What is Thread Safety?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Thread Safety
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss thread safety. Can anyone tell me what they think it means?

Isn't it when a class can be accessed by multiple threads safely?

Exactly! A class is considered thread-safe if multiple threads can interact with shared data without causing corruption or inconsistent results. Remember, safety in this context means no matter how threads execute or interleave, the outcomes remain predictable.

What happens if a class is not thread-safe?

Great question, Student_2! If a class isn't thread-safe, it could lead to various problems, such as race conditions and inconsistent data. Can someone give me an example of a scenario where this might happen?

Maybe when two threads try to update the same value at the same time?

Yes, that's a perfect example of a race condition, where the final state depends on the timing of the threads. To sum up, thread safety is paramount in ensuring that our Java applications behave as expected in multi-threaded environments.
Challenges of Achieving Thread Safety
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand what thread safety is, let's discuss why achieving it can be difficult. Can anyone name some issues that might arise?

Race conditions?

Absolutely, race conditions are a significant threat to thread safety. They occur when the outcome of an operation depends on the timing of threads. What other issues could we face?

Atomicity violations?

Correct! Atomicity violations happen when a compound action, like checking a value before updating it, is interrupted by another thread. This can lead to faulty logic in our applications.

And memory consistency errors?

Exactly! Memory consistency errors occur when a change made by one thread is not visible to another due to caching or optimization. It's vital to ensure that all threads have a consistent view of memory. This emphasizes the importance of managing shared data in multi-threaded applications.
Importance of Thread Safety
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into why thread safety is crucial in our applications. Why do you think it matters?

Because inconsistent results can lead to bugs?

Exactly right! Bugs in multi-threaded applications can be extremely hard to trace and fix. They may only occur under specific conditions, making them elusive. What would be the impact of these bugs in a real-world application?

Isn’t it potentially leading to data corruption or loss of important information?

Precisely! Data corruption can lead to significant issues, including financial losses in banking software or data integrity concerns in scientific calculations. Thus, ensuring that our Java applications are thread-safe is not just best practice; it's a necessity.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
A class is thread-safe if it can be accessed by multiple threads concurrently without leading to data corruption or inconsistent behavior. This section covers the fundamentals of thread safety in Java, emphasizing the challenges developers face in achieving it, including race conditions and memory consistency errors.
Detailed
What is Thread Safety?
A class is said to be thread-safe if it can be safely executed by multiple concurrent threads without leading to unpredictable outcomes. This concept is crucial in concurrent programming, as it addresses the safety and integrity of shared data. In multithreaded applications, threads often interact with each other, and if they're allowed to access shared data without proper synchronization, they might corrupt this data or produce inconsistent results. This section discusses the significance of thread safety and outlines common issues that can arise in multithreaded environments.
Youtube Videos


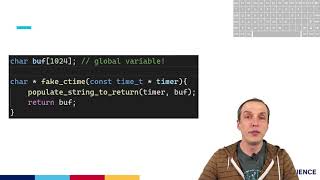






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Thread Safety
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A class is said to be thread-safe if multiple threads can access shared data without corrupting it or causing inconsistent results, regardless of the timing or interleaving of their execution.
Detailed Explanation
Thread safety refers to the property of a class or object whereby it functions correctly when accessed by multiple threads concurrently. When a class is thread-safe, it allows for safe interaction with shared data by ensuring that when one thread modifies this data, others are prevented from causing errors or inconsistencies. This means that the design of the class handles various timing and operational scenarios that arise from concurrent execution, giving developers confidence that they can use instances of the class safely in a multi-threaded application.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a shared office printer. If multiple people try to print their documents at the same time without any management system in place, documents could be mixed up, jammed, or lost. A printer that can handle multiple print jobs effectively without error is similar to a thread-safe class — it manages the competing requests to ensure everyone’s document prints cleanly and correctly, regardless of when each person hit 'print'.
Key Concepts
-
Thread Safety: The guarantee that a class can be accessed concurrently without data corruption.
-
Race Conditions: Bugs occurring from improper execution timing of threads.
-
Atomicity: Operations must complete as a single step to avoid inconsistency.
-
Memory Visibility: Ensuring all threads see the latest changes made in shared memory.
Examples & Applications
A shared bank account accessed by multiple threads, where balance checks and updates must be atomic to avoid overdraw issues.
A shared counter that increments in a multithreaded environment must ensure each increment operation is visible to all threads.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Thread safety's the key, let data be free!
Stories
Imagine a library with many readers. If two readers try to write in the same book at the same time without a librarian to coordinate, chaos will ensue. But with the librarian (thread synchronization), each reader takes turns, keeping the book clean.
Memory Tools
RACE: Race condition, Atomicity, Consistency, Execute safely.
Acronyms
THREAD
Tidy handling of resources enhances application durability.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Thread Safety
The property of a class or method that guarantees safe interaction among multiple threads without causing data corruption or inconsistent results.
- Race Condition
A situation where the output of a program depends on the sequence or timing of uncontrollable events such as thread execution.
- Atomicity Violation
An error that occurs when a compound action is not completed as a single, indivisible step, leading to data inconsistency.
- Memory Consistency Error
Issues arising when changes made by one thread are not visible to other threads due to optimization or caching mechanisms.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
