedding changes into your lifestyle).
Process of Institutionalizing Changes
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Embedding changes in organizational culture, policies, and rewards.
Detailed Explanation
Institutionalizing changes means integrating them into the everyday practices of the organization. This process often requires altering formal structures such as policies or procedures that govern how work is done. By making these adjustments, organizations can create an environment where new practices are taken for granted, and employees understand that these changes are the new norm.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a school that has introduced a new grading system. For the new system to be accepted by both teachers and students, the school creates guidelines and policies that outline how grades are assigned. Additionally, they may provide rewards for teachers who effectively use the new grading standards, thus ensuring that everyone uses the new system consistently.
Challenges in Refreezing
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Ensuring all employees adapt to and live the new changes.
Detailed Explanation
Throughout the refreezing stage, organizations face the challenge of ensuring that all employees not only adopt but also embrace the new changes. This may involve addressing residual resistance, providing additional training, or refining communication strategies to clarify expectations. The goal is to create a supportive environment where employees feel confident in continuing with the new practices.
Examples & Analogies
Picture a sports team that has changed its training approach. Some players may resist the new techniques because they prefer the old ways. To refreeze successfully, the coach holds team meetings, conducts extra training sessions, and highlights the benefits this new approach delivers, thereby helping all players move past their initial resistance and work towards the team's success.
Key Concepts
-
Refreezing: The process of solidifying changes within an organization.
-
Kurt Lewin's Model: Framework for managing change consisting of unfreezing, changing, and refreezing.
-
Resistance to Change: Hesitation or refusal to adapt to new changes within an organization.
-
Organizational Culture: Collective values and practices that shape employee behavior.
-
Support and Communication: Essential elements for reinforcing change and preventing regression.
Examples & Applications
A company implements a new feedback mechanism that encourages continuous improvement, thus embedding performance evaluation in their culture.
A team is rewarded for successfully adopting Agile methodologies, further enhancing their commitment to new practices.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To refreeze the stage, we set the page, policies change, behaviors rearrange.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a busy corporate land, a team embraced change. To ensure it would stay like a firm handshake, they created rewards and communications to freeze their new direction.
Memory Tools
Remember CPRS: Communication, Policies, Rewards, Support for effective Refreezing.
Acronyms
Use 'CARE'
Communication
Alignment
Reinforcement
Engagement to solidify changes.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Refreezing
The final stage of the change management process where changes are solidified and integrated into the organization.
- Kurt Lewin's Model
A theoretical framework for understanding organizational change, comprising three stages: unfreezing, changing, and refreezing.
- Resistance to Change
The reluctance of individuals or groups to adapt to changes within an organization.
- Organizational Culture
The shared values, beliefs, and norms that shape the behavior and practices within an organization.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
