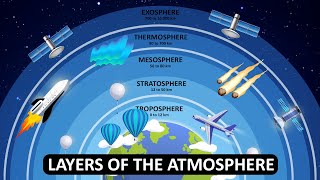
Mesosphere
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Mesosphere
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’ll explore the mesosphere. Can anyone tell me where the mesosphere is located in the atmosphere?

Is it above the stratosphere?

Exactly! It lies between the stratosphere and the thermosphere, typically from about 50 km to 80 km above the Earth's surface.

What happens to temperatures as we go up into the mesosphere?

Good question! The temperatures decrease as we ascend, reaching around -100°C at its peak, known as the mesopause. Remember 'M for Mesosphere, M for Minus temperatures'! This is a useful mnemonic to remember.

Why is that significant?

The decreasing temperatures are crucial for various atmospheric processes. Let’s summarize. The mesosphere is above the stratosphere, has decreasing temperatures, and extends from about 50 km to 80 km.
Role of Mesosphere in Atmospheric Dynamics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into the significance of the mesosphere. Can anyone think of a phenomenon that occurs in the mesosphere?

I’ve heard that meteors burn up there when they enter the atmosphere.

Yes, exactly! This is crucial because it protects the Earth from meteorite impacts. You can remember this with the phrase 'Meteors Melt in the Mesosphere' for easier recall.

Are there weather patterns affected by the mesosphere?

While most weather occurs in the troposphere, the mesosphere does influence dynamics. For instance, mesospheric winds can affect the movement of storm systems. Let’s recap: meteors burn up here and it can affect atmospheric dynamics.
Comparing Atmosphere Layers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We've talked about the stratosphere and the mesosphere. How do they compare in terms of temperature and function?

I think the stratosphere is warmer because of the ozone layer.

Correct! The stratosphere contains the ozone layer, which absorbs UV radiation, warming that layer. We use 'S for Stratosphere, S for Solar absorption' to remember.

So, does that make the mesosphere the coldest?

Yes! The mesosphere is the coldest atmospheric layer due to decreasing temperatures with altitude. Summarizing, the stratosphere warms due to ozone, whereas the mesosphere cools significantly.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The mesosphere, situated above the stratosphere, extends from 50 km to 80 km above the Earth's surface and is characterized by decreasing temperatures with increasing altitude, reaching temperatures as low as -100°C. This section explores the importance of the mesosphere, including its role in meteorological phenomena.
Detailed
Mesosphere Overview
The mesosphere is the third layer of the Earth's atmosphere, situated above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere, extending from approximately 50 km to 80 km above the Earth's surface.
Temperature Characteristics
In the mesosphere, temperatures decrease with altitude, reaching their lowest point around -100°C near the upper boundary, the mesopause. This cooling effect is significant as it contributes to the temperature profile of the atmosphere.
Importance of the Mesosphere
The mesosphere plays a critical role in the overall atmospheric dynamics and is associated with various meteorological and astronomical phenomena. For example, it is the layer where most meteors burn up upon entering the Earth's atmosphere, highlighting its importance in protecting the planet from space debris.
In summary, the mesosphere is crucial for understanding atmospheric science, including temperature variations and meteorological events, which directly impact our climate.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to the Mesosphere
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The mesosphere lies above the stratosphere, which extends up to a height of 80 km. In this layer, once again, temperature starts decreasing with the increase in altitude and reaches up to minus 100°C at the height of 80 km. The upper limit of mesosphere is known as the mesopause.
Detailed Explanation
The mesosphere is the middle layer of the Earth's atmosphere, situated above the stratosphere and extending to about 80 kilometers. This layer is characterized by a decrease in temperature as you go higher, reaching extremely cold temperatures of around -100°C at its top, known as the mesopause, which is the boundary between the mesosphere and the next layer, the thermosphere.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the mesosphere like a tall cake made of multiple layers. The lower layers are warmer (like the stratosphere), while the upper layer (the mesosphere) is much colder. Just like frosting can keep a cake warm, the lower layers of the atmosphere trap heat, but once you reach the mesosphere, it gets chilly quickly.
Characteristics of Temperature in the Mesosphere
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In the mesosphere, temperature decreases with increasing altitude, reaching up to -100°C.
Detailed Explanation
As you ascend through the mesosphere, the air becomes increasingly cold. This phenomenon occurs because this region does not contain significant amounts of gas that can retain heat, leading to lower temperatures at higher altitudes. Thus, flying from the lower parts of the atmosphere to this layer would feel like transitioning from a warm place to one that is freezing cold.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine climbing a mountain. At the base, you may feel warm and comfortable. But as you go higher, the temperature drops, and you might need warmer clothing. Similarly, as you move up in the mesosphere, the temperature drops significantly, highlighting the relationship between altitude and temperature in this atmospheric layer.
Significance of the Mesopause
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The upper limit of the mesosphere is known as the mesopause.
Detailed Explanation
The mesopause marks the transition between the mesosphere and the thermosphere. At this boundary, the temperature stops decreasing and starts to rise again in the thermosphere. This layer is crucial because it separates two atmospheric regions with very different characteristics, impacting phenomena such as atmospheric temperature and satellite orbits.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the mesopause as a door between two different rooms. One room (the mesosphere) is very cold, while the other room (the thermosphere) becomes warm. This door signifies a change in environment, just like the mesopause distinguishes a change from colder to warmer temperatures in the atmosphere.
Key Concepts
-
Mesosphere: The atmospheric layer above the stratosphere, characterized by decreasing temperatures.
-
Mesopause: The boundary between the mesosphere and thermosphere where temperatures reach a minimum.
-
Meteors: Small celestial bodies that burn up in the mesosphere.
Examples & Applications
An example of a meteor burning up in the mesosphere as it enters the Earth's atmosphere.
The distinction between the stratosphere's warmth due to the ozone layer compared to the cooling effect in the mesosphere.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the mesosphere, oh so cold, meteors disappear, or so I'm told.
Stories
Imagine a night sky full of stars, where meteors race fast but meet their end in the cold, the mesosphere.
Memory Tools
Remember 'M for Mesosphere, M for Meteroids Melt'.
Acronyms
M.E.S.O - Mesosphere, Extremely Cold, Shields Earth from meteors, Oxygen levels are low.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Mesosphere
The layer of the Earth's atmosphere above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere, typically ranging from 50 km to 80 km above the surface.
- Mesopause
The boundary between the mesosphere and the thermosphere, noted for the lowest temperatures in the atmosphere.
- Meteor
A small celestial body that burns up upon entering the Earth's atmosphere, commonly observed as a shooting star.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
