PLANT KINGDOM
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Algae
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’ll start with algae. Can anyone tell me what distinguishes algae from other plants?

Are they not all aquatic and green?

Good point! While most algae are aquatic, they can also be found in moist environments. Algae are primarily chlorophyll-bearing and categorized based on their pigments. For example, green algae belong to the class Chlorophyceae.

Do they have any commercial value?

Absolutely! Algae play a crucial role in carbon fixation and oxygen production. They are also used in food products, cosmetics, and even in medical applications. Remember the acronym 'FEEDS' for algae's roles: Food, Energy, Environmental balance, Disease resistance, and Source of compounds.

What are their reproductive methods?

They can reproduce vegetatively by fragmentation, asexually through spores, and sexually through gametes. The types of gamete fusion can be isogamous, anisogamous, or oogamous.

That’s interesting! So they are quite versatile!

Indeed! In summary, algae are vital for ecosystems and have significant benefits for humans.
Understanding Bryophytes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s move on to bryophytes. What makes them unique in the plant kingdom?

They need water to reproduce, right?

Exactly! Bryophytes are often found in damp areas and require water for the transfer of male gametes from the antheridia to the archegonia. Their life cycle is dominated by the gametophyte stage.

What about their structure?

They lack true roots, stems, and leaves but have structures that perform similar functions. Think of them as the 'amphibians' of the plant world.

Can you give an example of bryophytes?

Sure! Common examples include mosses like Sphagnum and liverworts like Marchantia. Remember, 'Moss and Marchantia, moisture's best friends!'

It’s cool how they play such an ecological role!

Absolutely! They are essential in soil formation and preventing erosion.
Exploring Pteridophytes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about pteridophytes. Who knows what separates them from bryophytes?

They have vascular tissues, right?

That's right! Pteridophytes are the first vascular plants and have true roots, stems, and leaves. They prominently feature a sporophyte generation for the life cycle.

Do they also need water for reproduction?

Yes! They require water for fertilization. The gametophyte, or prothallus, is photosynthetic and also needs a moist environment.

What about their spores?

Great question! They produce spores in sporangia. Some pteridophytes, like Selaginella, are heterosporous, producing two types of spores.

I get it now, they are more complex!

Exactly! So pteridophytes serve as a bridge between simpler plants and more advanced seed-bearing plants.
Understanding Gymnosperms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next on our list are gymnosperms. Can anyone tell me what 'naked seeds' means?

It means their seeds aren’t covered by a fruit, right?

Exactly! Gymnosperms have exposed ovules that develop into seeds post-fertilization. They mostly reproduce through cones.

What examples do we have?

Examples include pine trees and cedars. Remember the phrase 'Pine Cones, Naked Stones' to help you recall how they reproduce.

How are their reproductive structures organized?

Male cones produce pollen, while female cones contain ovules. The pollen must wind-pollinate to fertilize the ovules.

I see how they play an important role in ecosystems!

Right! Gymnosperms are crucial in many habitats and often foster biodiversity.
Diving into Angiosperms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss angiosperms. Who can tell me about their unique features?

They have flowers and fruits, correct?

Correct! Angiosperms are also known as flowering plants and are the most diverse group of plants.

What about their roles in our lives?

They provide food, medicine, and materials like wood. Think of the mnemonic 'Fruits and Flowers Feed Families!'

What are the two major subdivisions?

They are divided into monocotyledons and dicotyledons, each with distinct characteristics like leaf structure and seed formation.

That’s fascinating how adaptable they are!

Absolutely! They can grow in various habitats and are vital for ecological balance.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This chapter details the classification of plants within the Plant Kingdom, emphasizing the distinctions between algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms, including their structures, reproduction methods, and ecological significance.
Detailed
Plant Kingdom
The Plant Kingdom is diverse and comprises five major groups: algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms. Each group showcases unique features and adaptations that allow them to thrive in various environments.
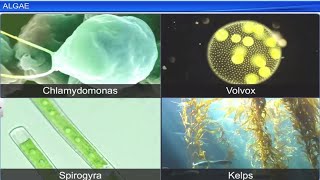
- Algae: Simple, thalloid, autotrophic organisms primarily aquatic, responsible for significant carbon dioxide fixation and oxygen production. Algae are classified into three major groups based on pigment and food storage - Chlorophyceae (green algae), Phaeophyceae (brown algae), and Rhodophyceae (red algae).
- Bryophytes: Known as the amphibians of the plant kingdom, they thrive in moist conditions and are characterized by a gametophyte dominant life cycle. Key reproductive structures include antheridia for male gametes and archegonia for female gametes.
- Pteridophytes: The first vascular plants, consisting of ferns and horsetails, with a dominant sporophyte generation. They reproduce via spores and require moisture for fertilization.
- Gymnosperms: These seed-producing plants have exposed seeds not enclosed by an ovary, and they include coniferous trees like pines and spruces. They are characterized by male and female cones.
- Angiosperms: Flowering plants that produce seeds enclosed in fruits, representing the largest group in the Plant Kingdom. They include a wide variety of sizes and forms divided into monocotyledons and dicotyledons.
This chapter underlines the evolution, classification, and ecological roles of these plant groups.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding the Plant Kingdom Classification
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In the previous chapter, we looked at the broad classification of living organisms under the system proposed by Whittaker (1969) wherein he suggested the Five Kingdom classification viz. Monera, Protista, Fungi, Animalia and Plantae. In this chapter, we will deal in detail with further classification within Kingdom Plantae popularly known as the ‘plant kingdom’. We must stress here that our understanding of the plant kingdom has changed over time.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk explains the classification of living organisms and highlights that the plant kingdom (Plantae) has evolved in how we understand it. Originally, it included Fungi, Monera, and Protista; however, these are now excluded. The focus now is solely on the five main groups that make up Plantae, emphasizing the need for continuous learning in science.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of the classification of living organisms like sorting books in a library. Initially, all types of books might be shelved together, but over time, librarians learn to categorize them more effectively—setting aside some types into specific sections according to their genres.
Reproductive Methods in Algae
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Algae reproduce by vegetative, asexual and sexual methods. Vegetative reproduction is by fragmentation. Each fragment develops into a thallus. Asexual reproduction is by the production of different types of spores, the most common being the zoospores. They are flagellated (motile) and on germination give rise to new plants. Sexual reproduction takes place through fusion of two gametes.
Detailed Explanation
Algae can reproduce in three primary ways. For vegetative reproduction, if a piece of the algae is broken off, it can grow into a new individual. In asexual reproduction, they produce zoospores that swim away to form new algae. Lastly, during sexual reproduction, two gametes come together to form a new organism. This illustrates the various survival strategies of algae in different environments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you have a plant that can grow a new shoot (vegetative reproduction), produce seeds that can spread in the wind (asexual reproduction), and also produce flowers to make more plants (sexual reproduction). Algae, like this plant, maximize their chances of survival by using different methods to reproduce.
Economic Importance of Algae
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Algae are useful to man in a variety of ways. At least a half of the total carbon dioxide fixation on earth is carried out by algae through photosynthesis. Being photosynthetic, they increase the level of dissolved oxygen in their immediate environment. Many species of Porphyra, Laminaria, and Sargassum are among the 70 species of marine algae used as food.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk highlights the significant role of algae in our ecosystem and economy. They are vital for photosynthesis, helping reduce carbon dioxide levels and boosting oxygen in the water, crucial for aquatic life. Moreover, various algae species serve as food, showcasing their importance in our diets and the structure of marine food webs.
Examples & Analogies
Think of algae as the lungs of the ocean: they breathe in carbon dioxide and exhale oxygen, just like we do. Moreover, just as you might enjoy a salad with various vegetables, many parts of the world use various seaweeds, like Porphyra (used in sushi), as food.
Classes of Algae
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The algae are divided into three main classes: Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae and Rhodophyceae.
Detailed Explanation
This section categorizes algae into three key classes based on their characteristics and pigments. Chlorophyceae are green algae abundant in freshwater, Phaeophyceae are brown algae mainly found in marine environments, and Rhodophyceae are red algae that thrive in a variety of habitats, including deeper waters.
Examples & Analogies
Just as animals can be categorized by color or habitat—like lions in savannahs or polar bears in ice—algae can be classified into green, brown, and red based on their distinct features and environments where they grow.
Key Concepts
-
Algae: Autotrophic organisms significant in aquatic ecosystems.
-
Bryophytes: Depend on water for reproduction and exhibit a gametophyte-dominant life cycle.
-
Pteridophytes: Vascular plants with a life cycle involving both sporophyte and gametophyte phases.
-
Gymnosperms: Seed plants with exposed seeds and reliance on cones for reproduction.
-
Angiosperms: Flowering plants that produce seeds encased in fruit.
Examples & Applications
Chlamydomonas and Spirogyra as examples of algae.
Sphagnum and Marchantia representing bryophytes.
Ferns like Dryopteris and horsetails like Equisetum in the pteridophyte group.
Pines and cedars as typical gymnosperms.
Rose and sunflower are common examples of angiosperms.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Algae grow, in water they flow, making air for us to grow.
Stories
Once upon a time in a green forest, algae and ferns were the best of friends, each contributing to the ecosystem. The algae provided oxygen while the ferns held the soil together, teaching us the importance of teamwork in nature!
Memory Tools
Use 'BAG for Bryophyte, Algae, Gymnosperms' to remember three plant types.
Acronyms
PGA for Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Algae
Simple, chlorophyll-bearing aquatic organisms that can undergo photosynthesis.
- Bryophytes
Non-vascular plants that require moist environments for reproduction, primarily mosses and liverworts.
- Pteridophytes
Vascular plants that reproduce via spores and have a dominant sporophyte generation, such as ferns.
- Gymnosperms
Seed-producing plants with exposed ovules and seeds, including conifers.
- Angiosperms
Flowering plants that produce seeds enclosed in fruits, constituting the largest group in the plant kingdom.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
