Modern Approaches to Management Thought (1980–Present)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss Total Quality Management, or TQM. It's a management approach that focuses on continuous improvement, customer focus, and employee involvement. Can anyone tell me why continuous improvement is vital?

Continuous improvement makes sure the company is always getting better, right?

Exactly! It's about consistently finding ways to enhance processes. We can remember TQM with the mnemonic 'CICE'—Continuously Improve Customer Engagement. What role do you think employees play in TQM?

They need to be involved to contribute ideas for improvements.

Correct! Engaging employees allows for a more holistic approach to quality control. In summary, TQM ensures that quality is not just the responsibility of one department but a collective effort. Remember the TQM principles: Continuous improvement, Customer focus, and Employee involvement.
Knowledge Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s shift into Knowledge Management. Why do you think it’s essential for software firms?

Because they rely on their knowledge base to stay competitive, right?

Exactly! A robust knowledge base helps firms innovate and make informed decisions. Remember the phrase: 'Knowledge is power.' How might data impact this?

Data can guide decisions and help firms understand their strengths and weaknesses.

Great point! Data informs the knowledge management process, ensuring that your shared insights are accurate and beneficial. To sum up, Knowledge Management is crucial for adapting in today’s fast-paced tech environment.
Agile and Lean Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on, let's talk about Agile and Lean Management. What do you think the key benefit of Agile management is?

It allows for quicker responses to changes in projects.

Exactly! Agile methodologies prioritize flexibility. A mnemonic for remembering Agile principles is 'DRAKE'—Deliver Rapidly, Adapt, Keep Engaging. What about Lean management?

Lean management is about minimizing waste and maximizing value, right?

Correct! Lean focuses on efficiency in processes. As we wrap up, Agile and Lean work together to push organizations towards responsiveness and value generation.
Evidence-Based Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let’s discuss Evidence-Based Management. What does it mean to make decisions based on evidence?

It means using data and analytics rather than just guesswork.

Exactly! This approach is essential in today’s data-driven environment. We can use the acronym 'EBD'—Evidence Before Decision. How does this influence sectors like HR?

In HR, it helps to make hiring and development decisions based on employee data and analytics.

Well said! It’s all about enhancing decision-making through reliable information. In summary, Evidence-Based Management enhances accountability and promotes informed decisions in organizations.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section discusses several key modern management approaches developed since 1980. Total Quality Management emphasizes continuous improvement and customer focus. Knowledge Management highlights the importance of organizational knowledge in tech environments. Agile and Lean Management prioritize flexibility and efficiency, while Evidence-Based Management uses data analytics to inform decisions. These approaches are particularly relevant for the technology-driven landscape of the 21st century.
Detailed
Modern Approaches to Management Thought (1980–Present)
In the contemporary landscape of management, several innovative approaches have arisen since the 1980s, each aiming to enhance organizational efficiency and responsiveness. Here are the pivotal concepts:
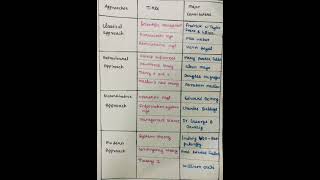
2.7.1 Total Quality Management (TQM)
- Continuous Improvement: Organizations focus on ongoing enhancements in processes and products.
- Customer Focus: TQM stresses the importance of meeting customer expectations and enhancing satisfaction.
- Employee Involvement: Engaging all employees at all levels to contribute to quality improvements.
2.7.2 Knowledge Management
- Focus Area: This approach centers around managing data, information, and intellectual assets effectively. It's particularly important for software firms and tech startups that rely on organizational knowledge for innovation and competitive advantage.
2.7.3 Agile & Lean Management
- Core Principles: Agile management emphasizes rapid prototyping and delivery, allowing organizations to adapt quickly to changes. Lean management aims to minimize waste and maximize value.
- Relevance: These methodologies are essential in tech product development, enabling teams to work efficiently in fast-paced environments.
2.7.4 Evidence-Based Management
- Definition: This approach highlights the importance of using analytics and data to drive decision-making.
- Importance: Especially prevalent in HR tech, fintech, and cloud-based systems, it ensures that decisions are backed by solid data rather than intuition or tradition.
These modern approaches are shaping how organizations function, particularly in technology-centric fields, as they encourage adaptability and continuous improvement.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Continuous improvement
- Customer focus
- Employee involvement
Detailed Explanation
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a management approach that seeks to improve quality and performance in all aspects of an organization's processes. The main components include continuous improvement, which means always finding ways to enhance processes and outputs. Customer focus ensures that the needs and expectations of customers are met, leading to higher satisfaction. Employee involvement emphasizes the idea that all members of the organization should be actively engaged in the process of improvement.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a restaurant that regularly seeks customer feedback. They use this input to refine their menu and service. By involving all staff in brainstorming sessions to improve service quality, the restaurant turns into a TQM model, ensuring continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Knowledge Management
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Focus on data, information, and intellectual assets
- Crucial for software firms and tech startups
Detailed Explanation
Knowledge Management involves systematically managing an organization’s knowledge assets to create value. This includes data, information, and intellectual assets, which are especially important for software firms and tech startups that rely on innovation and agility. By effectively managing knowledge, organizations can ensure that information flows freely and that employees can access and utilize the knowledge needed to make informed decisions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a tech startup that has a centralized online platform where all project documentation, code snippets, and best practices are stored. This allows team members to quickly find and share valuable information, leading to faster problem-solving and innovation.
Agile & Lean Management
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Rapid prototyping and delivery
- Minimizing waste
- Highly relevant in tech product development
Detailed Explanation
Agile and Lean Management are methodologies that focus on flexibility and efficiency in operations. Agile management emphasizes rapid prototyping and delivering products in shorter cycles, enabling organizations to respond quickly to changes in customer demands. Lean management focuses on eliminating waste in all forms to increase efficiency. This approach is particularly beneficial in tech product development, where customer feedback can be incorporated in real time.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a software development team that works in two-week sprints, releasing updates regularly. If customers identify issues or suggest improvements, the team can quickly adapt their work for the next sprint, minimizing wasted effort and delivering a product more aligned with user needs.
Evidence-Based Management
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Using analytics and data to drive decisions
- Popular in HR tech, fintech, and cloud-based systems
Detailed Explanation
Evidence-Based Management refers to the practice of making managerial decisions based on rigorously analyzed data and empirical evidence rather than intuition or past experiences. This approach has gained popularity in fields such as HR technology, fintech, and cloud-based solutions, where data analytics can provide insights to guide strategic choices and measure outcomes effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a company that uses data analytics to evaluate employee performance and identify productivity patterns. Instead of relying solely on annual performance reviews, the management utilizes real-time data to make informed decisions about training and development, leading to better employee engagement and productivity.
Key Concepts
-
Total Quality Management: A systemic approach to improving quality through continuous improvement and customer engagement.
-
Knowledge Management: The strategic approach to managing intellectual assets in an organization.
-
Agile Management: A proactive method that emphasizes flexibility and responsiveness in project management.
-
Lean Management: A management philosophy aimed at increasing efficiency by reducing waste.
-
Evidence-Based Management: Making decisions based on verified data and analytical evidence.
Examples & Applications
A software company implementing TQM to improve the quality of its products by engaging employees in the design process.
A tech startup using Knowledge Management systems to leverage its intellectual resources for innovation.
A project team using Agile methods to quickly adapt to market changes during product development.
An organization utilizing Evidence-Based Management to enhance hiring practices by analyzing employee performance data.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In TQM, we strive, quality's alive, with continuous improvement we thrive.
Stories
Imagine a tech startup that finds success through a shared knowledge platform where every employee contributes ideas, leading to breakthrough products.
Memory Tools
Remember 'A-DB: Agile = Develop, Build' to keep Agile principles clear.
Acronyms
TQM can be remembered as 'CICE'—Continuous Improvement, Customer Engagement.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Total Quality Management (TQM)
A management approach focused on continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and employee involvement.
- Knowledge Management
The process of capturing, distributing, and effectively using organizational knowledge.
- Agile Management
A flexible project management methodology that allows teams to respond swiftly to changes.
- Lean Management
A management philosophy focused on minimizing waste while maximizing value.
- EvidenceBased Management
The use of data and analytics to inform and guide decision-making processes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
