Angiosperms
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Angiosperms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’ll explore angiosperms. Can anyone tell me what distinguishes angiosperms from other plant groups?

They are flowering plants!

Correct! More specifically, angiosperms produce flowers and their seeds are enclosed in fruits. This feature is vital for their reproduction.

Why is enclosing the seeds important?

Great question! Enclosing seeds protects them and aids in dispersal. It helps ensure the survival of the next generation.

So, they must be really important for food sources?

Absolutely! They provide food, fodder, and many other resources essential for humans and wildlife. Remember, angiosperms are critical in various ecosystems.

To recap, angiosperms are distinguished by their flowers, fruits, and enclosed seeds. Does anyone have any further questions before we move on?
Classification of Angiosperms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve into the classification of angiosperms. Can anyone name the two classes of angiosperms?

Monocotyledons and dicotyledons!

Exactly! Monocotyledons have one seed leaf, while dicotyledons have two. What are some examples of each?

Bamboo and grass for monocots, and roses and daisies for dicots.

Good examples! They have different structures; for instance, monocots have parallel leaf veins, while dicots show branching.

What about their roots?

Great observation! Monocots typically have fibrous root systems, whereas dicots have a taproot system. Remember the acronym 'MD' - Monocots are fibrous, Dicots are taproots.

To sum up, angiosperms are classified into monocotyledons and dicotyledons, showing distinct structural differences and examples. Any questions?
Significance of Angiosperms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's discuss the significance of angiosperms. Why do you think they are crucial to ecosystems?

They provide food and oxygen.

Exactly! They are primary producers and contribute significantly to the oxygen supply. Can you think of any specific uses for angiosperms in human life?

Food, like fruits and vegetables, and also flowers for decoration.

Right! They are used for food, fodder, medicines, and even fuel. Think about how integrated they are in our daily lives.

So, they're really essential for both nature and humanity!

Exactly! Angiosperms’ role can’t be overstated. They’re vital in maintaining ecosystem balance and supporting human needs. Let’s remember this importance as we move forward!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Angiosperms, the largest group of plants, are defined by the presence of flowers and fruits that enclose their seeds. They are categorized into two classes: dicotyledons and monocotyledons, showcasing remarkable diversity in size and habitat. This section details their significance, classification, and reproductive strategies.
Detailed
Angiosperms
Angiosperms, also known as flowering plants, represent a diverse and significant group within the plant kingdom, distinguished by their ability to produce flowers and fruits. Unlike gymnosperms, where ovules are naked, angiosperms enclose their seeds in fruit, which aids in their protection and dispersal. Their adaptability and variation in size—from the minute Wolffia to towering Eucalyptus—mirror their ecological significance across various habitats.
Angiosperms are divided into two principal classes:
- Dicotyledons: These plants typically have two seed leaves (cotyledons) and exhibit a variety of leaf forms and vascular arrangements.
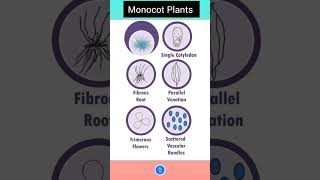
- Monocotyledons: With a single cotyledon, these plants usually possess parallel leaf venation and fibrous root systems.
The section discusses the essential characteristics that define angiosperms, their roles in ecosystems such as food and oxygen production, and their importance in human life, such as providing food, fodder, medicines, and various other products.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Angiosperms
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Unlike the gymnosperms where the ovules are naked, in the angiosperms or flowering plants, the pollen grains and ovules are developed in specialised structures called flowers. In angiosperms, the seeds are enclosed in fruits. The angiosperms are an exceptionally large group of plants occurring in wide range of habitats. They range in size from the smallest Wolffia to tall trees of Eucalyptus (over 100 metres). They provide us with food, fodder, fuel, medicines and several other commercially important products.
Detailed Explanation
Angiosperms, commonly known as flowering plants, are different from gymnosperms primarily because their reproductive structures, namely pollen grains and ovules, are enclosed within flowers. This enclosure leads to the formation of seeds which are protected by fruits. Angiosperms represent a vast diversity of plants, thriving in various environments, ranging from tiny water plants like Wolffia to towering trees like Eucalyptus which can exceed 100 meters. They play an essential role in human life by supplying food, fodder for livestock, and raw materials for medicines and other products.
Examples & Analogies
Think of flowers as protective cases that keep the plant's babies (seeds) safe until they're ready to grow. Just like how a baby is kept in a crib, angiosperm seeds are protected inside fruits. This enables them to be dispersed effectively, just as parents might carry a baby to different places.
Classification of Angiosperms
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
They are divided into two classes: the dicotyledons and the monocotyledons.
Detailed Explanation
Angiosperms are further classified into two major groups: dicotyledons (or dicots) and monocotyledons (or monocots). This classification is primarily based on the number of cotyledons, which are the first leaves that appear when seeds germinate. Monocots have one cotyledon, while dicots have two. This classification helps in distinguishing between various plant families, understanding their characteristics, and determining their ecological roles.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a family tree where one branch has people with one eye color (monocots) and another branch has people with two eye colors (dicots). Just like families have unique traits, these plants have different features based on their classifications.
Key Concepts
-
Angiosperms: Flowering plants with seeds enclosed in fruits.
-
Monocotyledons: One seed leaf, parallel veins in leaves.
-
Dicotyledons: Two seed leaves, branched veins in leaves.
Examples & Applications
Example of monocot: Corn, which has a single cotyledon.
Example of dicot: Sunflower, which has two cotyledons.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Angiosperms bloom with fruits galore, seeds are safe, that's what they're for.
Stories
Once upon a time, there lived two friendly plant families: the one-seed leaf family asked the two-seed leaf family about their different ways of life, leading to a tale of flowers, fruits, and varied habitats.
Memory Tools
MFD: Monocots have Fibrous roots, Dicots have a Taproot.
Acronyms
F3
Fruits
Flowers
and Fresh air - key features of angiosperms.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Angiosperms
Flowering plants that produce seeds enclosed in fruits.
- Monocotyledons
Plants with one seed leaf, parallel leaf venation, and fibrous roots.
- Dicotyledons
Plants with two seed leaves, branched leaf venation, and often a taproot.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
