High-Level Design (Architectural Design)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Processor Selection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss processor selection in SoC design. Why do you think the choice of processor is important?

Because it affects how fast the SoC can work, right?

Exactly! The chosen processor dictates performance capabilities. For example, would you prefer a general-purpose ARM core or a custom-designed processor?

A custom-designed one could do specific tasks better, like AI processing!

That's a great point! So, how would you approach balancing performance with other factors, like power consumption?

Maybe we'd look for benchmarks or comparisons?

Absolutely! It's about trade-offs. Remember, we also have to consider the SoC's intended application.

In summary, the processor choice greatly influences the performance characteristics of the SoC.
Memory Architecture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's move on to memory architecture. Why is it critical in SoC design?

Because memory impacts how fast data is processed, right?

Exactly! When designing an SoC, what types of memory might we consider?

On-chip memory like SRAM, and off-chip memory like DRAM.

Correct! Each has its place based on performance and power constraints. Can you explain how these decisions are made?

It depends on the application needs and how much power we want to save.

You've got it! Balancing performance versus power consumption is a common theme in SoC design.

In conclusion, an efficient memory architecture is pivotal to a successful SoC.
Peripherals and I/O Interfaces
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss peripherals and I/O interfaces. Why might choosing the right peripherals matter?

They determine what functions the SoC can perform!

Exactly! We also need to consider how these peripherals connect to the processor. What protocols do we have?

Protocols like USB or HDMI, right?

Yes! The right interface directly affects the SoC’s usability. Can you think of an application where specific peripherals are beneficial?

In smartphones, having good camera interfaces is essential!

That's a perfect example! Remember, the integration of peripherals aids in meeting specific user requirements.

To summarize, peripheral selection is vital for functionality and marketability of the SoC.
PPA Analysis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's talk about PPA analysis. What do you think this entails?

It’s about making sure the SoC performs well while not using too much power or space!

Exactly! Balancing these factors is crucial for design success, especially for mobile applications.

How do designers go about analyzing these trade-offs?

They use various simulation tools to analyze different scenarios and optimize the design.

Sounds complicated! Are there specific tools you can think of?

Tools like Cadence or Synopsys are often used. They help in assessing the impacts of design choices.

In summary, thorough PPA analysis ensures that the design meets the necessary requirements without unnecessary compromises.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
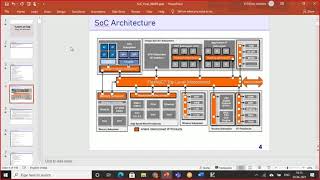
In high-level design, various architectural decisions are made for the SoC, including choosing processors, defining memory architectures, and assessing the inclusion of peripherals. In addition, power, performance, and area (PPA) analysis is conducted to ensure that the design meets the application-specific requirements, using high-level simulation tools for verification purposes.
Detailed
High-Level Design (Architectural Design)
This section discusses high-level design, a critical phase in the SoC design flow that follows the specification stage. At this juncture, key architectural decisions are made to define how the SoC will function. Key areas of focus include:
Processor Selection
This involves deciding on the type of CPU and GPU, along with any specialized accelerators needed for specific tasks. For instance, one might choose between a general-purpose ARM core or custom-designed processors tailored for AI applications.
Memory Architecture
Designing the memory subsystem is crucial, including on-chip and off-chip memory configurations. Factors influencing these decisions include performance needs and power limitations.
Peripherals and I/O Interfaces
In this phase, decisions about which peripherals to integrate, like USB and HDMI, are made, alongside the necessary communication protocols that will facilitate connections between memory and processors.
PPA Analysis
Power, Performance, and Area (PPA) analysis becomes paramount. The architect must balance performance enhancements against power consumption limits and physical area constraints to ensure design feasibility for the intended application.
Overall, high-level design is vital since it lays the groundwork for subsequent phases of the SoC design process, where further specifics will be fleshed out using high-level simulation tools and system-level modeling to verify functionality and performance.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Processor Selection
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Deciding on the type of CPU, GPU, and any specialized accelerators needed for the application. For example, choosing between a general-purpose ARM core or a custom-designed processor for specific tasks (e.g., AI or signal processing).
Detailed Explanation
In the high-level design phase of SoC development, one of the most important decisions is processor selection. This involves evaluating the specific needs of the application to determine the best type of processor to use. It could be a general-purpose processor, such as an ARM core, which is widely used for many applications, or a custom processor designed for specialized tasks like artificial intelligence (AI) or signal processing, which require unique processing capabilities. This decision significantly affects the performance and efficiency of the SoC.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a chef selecting kitchen tools for a specific recipe. If they are preparing a delicate soufflé, they might choose a whisk and a fine sieve instead of a heavy-duty mixer. Similarly, in SoC design, choosing the right processor is like picking the right tool that perfectly fits the task at hand.
Memory Architecture
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Designing the memory subsystem, including on-chip memory (e.g., SRAM, cache) and off-chip memory (e.g., DRAM). Decisions are made based on performance and power constraints.
Detailed Explanation
The memory architecture is a crucial aspect of high-level design. It involves planning how data will be stored and accessed in the SoC. On-chip memory, such as SRAM (static random-access memory) and cache, provides fast access for frequently used data, while off-chip memory like DRAM (dynamic random-access memory) offers larger storage space. The choice of how much of each type of memory to include depends on the desired performance (speed) and power efficiency, as different types of memory consume different amounts of power.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a library. If you have a small home library (on-chip memory) with only the books you read frequently and a large public library (off-chip memory) that has everything but takes longer to access. A good balance between these two ensures quick access to resources without overwhelming power consumption.
Peripherals and I/O Interfaces
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Deciding on which peripherals to include (e.g., USB, HDMI, Ethernet) and how they interface with the processor and memory. This also includes defining the communication protocols used by the system.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we discuss peripherals and I/O interfaces, which are essential for the SoC to interact with the outside world. Peripherals could include connectivity options like USB for data transfer or HDMI for video output. The designer must decide which peripherals are necessary for the intended use of the device. Furthermore, it’s vital to define the communication protocols, such as how the processor talks to the memory and peripherals, ensuring smooth data flow and functionality.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine planning a party. You need to decide on the catering service (peripherals) to ensure food and drinks are available. You also have to arrange how guests will interact with the service (communication protocols) to create a seamless experience. Just like this, peripherals and I/O interfaces make interactions possible in SoC design.
Power, Performance, and Area Analysis (PPA)
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Analyzing trade-offs between performance, power consumption, and the area occupied by the SoC. These factors are crucial for ensuring the design meets application-specific requirements.
Detailed Explanation
PPA analysis is a critical aspect of high-level design that requires careful consideration of trade-offs. Designers must evaluate how changes in design might improve performance but potentially increase power consumption and chip area. Each design decision can impact these three factors—performance (how fast the SoC operates), power (energy consumption), and area (the physical size of the chip). Striking a balance between them is essential to meet the specific needs of the application, whether it be a high-performance gaming console or a power-efficient IoT sensor.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a car engine. A sports car (high performance) may consume more fuel (higher power) and take up more space (area) than a compact car designed for fuel efficiency. The difference in design reflects the needs and preferences of the drivers. Similarly, in SoC design, the target application will determine the best balance of power, performance, and area.
High-Level Simulation and Verification
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
During this phase, high-level simulation tools and system-level modeling are often used to verify the architecture’s functionality and performance.
Detailed Explanation
Once the architectural choices for the SoC have been made, high-level simulation and system-level modeling come into play. These tools allow designers to create prototypes of their designs in a simulated environment. This means they can test how the architecture will perform under various conditions before committing to actual hardware. By running simulations, designers can identify and fix potential issues early in the design process, leading to more reliable and efficient final products.
Examples & Analogies
It’s similar to a film director using storyboards to visualize a movie before shooting begins. By mapping out scenes and sequences, the director can spot errors or make adjustments, ensuring the final product is well-planned and executed. In SoC design, simulations help catch mistakes early, saving time and resources.
Key Concepts
-
Processor Selection: The process of choosing the appropriate CPUs and GPUs to enable specific functionalities.
-
Memory Architecture: The structuring of both on-chip and off-chip storage to fit performance and power needs.
-
PPA Analysis: A critical examination of power usage, performance metrics, and the physical area required for the SoC.
Examples & Applications
Selecting an ARM Cortex processor for a smartphone application due to its low power consumption and sufficient processing power.
Designing a memory architecture that includes 1 MB of SRAM for caching and 4 GB of DRAM for main memory in a gaming console.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Select the cores, optimize the scores, with memory that's fast, your design will last.
Stories
Imagine you're building a small city (SoC) where you need to decide whether to build high-rise apartments (CPU) or individual houses (custom processors) based on how many people will live there (performance needs) and how much space you have (area constraints).
Memory Tools
PPA: Protecting Performance and Area in your design!
Acronyms
M.P.P
Memory
Processor
Peripherals - the trio to prioritize in design.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- SoC
System on Chip; an integrated circuit that incorporates all components of an electronic system into a single chip.
- Processor Selection
Choosing the appropriate CPU or GPU for the SoC design based on performance and application requirements.
- Memory Architecture
The design and organization of memory components, including on-chip and off-chip memory.
- PPA Analysis
Analysis of Power, Performance, and Area trade-offs in SoC design to optimize functionality and efficiency.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
