Centrosome and Centrioles
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Centrosomes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to explore centrosomes and their crucial role in cell division. Can anyone tell me what a centrosome is?

Isn't it an organelle that contains centrioles?

Exactly! The centrosome is made up of two centrioles, and they are positioned perpendicularly to each other. This arrangement is vital during cell division.

What do the centrioles do during cell division?

Great question! They form spindle fibers that help separate chromosomes during mitosis. Remember, 'centrosome' and 'centrioles' both begin with 'centri-' which can help you remember they go together.

So, the centrioles are necessary for cell movement too?

Absolutely! They are the basal bodies for cilia and flagella, just like the spokes of a wheel support its structure. In summary, centrosomes are essential for both cell division and motility.
Structure of Centrioles
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's look at the structure of the centrioles. Each centriole consists of nine triplets of microtubules arranged in a circular pattern. Can anyone visualize this structure?

Are they like tiny tubes that make a circle?

Yes, they are! You can think of it like a cartwheel. The arrangement is crucial for their function in cell division.

What links the triplets together?

Excellent question! They are linked by proteins which help maintain the structure. Also, each centriole has a central hub connected by radial spokes of proteins. Remember, ‘triplet arrangement’ can remind you of how they group together for efficiency.

So, the design supports its function?

Exactly! The structure is directly related to its role in forming the spindle apparatus during cell division.
Function of the Centrosome
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What are some functions of the centrosome that we haven't discussed yet?

It helps with the movement of cells?

Correct! It also plays a crucial role in organizing the microtubules in the cytoskeleton, contributing to the cell's overall shape and stability.

Can you give us an example of how it's involved in cell movement?

Certainly! During cellular movements, such as in a ciliated cell, the centrioles help anchor the cilia which push fluid across the cell's surface.

So, are they essential only in animal cells?

Good point! Centrioles are primarily found in animal cells and some lower plant forms. So, understanding their function indeed gives us insight into cellular dynamics.
Importance of the Centrosome in Cells
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's wrap up by exploring why centrosomes are crucial in biology.

Is it because they help in proper cell division?

Exactly! They ensure that chromosomes are evenly distributed between daughter cells.

What happens if something goes wrong with them?

That's a great inquiry! Errors in centrosomal function can lead to cell division errors, which can contribute to diseases like cancer. It's essential to comprehend their role for both functional and clinical reasons.

So, learning about them helps us in understanding health better?

Exactly! They bridge basic biology with health and disease, highlighting their significance.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The centrosome is a vital organelle characterized by a pair of centrioles arranged perpendicularly, enveloped by pericentriolar material. These centrioles are instrumental in cell division, forming spindle fibers that assist during mitosis and also serve as a base for cilia and flagella.
Detailed
Centrosome and Centrioles
The centrosome is a key organelle found in animal cells, primarily composed of two cylindrical structures known as centrioles, which are critical for cell division and the formation of motile structures. Centrioles are organized perpendicularly to each other, resembling a cartwheel construction—this arrangement aids their function in the cell cycle. The structure of each centriole is characterized by nine sets of triplet microtubules arranged in a circular fashion, with each triplet linked to its neighbors by protein connections. The central hub of the centriole is also proteinaceous, providing structural integrity.
During cell division, centrioles are essential in forming the spindle apparatus, which helps distribute chromosomes to daughter cells. Additionally, they serve as basal bodies for the cilia and flagella, enabling cell locomotion and fluid movement across cell surfaces. Understanding the structure and function of the centrosome and centrioles is crucial for comprehending cell motility and division, making them integral to the study of cellular biology.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Centrosome
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
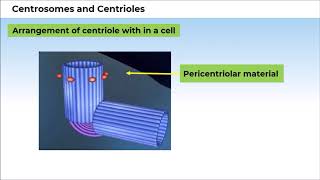
Centrosome is an organelle usually containing two cylindrical structures called centrioles. They are surrounded by amorphous pericentriolar materials.
Detailed Explanation
The centrosome is a crucial part of a cell's structure, particularly in animal cells. It usually contains two centrioles, which are cylindrical structures. These centrioles are surrounded by a material that provides support and organization, known as pericentriolar material. This arrangement is necessary for the movement and organization of microtubules within the cell.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the centrosome as a control center in a factory that coordinates the movement of machines (microtubules) that help assemble products (cell structures). Just like a factory needs a control center for efficiency, cells need centrosomes for effective organization.
Structure of Centrioles
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Both the centrioles in a centrosome lie perpendicular to each other in which each has an organisation like the cartwheel. They are made up of nine evenly spaced peripheral fibrils of tubulin protein.
Detailed Explanation
Centrioles are structurally unique as they lie at right angles to each other, resembling a cartwheel. Their construction consists of nine sets of three tubulin proteins making up their walls. This specific arrangement allows them to play a vital role in cell division and the formation of cilia and flagella, essential for cell movement.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a bicycle wheel (the centriole) with nine spokes (the peripheral fibrils). Each spoke ensures the wheel remains strong and can rotate effectively, mirroring how centrioles maintain the structure and function needed for the cell's activity.
Function of Centrioles
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The centrioles form the basal body of cilia or flagella, and spindle fibres that give rise to spindle apparatus during cell division in animal cells.
Detailed Explanation
Centrioles have two primary functions. First, they serve as the basal body from which cilia and flagella arise, enabling movement. Second, they are instrumental during cell division, where they assist in forming the spindle apparatus that separates chromosomes into daughter cells. This ensures accurate distribution of genetic material.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the centrioles being like the base of an umbrella (basal body) that opens up (cilia and flagella) to protect you from rain. They also act like a referee during a football game (cell division), helping ensure that each team (daughter cells) gets the right number of players (chromosomes).
Key Concepts
-
Centrosome: The main role is to organize microtubules and is crucial for cell division.
-
Centrioles: Arrange perpendicularly to each other and are composed of nine triplet microtubules.
Examples & Applications
In animal cells, centrosomes are involved in forming the spindle fibers necessary for accurate chromosome separation.
In ciliated cells, centrioles serve as the base structures that anchor cilia, facilitating movement.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Centrosomes act as cell guides, with centrioles leading during division rides.
Stories
Imagine a race where two centrioles work together to help cells split their prizes evenly!
Memory Tools
C-C for Centrosome and Centrioles; remember they work together in cell division.
Acronyms
C-C-T
Centrosome
Centrioles
and their role in cell division.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Centrosome
An organelle in eukaryotic cells that plays a key role in cell division; contains two centrioles.
- Centriole
A cylindrical structure found in pairs within the centrosome, essential for organizing spindle fibers during cell division.
- Spindle Fibers
Microtubules that form the mitotic spindle, essential for the separation of chromosomes during cell division.
- Microtubules
Filaments that form part of the cytoskeleton; play roles in cell shape and division.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
