SUMMARY
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Plant Kingdom
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into the fascinating realm of the plant kingdom. What do you think are the main groups?

I think there are just trees and flowers!

That's a common thought! But trees and flowers are part of broader groups. The plant kingdom includes algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms. Can anyone tell me what algae are?

Aren't they simple, water plants?

Exactly! Algae are chlorophyll-bearing and mostly aquatic. They can be classified based on their pigments into Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. Remember this with the acronym CPR for Chlorophyll, Pigments, and Reproduction!

What about how they reproduce?

Great question! Algae reproduce in three main ways: vegetative, asexual, and sexual. The sexual aspect can show different forms like isogamy or oogamy. Let’s move on to bryophytes.
Bryophytes Characteristics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, can anyone tell me about bryophytes and where they thrive?

Are they like moss?

Yes, that’s right! Bryophytes include mosses and liverworts. They live in soil but depend on water for sexual reproduction. They have structures akin to roots, leaves, and stems called rhizoids, leaf-like, and stem-like structures. What do we call the main body of the bryophytes?

Is it the gametophyte?

Exactly! The gametophyte produces male and female gametes in antheridia and archegonia. When they fuse, they form a zygote that develops into a sporophyte.
Pteridophytes to Angiosperms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s shift our focus to pteridophytes. How do they differ from bryophytes?

Pteridophytes have true roots, stems, and leaves, right?

Correct! These distinctive features also involve well-differentiated vascular tissues. They reproduce with spores that, like bryophytes, form gametophytes needing damp conditions. Now, what's unique about gymnosperms?

They have naked seeds!

That's right! Gymnosperms have exposed ovules without an ovary wall. Now, angiosperms are the most advanced group. Can anyone name the two subcategories?

Monocots and dicots!

Well done! Angiosperms lead to a diverse range of plants we encounter daily.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The plant kingdom is classified into several groups, each with unique features and reproductive strategies. Algae, as chlorophyll-bearing and aquatic organisms, are further classified based on pigments. Bryophytes require water for reproduction, while pteridophytes exhibit true root, stem, and leaf structures. Gymnosperms are characterized by exposed seeds, and angiosperms are divided into monocots and dicots.
Detailed
Overview of the Plant Kingdom
The plant kingdom is categorized into five main groups:
- Algae: Simple, thalloid, autotrophic organisms that predominantly live in water. They are classified into three groups—Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae—based on their pigments and types of stored food. Reproduction can be vegetative, asexual via spores, or sexual through gamete formation, displaying forms such as isogamy, anisogamy, and oogamy.
- Bryophytes: These are more complex than algae, living in soil but relying on water for sexual reproduction. They possess thallus-like structures attached to substrates by rhizoids and are divided into liverworts and mosses. The gametophyte is the main plant body, producing gametes in antheridia and archegonia, leading to zygote formation and sporophyte development.
- Pteridophytes: Here, the sporophyte is the dominant phase, featuring true roots, stems, and leaves with well-differentiated vascular tissues. They reproduce via spores forming gametophytes, which need damp environments for growth.
- Gymnosperms: Known as naked-seeded plants, gymnosperms have ovules that are not enclosed by an ovary wall. Their reproductive structures consist of male and female cones where microspores and megaspores are produced.
- Angiosperms: The most advanced group, angiosperms are further divided into dicotyledons and monocotyledons, distinguished by seed structure and vascular formation.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of the Plant Kingdom
Chapter 1 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The plant kingdom includes algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Detailed Explanation
The plant kingdom is a diverse group of organisms classified into different types. These include algae (simple aquatic organisms), bryophytes (like mosses), pteridophytes (ferns), gymnosperms (naked-seeded plants), and angiosperms (flowering plants). Each of these groups has unique characteristics and adaptations that allow them to thrive in their environments.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the plant kingdom like a big family reunion where each branch of the family has its own different traits and stories. Some members are very simple and young, like algae, while others are mature and diverse, like angiosperms.
Characteristics of Algae
Chapter 2 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
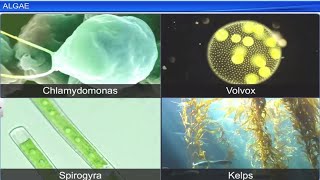
Algae are chlorophyll-bearing simple, thalloid, autotrophic and largely aquatic organisms. Depending on the type of pigment possessed and the type of stored food, algae are classified into three classes, namely Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae and Rhodophyceae.
Detailed Explanation
Algae are important aquatic plants that have chlorophyll, allowing them to perform photosynthesis. They can be categorized into three main classes based on their pigments and types of stored food: Chlorophyceae (green algae), Phaeophyceae (brown algae), and Rhodophyceae (red algae). Understanding these classes helps us recognize the variety in plant life, especially in aquatic environments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine algae as the different types of ice cream. Just like ice cream can come in many flavors (like chocolate or vanilla), algae can have different colors and types based on their pigments—green, brown, or red!
Reproduction in Algae
Chapter 3 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Algae usually reproduce vegetatively by fragmentation, asexually by formation of different types of spores and sexually by formation of gametes which may show isogamy, anisogamy or oogamy.
Detailed Explanation
Algae reproduce in three main ways: vegetative reproduction (breaking into pieces and growing into new algae), asexual reproduction (creating spores), and sexual reproduction (forming gametes). Gametes can be similar (isogamy), different in size (anisogamy), or formed in distinct structures (oogamy). This diversity in reproduction methods ensures the continuation and genetic variation of algae.
Examples & Analogies
Think of algae reproduction like creating new plants from a single leaf. Sometimes, a leaf can grow roots and become a new plant (vegetative), or it can drop seeds (asexual), and sometimes it might need pollen from a different plant to make a seed (sexual).
Understanding Bryophytes
Chapter 4 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Bryophytes are plants which can live in soil but are dependent on water for sexual reproduction. Their plant body is more differentiated than that of algae. It is thallus-like and prostrate or erect and attached to the substratum by rhizoids.
Detailed Explanation
Bryophytes, which include mosses and liverworts, can grow on land but still need water to reproduce. Unlike algae, they have a more complex structure with roots, stem-like, and leaf-like parts called rhizoids that help anchor them to the soil. Bryophytes are essential for soil formation and preventing erosion.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine bryophytes as the tough little plants that can grow in rocky places, holding the soil together. Just like how we need water to drink and grow, bryophytes need moisture to produce their offspring.
The Structure of Pteridophytes
Chapter 5 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In pteridophytes the main plant is a sporophyte which is differentiated into true root, stem and leaves. These organs possess well-differentiated vascular tissues. The sporophytes bear sporangia which produce spores.
Detailed Explanation
Pteridophytes are more advanced plants like ferns. They have true roots, stems, and leaves, which differentiate them from bryophytes. Their vascular tissues allow for effective transport of water and nutrients. They produce spores in sporangia, which are necessary for their reproduction.
Examples & Analogies
Think of pteridophytes as the mini trees of the plant world. Just like a tree has branches, leaves, and roots, pteridophytes also have these structures, but they reproduce with tiny spores rather than seeds.
Gymnosperms: Naked-Seeds
Chapter 6 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The gymnosperms are the plants in which ovules are not enclosed by any ovary wall. After fertilisation the seeds remain exposed and therefore these plants are called naked-seeded plants.
Detailed Explanation
Gymnosperms differ from flowering plants in that their seeds (ovules) are not enclosed in a fruit. This means the seeds are 'naked' and exposed. This trait is common among coniferous plants such as pine trees, which produce cones instead of flowers for reproduction.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine gymnosperms as a gift wrapped in clear cellophane instead of a nice box. You can see the gift inside, similar to how seeds are exposed in gymnosperms, making them distinct from other plants.
Angiosperms: The Flowering Plants
Chapter 7 of 7
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The angiosperms are divided into two classes – the dicotyledons and the monocotyledons.
Detailed Explanation
Angiosperms are the most diverse group of plants. They are divided into two main categories based on the number of embryonic leaves (cotyledons): dicotyledons (two leaves, e.g., beans, roses) and monocotyledons (one leaf, e.g., grasses, lilies). This classification helps in identifying and studying the vast number of flowering plants and their characteristics.
Examples & Analogies
Think of angiosperms like the variety of books in a library. The fiction section might represent dicots (two main genres) while the non-fiction section represents monocots (one main genre). Each section has diverse titles and topics, just like flowering plants have multiple types and uses.
Key Concepts
-
Algae: Aquatic, chlorophyll-bearing organisms that reproduce in various ways.
-
Bryophytes: Depend on water for reproduction and possess thallus-like structures.
-
Pteridophytes: Characterized by true roots, stems, and leaves with vascular tissues.
-
Gymnosperms: Have naked seeds where the ovules are not enclosed by an ovary wall.
-
Angiosperms: Most advanced plants, categorized into monocots and dicots.
Examples & Applications
Common algae include seaweed and pond scum.
Mosses like the Sphagnum and liverworts are typical examples of bryophytes.
Ferns serve as classic representatives of pteridophytes.
Pine trees represent gymnosperms, while flowering plants exemplify angiosperms.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In water algae float and sway, plants on land come out to play.
Stories
Once upon a time in a wetland, algae danced while bryophytes grew roots, and pteridophytes waved their leaves like elegant dancers under the sun.
Memory Tools
Remember 'BAP-GA' for the plant classes: Bryophytes, Algae, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms.
Acronyms
CAP-GA for groups
Chlorophyceae
Algae
Pteridophytes
Gymnosperms
Angiosperms.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Algae
Chlorophyll-bearing simple organisms, primarily aquatic, classified into various groups based on pigments.
- Bryophytes
Plants living in soil, dependent on water for reproduction, with structures resembling roots, stems, and leaves.
- Pteridophytes
Sporophyte-dominant plants possessing true roots, stems, and leaves with vascular tissues.
- Gymnosperms
Plants with naked seeds, where ovules are not enclosed by an ovary wall.
- Angiosperms
The most advanced group of plants, characterized by flowers and divided into monocots and dicots.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
