Golgi apparatus
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Golgi Apparatus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's discuss the Golgi apparatus. Who can tell me what they think its main function is?

Isn't it involved in processing and packaging proteins?

Exactly! The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum. Can anyone tell me what this structure looks like?

I've read that it has a series of flat sacs stacked together?

Correct! These stacks are called cisternae. Remember the acronym GROW to help you recall its functions: G for Glycoproteins synthesis, R for Receiving proteins from ER, O for Organizing them, and W for Wrapping them in vesicles.

What happens to those vesicles once they are wrapped?

Great question! Vesicles travel to the target areas inside or outside the cell. The trans face of the Golgi is responsible for this shipping process.

So, does this mean Golgi works closely with the endoplasmic reticulum?

Yes, very closely! They often function together to ensure proteins are correctly modified and sent out. To sum up, the Golgi apparatus is essential for protein processing and cellular communication.
Functions of the Golgi Apparatus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've covered the structure, let’s dive into its specific functions. What capabilities does the Golgi apparatus possess?

Does it modify proteins chemically?

Exactly! It can add carbohydrate groups to proteins, which is crucial for their function. Can anyone name the types of molecules that the Golgi processes?

Proteins and lipids?

Correct! The Golgi is pivotal in modifying these macromolecules to make them functional. Remember, each modification plays a role in how the molecules will behave in the body.

What happens when the Golgi doesn't function properly?

Good inquiry! When it malfunctions, it can lead to diseases, as proteins may not be properly modified or sent to their destinations. This is why studying the Golgi is so important!

So, it’s critical for normal cellular operations and overall health?

Precisely! Let’s recap: the Golgi apparatus modifies proteins, synthesizes glycoproteins, and is vital for cellular communication. Keep these points in mind as you continue your studies.
Golgi Apparatus in Cellular Health
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We have learned about the structure and function of the Golgi apparatus. Now let’s see how critical it is for cellular health. Why is its proper functioning vital?

Because it affects protein modification?

Exactly! Improperly modified proteins can cause dysfunction. Can anyone think of a disease linked to Golgi malfunction?

I remember reading about neurodegenerative diseases.

That's right! Diseases like Alzheimer’s can involve issues with the Golgi apparatus. Now, think of the acronym MICE, to remember the effects of Golgi dysfunction: M for Misfolded proteins, I for Issues with cellular communication, C for Cell death, and E for Edema - response of cells to injury.

How do we actually study the Golgi apparatus?

Excellent question! We often use microscopy techniques and fluorescent tagging to visualize its functions. Overall, the Golgi apparatus is essential not only for normal cell function but also for preventing diseases. Remember these key points as we conclude today’s lesson!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
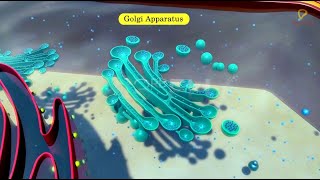
The Golgi apparatus consists of stacked, flattened sacs known as cisternae, which modify, sort, and package proteins and lipids received from the endoplasmic reticulum. Its role is essential for effective cellular communication and secretion.
Detailed
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi complex or Golgi body, is a vital organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It is responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids that have been synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). This organelle comprises a series of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae, which are arranged parallel to each other. The Golgi apparatus has two distinct faces: the convex cis face that receives vesicles containing materials from the ER and the concave trans face that ships modified materials to their destined locations inside or outside the cell.
Significance
The Golgi apparatus plays a crucial role in the secretion of substances, including hormones and enzymes, by packaging them into vesicles. It is also involved in the synthesis of glycoproteins and glycolipids, which are essential for cell recognition and signaling processes. Understanding the structure and function of the Golgi apparatus helps to elucidate cellular processes vital for life and demonstrates the organelle's impact on the overall function of cells.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to the Golgi Apparatus
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Camillo Golgi (1898) first observed densely stained reticular structures near the nucleus. These were later named Golgi bodies after him. They consist of many flat, disc-shaped sacs or cisternae of 0.5µm to 1.0µm diameter.
Detailed Explanation
The Golgi apparatus is a crucial organelle in eukaryotic cells, first identified by the scientist Camillo Golgi. It consists of a series of stacked, flattened sacs known as cisternae. These sacs are small, ranging from 0.5 micrometers to 1.0 micrometer in diameter, and they play a key role in modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids that have been synthesized in the cell.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Golgi apparatus as a post office or a shipping center. Just as a post office sorts packages and sends them to their final destinations, the Golgi apparatus modifies proteins and lipids and dispatches them to various locations inside or outside the cell.
Structure of the Golgi Apparatus
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Varied number of cisternae are present in a Golgi complex. The Golgi cisternae are concentrically arranged near the nucleus with distinct convex cis or the forming face and concave trans or the maturing face.
Detailed Explanation
The structure of the Golgi apparatus includes several cisternae stacked together. These are arranged in a way that one side, called the 'cis face', is oriented toward the endoplasmic reticulum, where it receives proteins and lipids. The other side, known as the 'trans face', is where these substances are sent out after processing. The convex cis face is involved in the receiving process, while the concave trans face is responsible for shipping materials to their final destinations.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a factory that assembles gadgets. The side of the factory that receives raw materials is akin to the cis face of the Golgi, where new materials come in, while the side that ships out finished products represents the trans face where the final products leave for distribution.
Function of the Golgi Apparatus
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The golgi apparatus principally performs the function of packaging materials, to be delivered either to the intra-cellular targets or secreted outside the cell. Materials to be packaged in the form of vesicles from the ER fuse with the cis face of the golgi apparatus and move towards the maturing face. This explains, why the golgi apparatus remains in close association with the endoplasmic reticulum.
Detailed Explanation
The main function of the Golgi apparatus is to modify, sort, and package proteins and lipids for delivery within the cell or export outside the cell. When materials arrive from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), they enter the Golgi apparatus at the cis face. As they pass through the Golgi, they undergo modifications and are then packaged into vesicles that bud off from the trans face, ready for transport.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a bakery that takes raw ingredients (like flour and sugar) to make cakes. The kitchen (the ER) prepares the cakes, then they are brought to a packaging area (the Golgi apparatus), where they're decorated and boxed up before being shipped out to stores. This shows how the Golgi apparatus processes and prepares materials for their next steps.
Role in Glycoprotein and Glycolipid Formation
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A number of proteins synthesized by ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum are modified in the cisternae of the golgi apparatus before they are released from its trans face. Golgi apparatus is the important site of formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids.
Detailed Explanation
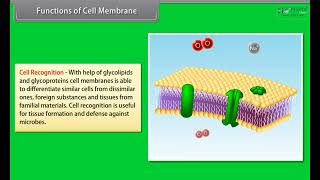
The Golgi apparatus plays a significant role in the formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids. These molecules are essential for various cellular functions, including cell communication and structural integrity. Proteins synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) often receive sugar chains added to them in the Golgi, creating glycoproteins. Similar modifications occur for lipids to form glycolipids. This process is crucial because it helps cells recognize each other and interact appropriately.
Examples & Analogies
Think of glycoproteins and glycolipids as name tags and business cards in a social gathering. Just as these items help people identify themselves and connect with others, glycoproteins and glycolipids help cells identify each other and communicate, ensuring that they function together in a cohesive manner.
Key Concepts
-
Structure of Golgi Apparatus: Comprised of stacked cisternae which modify and package cellular products.
-
Function of Golgi Apparatus: Essential for processing proteins and lipids necessary for cellular functions.
-
Importance in Health: Golgi apparatus dysfunction can lead to diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders.
Examples & Applications
The Golgi apparatus modifies insulin, a protein hormone, to ensure it is correctly structured before being released into the bloodstream.
In plant cells, the Golgi apparatus helps synthesize and transport components of the cell wall.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the Golgi, proteins groove, With cisternae stacked, they improve. Wrapped in vesicles, they then move, To help the cell smoothly prove.
Stories
Once there was a magical post office called the Golgi, where all the proteins arrived. They would get dressed up, receiving decorations for their trips before heading out to deliver vital messages throughout the body!
Memory Tools
Remember GROW for the Golgi's functions: G - Glycoprotein synthesis, R - Receiving proteins, O - Organizing them, W - Wrapping them in vesicles.
Acronyms
MICE
Misfolded proteins
Issues with communication
Cell death
Edema - effects of Golgi dysfunction.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Golgi apparatus
An organelle involved in modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
- Cisternae
Stacked, flattened membrane-bound sacs that comprise the Golgi apparatus.
- Vesicles
Membrane-bound sacs that transport proteins and lipids within and outside the cell.
- Glycoproteins
Proteins that have carbohydrate groups attached, important for cell recognition and communication.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
A network of membranes within a cell involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
