Characteristics of Groups
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Shared Goals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with our first characteristic of groups: shared goals. Can anyone tell me why shared goals might be important in a team setting?

I think it helps everyone work towards the same objective, so we stay focused.

Exactly! Shared goals unify the team. When everyone is aligned on objectives, it creates a sense of direction. Remember the acronym S.M.A.R.T. Goals: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound.

Does that mean if a team doesn't have clear goals, they are likely to struggle?

That's correct. Lack of clear goals can lead to confusion and low motivation. Let's summarize: shared goals foster alignment and focus.
Interdependence
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss interdependence. What does that mean for our group dynamics?

It means we depend on each person to contribute their part.

Right! Interdependence means each member's effort impacts the rest of the group. Can you think of a project where interdependence was clear?

Yes! When I worked on a software development project, my coding needed to integrate with others’ work.

Excellent example! Interdependence enhances collaboration. Let’s recap: interdependence means each member’s contribution is essential to overall success.
Group Norms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we have group norms. Why do you think these are important?

They help guide how we interact and behave.

Correct! Norms create a standard for acceptable behavior. Can anyone give an example of a norm in a team?

Meeting deadlines can be one of those norms.

Absolutely! Norms can significantly impact group cohesion and performance. To summarize, norms guide interactions, helping establish a positive group culture.
Roles and Statuses
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s shift our focus to roles and statuses. Why are these aspects vital in a group?

They help us understand what each person is meant to do.

Exactly! Different roles create structure within the group. Can you identify some common roles?

Like a leader, a facilitator, and a coder?

Great! Understanding roles helps clarify responsibilities, which can improve effectiveness. Recap: roles and statuses provide structure and clarity in teams.
Group Cohesiveness
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s talk about group cohesiveness. What does it mean to you?

I think it’s how much we want to stay together and work together.

Exactly! Cohesiveness refers to the bonds that tie the members together. How can high cohesiveness affect a group?

It can lead to better collaboration and productivity.

Correct! High cohesiveness, coupled with positive norms, often results in high productivity. Remember: cohesiveness builds connections and enhances group effectiveness.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The characteristics of groups include shared goals, interdependence, structured interaction, group norms, roles and statuses, and group cohesiveness. These attributes help facilitate effective teamwork and collaboration, especially in modern organizations where teamwork is critical.
Detailed
Characteristics of Groups
Groups, particularly in organizational settings, possess distinct characteristics that influence their dynamics and performance. Understanding these characteristics is essential for fostering effective teamwork. This section highlights six key characteristics:
- Shared Goals: Members of a group work towards common objectives, which cultivate a sense of purpose.
- Interdependence: Individuals rely on one another to carry out tasks, making the success of the group a mutual effort.
- Structured Interaction: Interactions within the group follow certain patterns or guidelines, leading to organized teamwork.
- Group Norms: These are the informal guidelines that dictate acceptable behavior within the group, impacting how members engage with one another.
- Roles and Statuses: Group members often assume specific roles that define their contributions and establish a hierarchy within the group.
- Group Cohesiveness: This refers to the level of attraction members feel towards one another and their commitment to remaining in the group, which can significantly impact productivity.
In summary, recognizing and nurturing these characteristics is crucial for anyone aiming to succeed in team-based environments.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Shared Goals
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Shared goals
Detailed Explanation
Shared goals refer to the common objectives that all group members strive to achieve together. When a group has shared goals, it reinforces cooperation among members, giving them a unified purpose. This common direction helps to align their efforts, making it easier to work collaboratively towards the accomplishment of these goals.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a marathon running team. Each member of the team shares the goal of completing the marathon, which motivates them to train together, support each other, and push each other to do their best. This shared objective makes their training sessions more productive and enjoyable.
Interdependence
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Interdependence
Detailed Explanation
Interdependence means that the members of the group rely on each other to achieve their goals. The success of one member often contributes to the success of others, creating a bond that emphasizes teamwork. Each person's actions can influence the rest of the group, and this interconnectedness strengthens group dynamics.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a symphony orchestra. Each musician plays a different instrument, but they all depend on each other to create beautiful music. If one musician plays out of tune or at the wrong time, it affects the entire performance. Their interdependence is crucial for a successful concert.
Structured Interaction
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Structured interaction
Detailed Explanation
Structured interaction refers to the way members of a group communicate and collaborate with one another according to certain protocols or formats. This structure can include regular meetings, defined roles, or specific processes that guide how the group functions. When interaction is structured, it helps prevent misunderstandings and promotes efficient collaboration.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a project team using Agile methodology. They have daily stand-up meetings where each member shares what they did yesterday, what they're doing today, and any obstacles they face. This structured interaction keeps everyone informed and engaged, making the project progress smoothly.
Group Norms
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Group norms
Detailed Explanation
Group norms are the unwritten rules or expectations that govern the behavior of group members. These norms can include standards for communication, deadlines, and mutual respect. Group norms develop over time, often shaping how members interact with each other and the work they produce.
Examples & Analogies
In a sports team, a norm might be that all players arrive fifteen minutes early to practice. This unwritten rule ensures that everyone is ready to start on time, promoting discipline and commitment within the team.
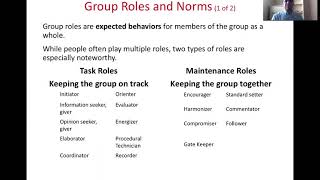
Roles and Statuses
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Roles and statuses
Detailed Explanation
Roles and statuses refer to the specific positions and responsibilities that individuals hold within the group. Each member may take on different roles—such as leader, facilitator, or supporter—depending on their skills and the needs of the group. Understanding these roles helps maintain organization and clarity within the group.
Examples & Analogies
In a theater production, there are various roles such as the director, actors, stage crew, and lighting technicians. Each person has a specific function and responsibility, and their understanding of these roles contributes to a successful performance.
Group Cohesiveness
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Group cohesiveness
Detailed Explanation
Group cohesiveness is the degree to which group members are drawn to one another and motivated to stay in the group. High cohesiveness can lead to better teamwork, increased satisfaction, and improved performance as members feel a stronger connection and commitment to each other.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a close-knit family that enjoys doing activities together—like family game nights or vacations. Their strong bonds and shared experiences create cohesiveness, making them more likely to work together to solve problems and support one another.
Key Concepts
-
Shared Goals: The primary objectives all members strive to achieve together.
-
Interdependence: The reliance of members on one another to achieve group objectives.
-
Structured Interaction: The organization of communication within the group.
-
Group Norms: The shared expectations and rules that guide behavior.
-
Roles and Statuses: The defined responsibilities and hierarchy within the group.
-
Group Cohesiveness: The connectedness and unity among group members.
Examples & Applications
A software development team working towards a common project deadline exemplifies shared goals, interdependence, and structured interaction.
A football team operates under group norms that dictate players' behavior on and off the field, influencing cohesiveness and performance.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a team we all aim, with goals that are the same; interdependence binds us tight, norms guide our shared insight.
Stories
Once there was a band of adventurers, each with a different skill but united by one quest. Their shared goal was to retrieve the golden key from the mythical cave. With every challenge, they relied on each other—one climbed, while another mapped the way. Their norms dictated respect and teamwork, and everyone found their role. Only together could they unlock the mysteries of the cave and emerge victorious.
Memory Tools
To remember the characteristics, think S.I.N.G.C: Shared goals, Interdependence, Norms, Group Cohesiveness, Conflict Roles.
Acronyms
Use the acronym R.I.N.G.S. to recall the key aspects of group dynamics
**R**oles
**I**nterdependence
**N**orms
**G**roup Cohesiveness
and **S**hared Goals.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Shared Goals
Objectives that all group members aim to achieve together.
- Interdependence
A situation where each group member relies on others to succeed.
- Structured Interaction
Organized forms of communication and collaboration within a group.
- Group Norms
Established standards of behavior that guide interactions among group members.
- Roles and Statuses
Specific responsibilities and hierarchy within a group that define member contributions.
- Group Cohesiveness
The degree of attraction and commitment among group members to stay united.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
