Balanced Chemical Equations
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Chemical Equations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to talk about balanced chemical equations. Does anyone know what a chemical equation is?

Is it a way to show what happens in a chemical reaction?

Exactly! A chemical equation shows us the reactants and products in a reaction. For example, the combustion of magnesium in oxygen produces magnesium oxide.

How do we write that in an equation?

Great question! We can write it as: Mg + O₂ → MgO. This is a skeletal equation. But what happens if we want to show that the equation is balanced?

Do we need to count the atoms on each side?

That’s right! By counting, we ensure the law of conservation of mass is upheld. Remember, mass is conserved!

So, balancing is like a math problem?

Exactly! We will learn how to adjust coefficients to balance equations, ensuring they follow the right math and chemistry rules.
Steps to Balance a Chemical Equation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s delve into the steps to balance chemical equations. Can anyone remember what the first step is?

We need to write the unbalanced equation first.

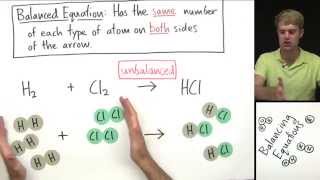
Correct! For example, if we take H₂ + Cl₂ → HCl, we first write it out without any coefficients. The second step is counting the atoms on both sides. Student_2, what do you get?

On the left, there are 2 H and 2 Cl, and on the right, there is 1 H and 1 Cl.

Right! Problem identified - we need to balance these. We can add a coefficient of 2 in front of HCl. What does that give us?

That makes it H₂ + Cl₂ → 2HCl.

Exactly! Now we have 2 H and 2 Cl on both sides. This means it’s balanced. Well done!
Types of Chemical Reactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand balancing, let's learn about types of reactions. Can anyone think of different types of chemical reactions?

There are combination and decomposition reactions!

Exactly! In combination reactions, two or more substances combine to form one compound. Can someone give an example?

Like when hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water?

Yes! H₂ + O₂ → H₂O is a great example. Now, what about decomposition reactions?

That’s when one substance breaks down into two or more products.

Exactly! Learning these types of reactions helps us understand how to approach balancing them effectively.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Balancing chemical equations is crucial to reflect the law of conservation of mass in chemical reactions. The section covers step-by-step methods to determine and balance equations, defining reactants and products, and introduces various types of chemical reactions.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
In this section, we explore the concept of balancing chemical equations, foundational to understanding chemical reactions. A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction, using chemical formulas to depict reactants and products. Balancing equations is essential to showcase that matter is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical transformation, a principle known as the law of conservation of mass.
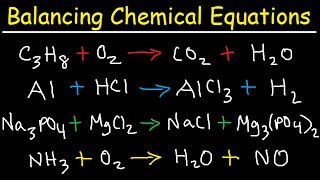
The section begins with the definition of a skeletal chemical equation, which provides an unbalanced equation. Several methods exist to balance these equations which require maintaining the same number of each type of atom on both sides of the equation.
Key Points Covered:
- Balanced vs. Unbalanced Equations: An equation is balanced when the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides. Otherwise, it is unbalanced.
- Steps to Balance an Equation: Techniques are provided to count atoms of each element, identify imbalances, and make adjustments using coefficients while keeping the integrity of the compounds intact.
- Representation of Physical States: State symbols (s, l, g, and aq) help indicate the physical state of reactants and products in a reaction.
Understanding these concepts is vital for students as it lays the groundwork for all further studies in chemical reactions, enabling them to analyze and predict reaction outcomes effectively.
Youtube Videos







Key Concepts
-
Balanced Equations: Represents a state where the number of atoms is equal on both sides.
-
Conservation of Mass: States that mass is conserved in chemical reactions.
-
Coefficients: Numbers used to balance chemical equations, showing the number of molecules involved.
Examples & Applications
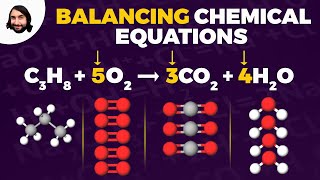
Example of a balanced equation: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
Example of a skeletal equation: C + O₂ → CO₂
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To balance a chemical equation true, Count those atoms, it’s all you do!
Stories
Imagine a cooking recipe where you need exactly the same number of ingredients on both sides to avoid a mess – that's how chemical equations work!
Memory Tools
Count Atomic Balance (CAB) to remember to count the number of atoms before adjusting.
Acronyms
B.O.C. (Balanced, Observable, Coefficients) to remember what a balanced equation requires.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Skeletal Equation
An unbalanced chemical equation that shows the reactants and products of a reaction.
- Balanced Equation
A chemical equation that has the same number of each atom type on both sides of the equation.
- Reactants
The starting substances in a chemical reaction.
- Products
The substances formed as a result of a chemical reaction.
- Coefficients
Numbers placed before the formulas in a chemical equation to indicate how many molecules of each substance are involved.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
