Agile & Lean Management
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Agile Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss Agile Management. It emphasizes rapid iterations and responsiveness to change. Can anyone tell me what key benefit Agile brings to project management?

It allows teams to adapt quickly to changes based on customer feedback.

Exactly! We can remember this with the acronym 'CARE' - Collaborate, Adapt, Respond, Execute. Agile thrives on collaboration and adaptability. What do you think happens when teams follow Agile principles?

They can deliver features faster and improve the product based on real user input!

Great point! Agile also emphasizes teamwork and communication. Let's summarize: Agile management leads to improved responsiveness and faster delivery.
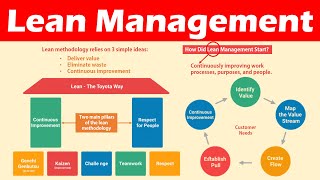
Lean Management Principles
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's connect Lean Management with Agile. Lean aims to eliminate waste in processes. What does ‘waste’ mean in this context?

It refers to anything that doesn't add value to the customer, like unnecessary steps in a process.

Precisely! A mnemonic to remember Lean's focus is 'WASTE' - 'Wait time, Activities not adding value, Supplies excess'. Can anyone share how Lean can be implemented in a tech project?

By simplifying processes and focusing only on features that users need, thus speeding up delivery time.

Absolutely! So, Lean management complements Agile by ensuring we focus our efforts efficiently. In summary, Lean drives efficiency, while Agile fosters flexibility.
Application of Agile and Lean in Tech Projects
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s understand how these two methodologies work together in tech projects. With Agile, teams work in sprints, while Lean phases out unnecessary tasks. How do you think this impacts project success?

It reduces product development time and helps in launching quality products that better meet user needs.

Exactly! Companies gain a competitive edge. To summarize, using Agile with Lean leads to efficient processes and high-quality outputs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines Agile and Lean Management principles, emphasizing their importance in tech environments for swift delivery and efficiency in processes. It highlights the operational benefits of adopting these methodologies in software and IT project management.
Detailed
Agile and Lean Management represent modern paradigms in project management characterized by their focus on efficiency, responsiveness, and stakeholder value. Agile management techniques prioritize customer collaboration and adaptability through short development cycles or iterations, allowing teams to respond promptly to changes and feedback. On the other hand, Lean management advocates for the elimination of waste—defined as anything that doesn't add value to the customer. Together, these methodologies support rapid prototyping and delivery, enhancing productivity and innovation within technology-driven sectors. Their significance is increasingly apparent in software development practices that demand flexibility, quick turnarounds, and minimized inefficiencies.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Agile Management
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Rapid prototyping and delivery
Detailed Explanation
Agile management focuses on creating products in smaller, incremental steps instead of one large, complete project. This method allows teams to adapt more quickly to changing requirements. Rapid prototyping is a key aspect, where teams create basic models or versions of the product and then keep improving them based on feedback. This flexibility is crucial, especially in technology development, where requirements may change frequently.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chef trying to create a new dish. Instead of preparing a full course meal right away, the chef makes a small tasting plate first. After getting feedback from tasters, the chef adjusts the seasoning and ingredients, refining the dish gradually. This practice is similar to agile management, where small changes lead to a final product that meets everyone's expectations.
Lean Management
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Minimizing waste
Detailed Explanation
Lean management focuses on optimizing efficiency by minimizing waste – whether it be time, resources, or effort. Waste can come in many forms, such as overproduction, delays, or unnecessary processes. The goal is to streamline operations so that every component adds value to the final product. By identifying and eliminating wasteful practices, organizations can enhance productivity and improve their bottom line.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a factory assembly line. If a worker spends too much time moving between stations or if parts are sometimes available only after delays, that's waste. A lean methodology encourages rearranging the layout or improving supply chains so workers spend more time building products and less time waiting, just as a chef organizes their kitchen for quick access to ingredients to streamline the cooking process.
Relevance in Tech Product Development
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Highly relevant in tech product development
Detailed Explanation
The principles of Agile and Lean management are especially relevant in tech product development because technology is often complex and rapidly evolving. Agile allows teams to incorporate user feedback and adapt to new ideas quickly, while Lean ensures that the development process is efficient and free of unnecessary steps. This alignment helps tech teams deliver high-quality products that better meet user needs and market demands.
Examples & Analogies
Think about developing a mobile app. Using Agile, a team might start with a basic version of the app, release it to users for feedback, and then iterate based on what users liked or didn’t like. Meanwhile, applying Lean principles might mean cutting down on unnecessary features that don’t add value, helping the team focus on what really matters to the users. This way, the final app is user-friendly, efficient, and fulfilling.
Key Concepts
-
Agile Management: Focuses on iterative development and responsiveness to change.
-
Lean Management: Emphasizes waste elimination to increase efficiency.
-
Sprints: Time-boxed development phases within Agile.
-
Waste: Non-value adding activities identified in Lean principles.
Examples & Applications
A software development team using Agile methodologies runs biweekly sprints to incorporate client feedback.
A company adopting Lean Management restructures its project workflow to eliminate redundant approvals and streamline operations.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Agile and Lean, so crisp and clean, reduce the waste, to reach your dream.
Stories
Once in a tech startup, Agile and Lean worked together, with Agile swiftly adapting to changes while Lean trimmed unnecessary efforts, leading to a successful product launch that wowed users.
Memory Tools
LEAN: Look for efficiency, Eliminate waste, Add value, Nourish growth.
Acronyms
CARE for Agile
Collaborate
Adapt
Respond
Execute.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Agile Management
A project management methodology focused on iterative development and customer feedback.
- Lean Management
A methodology that emphasizes waste reduction in processes to increase productivity.
- Sprint
A time-boxed period in Agile where specific tasks are completed.
- Waste
Any activity that does not add value to the customer in Lean Management.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
