Reference Counting and Garbage Collection
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Reference Counting
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about reference counting, which is a key method Python uses for memory management. Can anyone tell me what reference counting means?

Is it about how many times an object is referenced in the code?

Exactly, Student_1! Each object in Python has a reference count which is incremented when a new reference to it is created and decremented when a reference is deleted. Once the count drops to zero, that means no references point to the object anymore, and Python can safely deallocate it.

What happens if there are circular references though?

Great question, Student_2! That's where reference counting can struggle. If two objects reference each other, their reference counts never drop to zero. This leads us to our next concept: cyclic garbage collection. Let's break down that idea now.
Cyclic Garbage Collection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

So, as we discussed, reference counting fails with circular references. Python uses the `gc` module to implement cyclic garbage collection, which periodically checks for reference cycles. Could anyone explain how this works?

Doesn't it just look for objects that are no longer accessible?

Exactly, Student_3! The garbage collector identifies objects that are unreachable (i.e., cannot be accessed anymore) and removes them from memory. This ensures that memory is freed even when circular references are involved.

Can you show us an example of how to use the `gc` module?

Sure! Here's a quick example using a simple class with circular references. We'll create a `Node` class and demonstrate using `gc.collect()` to clear unused objects. Let's dive into that code.
Practical Application of Garbage Collection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, who can help me outline how to implement cyclic garbage collection in Python using the `gc` module? What steps do we take for this?

First, we need to import the gc module, right?

Correct, Student_1! Then, we would create our objects that reference each other and delete them afterward. Finally, we can call `gc.collect()` to force garbage collection. It's always a good practice to run this in memory-intensive applications.

So the code would help in cleaning up memory automatically?

Yes, precisely! By leveraging this module, we ensure that our application remains efficient and responsive. Remember, managing memory effectively can greatly enhance performance.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In Python, every object has a reference count that indicates how many references point to it. When the count drops to zero, the memory is deallocated. However, reference counting struggles with circular references, which are addressed by Python's cyclic garbage collection.
Detailed
Reference Counting and Garbage Collection
Python employs an automatic memory management system that primarily relies on reference counting, where each object maintains a count of references pointing to it. When this count reaches zero, it signifies that the object is no longer in use and can be deallocated, freeing up memory resources. However, this system falters in cases of circular references—situations where two or more objects reference each other, preventing their reference counts from dropping to zero, even when they are no longer accessible from the program. To remedy this issue, Python implements a cyclic garbage collector via the gc module, which periodically scans for unreachable objects that are part of reference cycles. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for optimizing memory usage in Python applications.
Youtube Videos
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Reference Counting
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
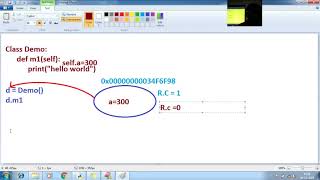
Every object in Python has a reference count: a number that indicates how many references point to that object.
import sys a = [] b = a print(sys.getrefcount(a)) # Usually 3: a, b, and argument to getrefcount
- When the reference count drops to zero, the memory is deallocated.
- This is the primary mechanism for memory management.
Detailed Explanation
Reference counting is a technique used by Python to manage memory. Each object in Python keeps track of how many references point to it through a reference count. When you create a new object, like an empty list in our example, its reference count increases by one for each variable or input that refers to it. In the example provided, both 'a' and 'b' reference the list, hence the reference count is 3 (including the internal reference made by the function getting the reference count). Once the references to the object drop to zero, meaning no part of the program is using it anymore, Python automatically frees the memory associated with that object.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a library where each book (object) has a counter (reference count) that tracks how many people have checked it out (references). If everyone returns the book, the counter drops to zero, and the library can remove it from the shelf (deallocate memory). If someone continues to check it out, the book remains on the shelf.
Cyclic Garbage Collection
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Reference counting fails when there are circular references (objects referring to each other), which keep each other alive.
import gc
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.ref = self
a = Node()
del a # This won't immediately free memory
gc.collect() # Forces a garbage collection cycle
- Python’s gc module handles cyclic references.
- The garbage collector periodically scans for unreachable objects in cycles.
Detailed Explanation
Cyclic garbage collection addresses a notable limitation of reference counting: circular references. A circular reference occurs when two or more objects reference each other, preventing their reference counts from ever reaching zero. In the provided code, when we create an instance of 'Node', it references itself, forming a cycle. Even if we delete the reference to 'a', the reference count does not become zero because the instance still refers to itself. The garbage collector, managed by the 'gc' module, identifies these cycles and clears the memory periodically by scanning for objects that can no longer be accessed, enabling Python to reclaim memory effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a group of friends who each keep in touch with one another. If Friend A calls Friend B, and Friend B calls Friend A back, they are in a loop of communication. If neither makes a new friend (loses contact with someone), they remain connected indefinitely. The garbage collector acts like a mediator who comes in, evaluates the situation, and determines that they can both move on and disconnect if they are not communicating with anyone else.
Key Concepts
-
Reference Counting: A mechanism where each object tracks how many references point to it to manage memory.
-
Cyclic Garbage Collection: A process that handles memory cleanup for unreachable objects that may be involved in reference cycles.
-
gc module: Python's built-in library for managing garbage collection, particularly useful for cyclic references.
Examples & Applications
Using sys.getrefcount() to check the reference count of an object can give insight into whether that object can be safely deallocated.
Class instances with circular references require manual cleanup using the gc.collect() method to prevent memory leaks.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Memory counting, reference rounding, zero it drops, memory is founding!
Stories
Imagine two friends, Alice and Bob. They each write down every time they talk to each other. But if they only talk to each other and no one else, their notes never get to zero!
Memory Tools
Remember 'RAG' for Reference counting, Automated Garbage collection, to recall the two key memory management concepts.
Acronyms
CYCLE for Recognizing Circular references impacting garbage collection
Check
Yield
Collect
Lose
Eliminate.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Reference Count
A number indicating how many references point to an object in Python.
- Cyclic Garbage Collection
A method that identifies and collects objects involved in reference cycles that are no longer reachable, preventing memory leaks.
- gc module
A built-in Python module that provides functions to interact with the garbage collection facility, enabling the management of cyclic garbage collection.
- Memory Deallocation
The process of releasing memory that is no longer needed by the program.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
