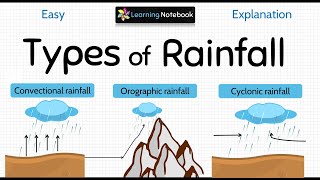
Types of Rainfall
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Convectional Rain
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will explore convectional rainfall. This type happens when the air is heated, becomes light, and rises. Can someone tell me what happens to the rising air?

It cools and expands?

Exactly, as it cools, the moisture in the air condenses and forms clouds. Who can explain what happens next?

It leads to heavy rainfall?

Right! This rainfall is common in tropical areas, especially during hotter parts of the day. Remember, we can use the acronym 'HEAT' to remember: Heating causes Evaporation, Air rises, then Thunderstorms occur.

That’s a good way to remember!

Let’s summarize: convectional rain occurs from heated, rising air that cools and condenses to form rain, commonly seen in summer.
Exploring Orographic Rain
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss orographic rain. What do you think happens when humid air encounters a mountain?

Does it have to go up?

Yes! As the air rises, it cools and condenses, resulting in rainfall. What happens to the air after it crosses the mountain?

It gets warmer and dries out?

Correct! This is why the windward side gets more rain while the leeward side becomes dry—a concept we call the rain-shadow effect.

So, mountains can dramatically change weather patterns!

Exactly! And remember this with the phrase: 'Mountains lift, rain drifts.'
Understanding Cyclonic Rain
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Our last type is cyclonic rain. This occurs when warm and cool air masses collide. What can this lead to?

Tornadoes or storms?

Both can happen, but here we mean rain. The warm air rises over the cool air, leading to cloud formation and precipitation.

So cyclonic rain can occur anywhere there’s a weather front?

Exactly! It's common across many climates. Let’s use the mnemonic ‘Rising Warmth’ to remember: Rain comes from Rising Warm air.

That makes it easier!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section outlines the different types of rainfall, describing convectional rainfall that occurs due to heated air rising, orographic rainfall caused by air rising over mountains, and cyclonic rainfall associated with weather fronts. Each type has unique characteristics and impacts on the surrounding environment.
Detailed
Types of Rainfall
Rainfall is an essential aspect of weather and climate, playing a critical role in the hydrological cycle. It can be classified into three main types based on its origin: convectional, orographic, and cyclonic.
1. Convectional Rain
Convectional rain occurs when the sun heats the Earth’s surface, causing the air above to warm up and rise. As this warm air ascends, it cools, expands, and ultimately reaches a point where the moisture it carries condenses, forming cumulus clouds, leading to heavy rainfall often accompanied by thunder and lightning. This type of rain is more common in tropical regions and tends to occur in the afternoon during summer.
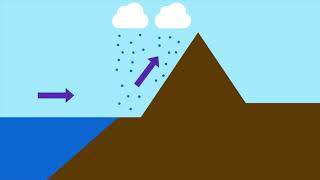
2. Orographic Rain
Orographic rain takes place when humid air is lifted over a mountain range. The rising air cools, leading to condensation of moisture and precipitation on the windward slopes of the mountain, which receive heavy rainfall. Conversely, as this air descends on the leeward side of the mountain, it warms up, leading to drier conditions, creating a rain-shadow area.
3. Cyclonic Rain
Cyclonic or frontal rainfall occurs when two air masses meet, typically when warm moist air collides with cooler air. This situation often results in the warm air rising over the cool air, leading to cloud formation and precipitation. Cyclonic rain can bring substantial rainfall and is associated with storm systems.
Overall, understanding the types of rainfall is critical for weather forecasting and agriculture, as different regions experience varying amounts and types of rainfall.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Types of Rainfall
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
On the basis of origin, rainfall may be classified into three main types – the convectional, orographic or relief and the cyclonic or frontal.
Detailed Explanation
Rainfall can be categorized into three distinct types based on how it is formed. Understanding these types is essential for recognizing patterns in weather and climate across different regions. The three types are convectional rain, orographic (or relief) rain, and cyclonic (or frontal) rain. Each type has unique characteristics and processes that determine when and where it occurs.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine rainfall as a recipe; depending on the ingredients (types of air masses, temperature, and geography), you can create different types of dishes (rainfall). Just like how a chef uses different techniques to prepare various meals, nature utilizes distinct processes to generate different types of rain.
Convectional Rain
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The air on being heated, becomes light and rises up in convection currents. As it rises, it expands and loses heat and consequently, condensation takes place and cumulus clouds are formed. With thunder and lightning, heavy rainfall takes place but this does not last long. Such rain is common in the summer or in the hotter part of the day. It is very common in the equatorial regions and interior parts of the continents, particularly in the northern hemisphere.
Detailed Explanation
Convectional rain occurs when the sun heats the earth's surface, causing the air above it to warm up. This warm air is lighter and rises. As it ascends, it cools down, leading to condensation where water vapor forms droplets, resulting in cumulus clouds. Eventually, these clouds can produce heavy rain, often accompanied by thunderstorms. This type of rain is most common during warm summer days, especially in equatorial regions where it can occur frequently.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a pot of water on the stove. As the water heats up, steam rises. Similarly, hot air rises from the earth's surface, creating convection currents. Just like how the steam eventually condenses back into droplets, the rising warm air cools and forms clouds, ultimately leading to rain.
Orographic Rain
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
When the saturated air mass comes across a mountain, it is forced to ascend and as it rises, it expands; the temperature falls, and the moisture is condensed. The chief characteristic of this sort of rain is that the windward slopes receive greater rainfall. After giving rain on the windward side, when these winds reach the other slope, they descend, and their temperature rises. Then their capacity to take in moisture increases and hence, these leeward slopes remain rainless and dry. The area situated on the leeward side, which gets less rainfall is known as the rain-shadow area. It is also known as the relief rain.
Detailed Explanation
Orographic rain occurs when moist air encounters mountains. As the air rises over the mountain, it expands and cools, resulting in condensation and precipitation on the windward side of the mountain. This area gets significant rainfall. Conversely, as the air descends on the leeward side, it warms up and can hold more moisture, leading to a drier climate known as a rain-shadow area. This phenomenon explains why some regions are lush and green while others, just a few miles away, are arid.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine blowing up a balloon. As you blow air into it, the balloon expands. When air hits a wall, it rises, and the behavior changes. Similarly, moist air rises over mountains, leading to rainfall on one side but leaving the other side dry, just like how a wall alters the flow of air.
Cyclonic Rain
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
You have already read about extra tropical cyclones and cyclonic rain in Chapter 9. Please consult Chapter 9 to understand cyclonic rainfall.
Detailed Explanation
Cyclonic rain is associated with weather systems known as cyclones, which are large-scale air mass systems characterized by low atmospheric pressure. When warm, moist air meets cold air, they create a cyclone, leading to significant rainfall as the air rises and cools rapidly. Detailed understanding of cyclonic rainfall can be found in Chapter 9, where the processes of cyclone formation and their role in bringing rain to various regions are discussed.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a spinning top. When it spins, the air around it swirls. Similarly, cyclones drag warm air upwards, forming a spinning mass of clouds and rain. Just like how a spinning top can create a whirlwind, cyclonic systems can generate large storms that bring heavy rainfall.
Key Concepts
-
Convectional Rain: Rainfall caused by warm air that rises and cools, forming precipitation.
-
Orographic Rain: Rain resulting from air being lifted over mountains, causing condensation.
-
Cyclonic Rain: Precipitation caused by the collision of warm and cool air masses.
Examples & Applications
In the Congo Basin, convectional rain is frequent due to the intense heat and moisture in the equatorial region.
The Western Ghats in India experience heavy orographic rain as moist air from the coast is uplifted over the mountains.
Cyclonic rain is often seen in temperate regions where warm, moist air from the ocean collides with cold continental air.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For rain that’s in convection, heat’s the main connection!
Stories
Once upon a time, in a land of mountains, warm air rose but as it climbed high, it cooled and cried rain on the peaks—but down below, the land was dry, where the air flowed fast and high.
Memory Tools
Remember 'WARM' for Cyclonic rain: Warm air Aboves Rising mountains.
Acronyms
COC for rainfall types
CDe (for Convectional)
ORA (for Orographic)
Cyclonic.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Convectional Rain
Rain that occurs when warm air rises, cools, and condenses into precipitation.
- Orographic Rain
Rain produced when moist air ascends over mountains, causing cooling and condensation.
- Cyclonic Rain
Rainfall that happens due to the collision of warm and cool air masses, leading to precipitation.
- Rainshadow Area
The dry region on the leeward side of a mountain range that receives less rainfall.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
