Augmented Reality (AR) for HRC
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Augmented Reality (AR)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore Augmented Reality, or AR. This technology overlays digital information in the real world. In civil engineering, it's instrumental in enhancing how we interact with robots.

How exactly does AR improve collaboration with robots?

Great question! AR allows engineers to give commands to robots through gestures or voice, which makes the interaction more intuitive. Imagine pointing to a location and the robot understanding where to go!

That sounds fascinating! Does it make the working environment safer?

Absolutely! By facilitating more efficient communication, AR helps reduce errors that could lead to accidents. Therefore, safety is significantly enhanced.

How do engineers know what commands to give when using AR?

AR systems usually come with user guides and visual prompts that help users understand available commands, aiding quick learning.

In summary, AR streamlines command execution, enhancing both collaboration and safety.
Benefits of AR in HRC
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

One of the main benefits of AR in HRC is improved operational control. When engineers can visually interact with robots, they can make rapid adjustments based on real-time observations.

What about the learning curve? Is it hard to adapt to this technology?

Initially, users may find it overwhelming, but the intuitive nature of gesture-based commands simplifies the learning process considerably.

Are there industries other than civil engineering using AR for human-robot collaboration?

Yes! Manufacturing and healthcare also utilize AR to enhance collaboration between humans and machines. But today, our focus is how it revolutionizes civil engineering.

Remember: AR not only enhances collaboration but also streamlines workflows, leading to increased productivity.
AR Interface Features
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

AR interfaces often include features such as real-time visualization of robot tasks and diagnostic information.

Can AR show us live data from robotic sensors?

Yes! AR can display data in an easily digestible format, ensuring that the users remain informed during their tasks.

How does this help with project management?

It allows for better monitoring of progress and quick identification of any deviations from the planned workflow.

In conclusion, AR interfaces are a powerful tool for improving collaboration, safety, and efficiency on construction sites.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
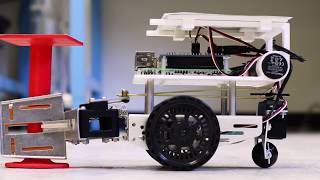
AR interfaces connect engineers with robotic systems through wearable headsets or mobile devices, allowing intuitive interactions via gestures or voice commands. This technology improves operational control and responsiveness, essential for complex construction tasks.
Detailed
Augmented Reality (AR) for HRC
Augmented Reality (AR) plays a crucial role in enhancing Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC) in civil engineering. AR interfaces allow engineers and field workers to interact with robotic systems through wearable devices like headsets or smartphones. By enabling intuitive command inputs via gestures or voice, AR significantly improves responsiveness and control in operational environments.
This innovative integration supports effective collaborations during construction tasks, where precision and timely actions are critical. As the construction industry embraces such advanced technologies, the fusion of AR with robotic systems not only optimizes workflows but also enhances safety and efficiency on job sites.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Augmented Reality (AR)
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AR interfaces enable engineers and field workers to interact with robots through wearable headsets or mobile devices.
Detailed Explanation
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information onto the real world. In the context of Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC) in civil engineering, AR allows engineers and field workers to see and interact with information and robotic systems using devices such as headsets or smartphones. This means that instead of just seeing one environment, users can see additional information that is useful for their tasks, such as plans, data visualizations, or even robot status indicators, right in their field of view.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are wearing special glasses while working on a construction site. Instead of just looking at the bricks and mortar, the AR glasses might show you where to place each brick based on the design, as well as real-time data about the robot that is helping you. This is similar to how navigation apps overlay directions onto a real-world map on your smartphone.
Commands and Interaction
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Commands can be given via gestures or voice, improving responsiveness and operational control.
Detailed Explanation
AR systems enhance the interaction between humans and robots by allowing users to give commands in ways that feel natural and efficient. For example, instead of using a remote control or typing on a computer, a field worker can simply use hand gestures or voice commands to direct a robot. This not only speeds up communication but also makes it easier to control robots in dynamic environments, where manual controls may be cumbersome or impractical.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how you can talk to a virtual assistant on your phone, like asking it to play music or check the weather. With AR, you could be on a construction site and, just by saying 'lift the beam,' a nearby robotic arm could respond instantly, lifting it into place without you needing to navigate through a complicated interface to issue the same command.
Key Concepts
-
Augmented Reality (AR): A technology that blends digital content with the physical world, enhancing interactions with robots.
-
Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC): The effective partnership between humans and robots in working environments.
-
Intuitive Command Input: The ability to give commands easily through gestures or voice thanks to AR technology.
Examples & Applications
Using AR goggles, construction workers can point to areas needing attention, allowing robots to immediately respond and take actions.
Field managers can visualize robotic sensor data in real-time to track the performance of autonomous construction machines.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
With AR in the mix, commands you can fix, engineers and bots, in harmony like music.
Stories
Imagine a construction site where a worker lifts his hand, and a robot nearby responds by moving to the precise location, all thanks to AR—collaboration comes to life!
Memory Tools
Remember 'CAR': Collaboration, Augmented Reality enhances operational control, and Responsiveness is key to HRC.
Acronyms
AR
Amazing robot-friendly
enhancing synergy!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Augmented Reality (AR)
A technology that overlays digital information in the real world, enhancing interactions with robotic systems.
- HumanRobot Collaboration (HRC)
A synergistic interaction between humans and robots, leveraging their strengths in various tasks.
- Wearable Devices
Portable technology that can be worn on the body, enhancing user interaction with AR.
- GestureBased Commands
Commands given to robots through physical movements or gestures recognized by AR systems.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
