Symmetry
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Symmetry
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the fascinating world of animal symmetry! Can anyone tell me what symmetry means in biological terms?

I think it relates to how equal parts of an animal's body are arranged.

Exactly! There are mainly three types of symmetry we will focus on: asymmetrical, radial symmetry, and bilateral symmetry. Let's start with asymmetrical. Can anyone give an example of an animal that is asymmetrical?

Sponges! They don't have a defined shape.

Great job! Remember, sponges have unique structures which prevent them from having symmetry. Next, what about radial symmetry?

I think that's when you can divide an animal into equal parts from the center, like jellyfish.

Exactly right! Radial symmetry helps certain animals in movement as they capture prey from all directions. And lastly, can anyone name an example of bilateral symmetry?

Annelids and arthropods show bilateral symmetry, right? They can be divided into left and right halves.

Good observation! Bilateral symmetry is important in aiding movement and allowing for more complex structures.

Let's summarize: animals can either be asymmetrical, display radial symmetry, or exhibit bilateral symmetry based on their body plan. This classification is vital for understanding their biology and behavior.
Radial vs. Bilateral Symmetry
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Continuing our discussion, let's differentiate radial from bilateral symmetry a bit more. Student_1, can you remind us how radial symmetry could be an advantage for an animal?

It allows them to interact with the environment from multiple angles.

Exactly! This type of symmetry is often found in freely floating or devoid of motion organisms. Now, Student_2, how does bilateral symmetry benefit an animal?

It helps in coordinated movement and allows them to develop a distinct head region, which is important for sensory organs.

Well said! Bilateral symmetry is also linked to more advanced organ systems. To help you remember, consider the acronym 'AR-BS' for 'Asymmetrical-Radial-Bilateral Symmetry.' It simplifies our understanding of symmetry in animals!

In summary, radial symmetry facilitates multiple directional interaction, while bilateral symmetry enhances coordinated movement. Both types play a critical role in how animals interact with their environment.
Classification and Symmetry
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Alright, now let’s connect symmetry to classification. How does symmetry help us classify animals effectively?

It gives scientists a basis to group animals, making it easier to study them.

Exactly! Without these classifications, understanding the animal kingdom would be chaotic.

Can we say that symmetry shows evolutionary relationships?

Yes! Evolutionarily, it indicates adaptations as animals have evolved in their environments. To remember this concept, consider that 'Symmetry Sheds Light on Classification and Evolution'.

In conclusion, symmetry plays an essential role not just in classification but in understanding how species adapt and evolve. Fantastic participation today!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section elaborates on the classification of animals based on symmetry, highlighting that while sponges are asymmetrical, animals like coelenterates exhibit radial symmetry, and species such as annelids and arthropods display bilateral symmetry. This categorization helps in the systematic classification of diverse animal species.
Detailed
Symmetry in Animals
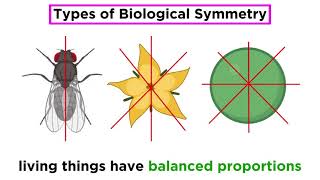
In animal classification, symmetry is pivotal in understanding the diverse forms found in nature. Animals can broadly be divided into three categories based on their symmetry: 1. Asymmetrical: Sponges are the most notable examples, exhibiting no definite shape or symmetry, where no plane can yield equal halves. 2. Radial Symmetry: Animals such as coelenterates (like jellyfish) show this kind of symmetry, meaning if a plane slices through the center, the organism divides into equal halves. This type is typical for creatures that are sessile or free-floating. 3. Bilateral Symmetry: Animals like annelids and arthropods can be split into identical left and right halves along a single plane, which is crucial for their movement and interaction with the environment. Grasping these basics of symmetry not only illuminates animal diversity but also aids in organizing them systematically through classification frameworks.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Asymmetry in Sponges
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Animals can be categorised on the basis of their symmetry. Sponges are mostly asymmetrical, i.e., any plane that passes through the centre does not divide them into equal halves.
Detailed Explanation
Asymmetry means that there is no specific arrangement of body parts. In sponges, if you were to draw a line through the center of the sponge, the two halves would not match at all. This is because sponges have a very irregular shape, similar to a pile of random materials. As a result, sponges don't fit into any symmetry category; instead, they represent a unique form of organization without symmetry.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a pile of clothes thrown on a bed; no matter how you slice through the pile, you wouldn’t get two matching halves. Just like that, sponges are a mixed array of cells stuck together without a definite shape.
Radial Symmetry
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When any plane passing through the central axis of the body divides the organism into two identical halves, it is called radial symmetry. Coelenterates, ctenophores and echinoderms have this kind of body plan.
Detailed Explanation
Radial symmetry allows an organism to be divided into similar halves by multiple planes that run through the center. This is common in animals like jellyfish and starfish, where if you draw lines down the center from different angles, each side will reflect each other. This type of symmetry is beneficial in environments where the organism needs to interact equally with its surroundings, such as in the water, because they can move and 'see' from all directions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a pizza: no matter how you cut it, each slice should have the same toppings and size. That’s what radial symmetry looks like in the animal kingdom; each segment is identical from the center outward, much like slices of pizza.
Bilateral Symmetry
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Animals like annelids, arthropods, etc., where the body can be divided into identical left and right halves in only one plane, exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Detailed Explanation
Bilateral symmetry refers to the property where the left and right sides of an organism are mirror images of each other. This type of symmetry is prevalent in many animals, including humans. This means that if you were to draw a line down the center of these organisms, both sides would look alike. Bilateral symmetry is associated with a higher level of complexity in structure, allowing for more sophisticated movement and the development of specialized body parts.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a butterfly; one side’s wings and patterns look just like the other side. If you fold the butterfly in half, both sides match perfectly. This mirror-like consistency is what bilateral symmetry embodies.
Key Concepts
-
Asymmetry: Absence of symmetry in an organism.
-
Radial Symmetry: Symmetry around a central axis allowing equal division.
-
Bilateral Symmetry: Symmetry along one plane, leading to left and right halves.
Examples & Applications
Sponges exemplify asymmetry as they lack a defined shape.
Coelenterates, such as jellyfish, demonstrate radial symmetry allowing them to capture prey effectively.
Annelids exhibit bilateral symmetry, aiding in their locomotion and interaction.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Symmetry's a way, helps animals to play, in shape and in style, they move mile after mile.
Stories
Once upon a time, in the sea, there lived an asymmetrical sponge. It wished to dance like the jellyfish but realized that it used its unique shape to filter feed. Hence, each had its place in the ocean's dance.
Memory Tools
Use the acronym 'ABR' for 'Asymmetrical, Bilateral, Radial' to remember the types of symmetry.
Acronyms
Remember 'S-R-B' to recall that Symmetry is categorized into Radial and Bilateral forms.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Asymmetrical
Lacking a defined shape or symmetry; cannot be divided into equal halves.
- Radial Symmetry
A body plan where any plane through the central axis divides the organism into equal halves.
- Bilateral Symmetry
A body plan where an organism can be divided into identical left and right halves along one plane.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
