Coelom
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Coelom
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the concept of **coelom**. Can anyone tell me what a coelom is?

Is it a body cavity?

Exactly! A coelom refers to a fluid-filled cavity between the body wall and the gut wall, lined with mesoderm tissue. This feature is essential for classifying animals. Can anyone tell me how animals are classified based on their coelom?

Are there different types of coelomates?

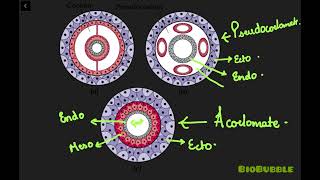
Yes! We have three categories: **coelomates**, **pseudocoelomates**, and **acoelomates**. Let's break these down.
Coelomates
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Coelomates are animals that have a true coelom completely lined by mesoderm. Examples include annelids, molluscs, and chordates. Why do you think having a coelom could be an advantage?

Maybe it allows for better movement and organ development?

Correct! The body cavity facilitates organ development and allows for more complex body structures and systems.
Pseudocoelomates
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss **pseudocoelomates**. These animals have a body cavity that is not completely lined with mesoderm. Any examples?

Isn't Ascaris a pseudocoelomate?

Yes! Ascaris is a classic example. This structure presents unique adaptations compared to true coelomates.
Acoelomates
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s look at **acoelomates**. Animals like flatworms fall into this category. What do you think could be the implications of lacking a coelomic structure?

Maybe they have simpler body systems?

Absolutely! Acoelomates often have simpler organ systems and rely on diffusion for nutrient distribution.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Coelom refers to the cavity between the body wall and gut wall, lined with mesoderm, and plays a significant role in the classification of animals. Animals can be classified as coelomates, pseudocoelomates, or acoelomates based on their body cavity structure, which impacts their overall physiology and organization.
Detailed
Coelom: Classification Importance
The coelom is a pivotal feature in the classification of animals, defined as a fluid-filled body cavity located between the outer body wall and the gut wall, which is lined with mesodermal tissue. This section provides insights into how the presence or absence of coelomic structures influences animal classification and physiology.
Key Classifications:
- Coelomates: Animals such as annelids, molluscs, arthropods, echinoderms, hemichordates, and chordates have a true coelom fully lined with mesoderm.
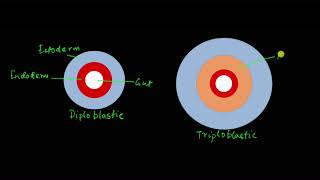
- Pseudocoelomates: In these animals, like aschelminthes, the body cavity exists but is not entirely lined with mesoderm; instead, mesoderm appears as scattered pouches between ectoderm and endoderm.
- Acoelomates: Examples such as platyhelminthes lack a body cavity altogether.
Understanding these classifications helps in studying animal biology by highlighting their structural complexity and evolutionary traits.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Coelom
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Presence or absence of a cavity between the body wall and the gut wall is very important in classification. The body cavity, which is lined by mesoderm is called coelom.
Detailed Explanation
The concept of coelom refers to a fluid-filled space found within the body of some animals. This cavity, which is located between the outer body wall and the internal organs, is lined by a tissue called mesoderm. Recognizing whether an animal has a coelom is crucial for classifying it within the animal kingdom because it influences the animal's physiology and development.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a coelom like the air-filled space in a balloon. Just as the air allows the balloon to maintain its shape and enables it to expand, a coelom provides structural support and allows for the development of complex organs in animals.
Coelomates
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Animals possessing coelom are called coelomates, e.g., annelids, molluscs, arthropods, echinoderms, hemichordates and chordates.
Detailed Explanation
Coelomates are animals that have a true coelom, which facilitates a complex body structure and system. This category includes diverse groups like annelids (earthworms), molluscs (snails), arthropods (insects), echinoderms (starfish), hemichordates, and chordates (vertebrates). The presence of a coelom allows for more efficient movement of fluids, greater organ development, and the ability to support larger body sizes.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine coelomates as the well-structured buildings that have well-defined rooms (the coelom) for different functions (like serving meals, sleeping, etc.). This is in contrast to simpler structures that might only have open space without internal partitions.
Pseudocoelomates
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In some animals, the body cavity is not lined by mesoderm, instead, the mesoderm is present as scattered pouches in between the ectoderm and endoderm. Such a body cavity is called pseudocoelom and the animals possessing them are called pseudocoelomates, e.g., aschelminthes.
Detailed Explanation
Pseudocoelomates are animals that have a body cavity, but this cavity is not entirely lined by mesoderm. In these organisms, the mesoderm forms various scattered structures rather than a continuous lining. This is seen in aschelminthes, which includes roundworms. Although pseudocoelomates have a cavity that allows for some bodily functions to occur, it is different from the fully functional coelom found in coelomates.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a room filled with furniture without any walls to define the space — that's similar to a pseudocoelom. It's still a space where things can happen (like movement and function), but it's less organized than a room with proper walls (a true coelom).
Acoelomates
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The animals in which the body cavity is absent are called acoelomates, e.g., platyhelminthes.
Detailed Explanation
Acoelomates are animals that do not possess a body cavity between the body wall and the gut. These organisms, like flatworms (platyhelminthes), have solid bodies with no internal cavity. This results in simpler body structures and often limits the complexity of their organ systems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of acoelomates like a compact suitcase that is filled to the brim — there is no extra space for items to shift around or for sections to be designated. Everything is tightly packed, which can limit how much can fit inside and how it can be organized.
Summary of Coelom Types
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In summary, animals can be classified based on the presence or absence of coelom into three categories: coelomates, pseudocoelomates, and acoelomates.
Detailed Explanation
The classification into coelomates, pseudocoelomates, and acoelomates provides a framework to understand the complexity and functions of different animal groups. Coelomates have the most complex systems thanks to their true coelom, pseudocoelomates have some level of organization but are less complex, and acoelomates have the simplest structure, which limits their biological processes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a toolbox that showcases different varieties: coelomates are like the multi-tool with numerous functions (a variety of tools in clearly defined compartments), pseudocoelomates are like a standard toolbox with tools loosely set inside, and acoelomates are like a small pouch holding just a few items, maximizing compactness but limiting functionality.
Key Concepts
-
Coelom: A cavity lined by mesoderm that is key in animal classification.
-
Coelomates: Include true coelom animals like annelids and arthropods.
-
Pseudocoelomates: Animals like roundworms with a cavity not fully lined by mesoderm.
-
Acoelomates: Organisms lacking a body cavity, such as flatworms.
Examples & Applications
Coelomates: Earthworms and mammals.
Pseudocoelomates: Ascaris (roundworm).
Acoelomates: Planaria (flatworm).
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Coelom is key, make a home, for organs that feel right at home.
Stories
Imagine a world where animals can be either fully equipped with coeloms or struggle flat and with no space – this is how they thrive or just survive.
Memory Tools
C for Coelom, P for Pseudocoelomate, A for Acoelomate – Remember the three types with this CPA.
Acronyms
CAP – Coelom, Acoelomate, Pseudocoelomate to remember body cavity classifications.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Coelom
A fluid-filled body cavity located between the outer body wall and the gut wall, lined by mesodermal tissue.
- Coelomates
Animals with a true coelom that is fully lined with mesoderm.
- Pseudocoelomates
Animals that have a body cavity not entirely lined with mesoderm.
- Acoelomates
Animals that lack a body cavity between the gut and body wall.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
