Thread Confinement and Local Variables
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Thread Confinement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing thread confinement, a strategy that helps in writing safe multithreaded applications. Can anyone tell me what they think thread confinement means?

Is it when a variable is only accessible by a single thread?

Exactly! Thread confinement ensures that a variable is only used by the thread that created it, preventing any interference. This way, we eliminate the need for synchronization.

So, it’s like keeping secrets in a box only I can open?

Great analogy, Student_2! Each thread has its own 'box', preventing other threads from peeking or interfering with its contents.

What kind of variables can we use with thread confinement?

Good question! Local variables are a prime example. They exist within a method and are not accessible outside, making them naturally confined. Does anyone remember how this relates to the `ThreadLocal` class?

`ThreadLocal` gives each thread its own copies of a variable!

Exactly! By using `ThreadLocal`, we minimize shared mutable state and reduce the risk of race conditions. Great participation today!
Using ThreadLocal Variables
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into `ThreadLocal`. Who can tell me how to create a `ThreadLocal` variable?

We can use the `ThreadLocal.withInitial()` method, right?

Correct! This method allows you to define an initial value for your thread-local variable. Can anyone give me an example?

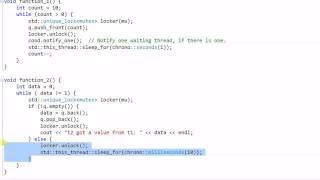
Sure, we could write something like `ThreadLocal<Integer> threadId = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> 0);`.

Perfect! Each thread will see `threadId` starting at 0. What are the advantages of using `ThreadLocal`?

It reduces synchronization overhead and makes each thread independent!

Absolutely! However, remember to clean up the `ThreadLocal` variables if they are no longer needed to prevent memory leaks. How would you do that?

You can use `ThreadLocal.remove()` method, right?

Yes! Great job! Let’s summarize: Thread confinement provides a safe way to use variables in multithreaded environments by limiting their visibility.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section explains thread confinement, where data is limited to a single thread, thereby eliminating concurrency issues. It introduces the ThreadLocal class in Java, which provides isolated variables for each thread, ensuring that each thread has its unique copy of the variable.
Detailed
Thread Confinement and Local Variables
In this section, we explore the concept of thread confinement, which is a method of achieving thread safety by restricting data visibility to a single thread. This approach avoids the overhead and potential errors associated with synchronization, as data confined in this way does not need to be shared across threads.
Key Concepts:
- Thread Confinement: Thread confinement restricts data access to a specific thread, meaning that the data is not accessible by other threads. This confinement can be achieved using local variables, which are only visible within the method they are declared.
-
ThreadLocal Variables: The
ThreadLocalclass in Java provides a mechanism for each thread to have its own isolated copy of a variable. Each thread can then manipulate its variable independently, enhancing performance and safety without requiring synchronization. An example usage is:
In this example, each thread has its own integer value for threadId, initialized to 0, ensuring no interference between threads.
In summary, by using thread confinement and ThreadLocal, developers can write more efficient and thread-safe applications without the complexities introduced by shared state and synchronization.
Youtube Videos




![Let's Look at Lambdas - Roger Orr [ ACCU 2021 ]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/NAuFNXIsbtw/mqdefault.jpg)

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Thread Confinement
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Data is confined to a single thread, no need for synchronization.
Detailed Explanation
Thread confinement is a concept where data is restricted to a single thread of execution. In this scenario, the data does not need to be synchronized because no other thread can access it. This means that any modifications made to the data by one thread are safely contained within that thread, eliminating the risk of race conditions or visibility issues that arise in multithreaded environments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a private diary that only one person is allowed to write in. No one else can read or modify its contents. Since it's only accessible by that one individual, they can write freely without the fear of someone else changing what they've written. This scenario illustrates thread confinement, where the diary is the data, and the individual is the thread that has exclusive access.
ThreadLocal
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Provides variables that each thread has its own isolated copy of.
ThreadLocal
Detailed Explanation
The ThreadLocal class in Java allows you to create variables that each thread can access but have their own distinct copies. Each thread accesses a thread-local variable through its own reference, making it independent from other threads' copies. This helps create thread-safe applications without the complexity of managing synchronization as each thread works with its own state without interference from others.
Examples & Analogies
Think of ThreadLocal as a personal locker at a gym. Each member has their own locker where they can store their belongings. When a member accesses their locker, they are the only one with the key to that specific locker, ensuring that no one else can interfere with their items. Similarly, with ThreadLocal, each thread has its own copy of a variable safe from other threads.
Key Concepts
-
Thread Confinement: Thread confinement restricts data access to a specific thread, meaning that the data is not accessible by other threads. This confinement can be achieved using local variables, which are only visible within the method they are declared.
-
ThreadLocal Variables: The
ThreadLocalclass in Java provides a mechanism for each thread to have its own isolated copy of a variable. Each thread can then manipulate its variable independently, enhancing performance and safety without requiring synchronization. An example usage is: -
ThreadLocal
threadId = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> 0); -
In this example, each thread has its own integer value for
threadId, initialized to 0, ensuring no interference between threads. -
In summary, by using thread confinement and
ThreadLocal, developers can write more efficient and thread-safe applications without the complexities introduced by shared state and synchronization.
Examples & Applications
Using local variables within a method to avoid sharing state between threads.
Creating a ThreadLocal variable to maintain a unique ID for each thread.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Threads in a box, safe and sound, / Within their walls, problems are drowned.
Stories
Imagine each thread as a gardener tending their own patch of flowers. They water and care for their own plants without worrying that someone else will trample their garden.
Memory Tools
CLONE: Confinement means Local Objects Never Expose (to other threads).
Acronyms
TL
Thread Local - Treats each thread as a unique local entity.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Thread Confinement
A programming approach where data is kept within a single thread to avoid synchronization issues.
- ThreadLocal
A class providing thread-local variables, where each thread has its isolated copy.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
