Exercises
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
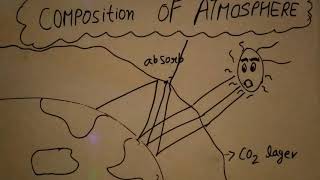
Understanding the Composition of the Atmosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let's discuss the composition of the atmosphere. What do you think is the major gas present in our atmosphere?

I think it's oxygen, right?

Close, but not quite! The major gas is actually nitrogen, making up about 78%. Can anyone tell me the role of carbon dioxide?

Isn't it responsible for the greenhouse effect?

Exactly! Remember, CO2 absorbs heat and helps keep our planet warm. A mnemonic to remember is 'Nitrous Oxygen Can' for Nitrogen, Oxygen, and Carbon Dioxide.

What about water vapor? How does that affect us?

Great question! Water vapor is crucial as it traps heat and influences weather patterns. In humid areas, it can make up to 4% of the atmosphere.

What happens to all these gases as we go higher in the atmosphere?

They decrease in concentration! For instance, oxygen becomes almost negligible at 120 km in altitude. Remember, it's important to understand how these gases function at different levels.

To summarize, the atmosphere primarily consists of nitrogen and oxygen, with carbon dioxide playing a crucial role in heat retention.
Structure of the Atmosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s dive into the structure of the atmosphere. Can anyone name the first layer?

The troposphere?

Correct! The troposphere is where all weather occurs. Its height varies—about 8 km at the poles and 18 km at the equator. What happens to temperature as you rise through this layer?

It decreases, right?

Yes! It decreases at roughly 1°C for every 165 m. How about the next layer, the stratosphere?

That’s where the ozone layer is, which protects us from UV radiation!

Exactly! The ozone layer absorbs harmful UV rays. A fun story to remember: think of the ozone as a superhero cape protecting the earth from harmful sun rays.

What about the mesosphere?

In the mesosphere, temperatures drop even further, reaching around -100°C. It’s important to note that this is where most meteors burn up upon entering the atmosphere.

In summary, the structure of the atmosphere is crucial for understanding climate and weather phenomena, with each layer having its own unique characteristics.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section contains multiple-choice questions, short and long answer prompts to evaluate comprehension of key concepts related to the atmosphere, including its composition, structure, and climatic elements. These exercises are designed to deepen students' understanding and retention of the material presented in the chapter.
Detailed
Exercises on Climate
This section lists a variety of exercises focused on the study of climate, emphasizing the atmosphere's composition, structure, and the fundamental elements that affect weather and climate. The exercises are categorized into multiple-choice questions, short answer, and detailed long answer questions to facilitate diverse learning and assessment styles.
Key Points Covered:
- Atmospheric Composition: Understanding the mixture of gases, the presence of water vapor, and dust particles.
- Layer Structure: Different layers of the atmosphere including troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere, along with their unique properties.
- Elements of Weather and Climate: Introduction to temperature, pressure, winds, humidity, clouds, and precipitation.
These exercises challenge students to recall, explain, and apply the concepts they have learned. Comprehensive assessment through these exercises plays a crucial role in academic assessments.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Multiple Choice Questions
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Multiple choice questions.
(i)Which one of the following gases constitutes the major portion of the atmosphere?
(a) Oxygen (c) Argon
(b) Nitrogen (d) Carbon dioxide
(ii)Atmospheric layer important for human beings is:
(a) Stratosphere (c) Troposphere
(b) Mesosphere (d) Ionosphere
(iii) Sea salt, pollen, ash, smoke soot, fine soil — these are associated with:
(a) Gases (c) W ater vapour
(b) Dust particles (d) Meteors
(iv) Oxygen gas is in negligible quantity at the height of atmosphere:
(a) 90 km (c) 100 km
(b) 120 km (d) 150 km
(v) Which one of the following gases is transparent to incoming solar radiation and opaque to outgoing terrestrial radiation?
(a) Oxygen (c) Helium
(b) Nitrogen (d) Carbon dioxide
Detailed Explanation
This chunk includes multiple-choice questions that assess knowledge about the atmosphere. Each question presents four possible answers, out of which one is correct. Understanding these concepts is important for grasping the fundamentals of atmospheric science and its components.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these questions like a quiz in a school where you pick the correct answer among several choices, helping you recall and strengthen your understanding of atmospheric concepts.
Short Answer Questions
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i)What do you understand by atmosphere?
(ii) What are the elements of weather and climate?
(iii) Describe the composition of atmosphere.
(iv) Why is troposphere the most important of all the layers of the atmosphere?
Detailed Explanation
This section prompts students to answer focused questions succinctly. Each question encourages students to summarize essential concepts related to the atmosphere, its composition, and the significance of the troposphere, which is crucial for life on Earth.
Examples & Analogies
Consider these questions as elevator pitches where you have just a few seconds to explain a complicated idea simply to someone you meet in an elevator.
Extended Response Questions
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Answer the following questions in about 150 words.
(i)Describe the composition of the atmosphere.
(ii) Draw a suitable diagram for the structure of the atmosphere and label it and describe it.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, students are required to elaborate on two topics: the composition of the atmosphere and its layered structure. This necessitates a deeper understanding and the ability to convey detailed information about these aspects, fostering critical thinking and expression.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine these as essays where you get to explore your thoughts in detail about a topic you find fascinating, just as you might write about your favorite book or movie.
Key Concepts
-
Atmospheric Composition: The atmosphere consists mainly of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%). Carbon dioxide plays a critical role in heat retention.
-
Troposphere: The layer of atmosphere closest to Earth where weather phenomena occur.
-
Stratosphere: Contains the ozone layer, essential for blocking harmful UV radiation from the sun.
-
Greenhouse Effect: The process by which greenhouse gases trap heat within the Earth's atmosphere.
Examples & Applications
The troposphere is where all the weather occurs, while the stratosphere protects life from harmful UV rays due to its ozone layer.
Carbon dioxide levels have risen due to fossil fuel consumption, impacting global temperatures through the greenhouse effect.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the sky so high, the troposphere does lay, Weather happens here, every single day.
Stories
Imagine Earth wearing a thick jacket (the troposphere) that protects it from the cold but has a superhero cape (the ozone in stratosphere) against harmful rays.
Memory Tools
Remember the layers with 'SEE ME EX' - Stratosphere, Exosphere, Mesosphere, Troposphere.
Acronyms
COMES for Composition of Atmosphere
Carbon Dioxide
Oxygen
Methane
and noble elements like Argon.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Atmosphere
The layer of gases surrounding the Earth, essential for supporting life.
- Troposphere
The lowest layer of the atmosphere where weather occurs, extending from the Earth's surface to about 8-18 km.
- Stratosphere
The layer above the troposphere, containing the ozone layer, extending up to 50 km.
- Greenhouse Effect
The warming of Earth's surface due to trapped outgoing infrared radiation by certain gases.
- Water Vapour
Water in its gaseous state, a significant component of the atmosphere that affects weather and climate.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
