Federalism
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Federalism in India
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll discuss the concept of federalism in India. Can anyone explain what you think federalism means?

I think it's about how power is divided between different levels of government, like the central and state governments.

Exactly! Federalism involves a division of powers. In India, we have a strong central government, but we also grant special privileges to certain states. Can anyone give me an example of such a privilege?

Article 371 gives special status to certain states like Nagaland.

Great! This shows how Indian federalism is asymmetric. Remember, 'ASymmetric is for special needs'.

So, it's not just one-size-fits-all; different regions get different rights?

Exactly! We aim to balance national unity with regional diversity.

How does this affect our identity as a nation?

It allows us to celebrate both our national identity and our unique regional cultures.

So in summary, federalism in India is unique because it combines a strong central government with a recognition of regional needs.
Asymmetric Federalism
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive deeper into asymmetric federalism. What do you think this means in relation to states like Nagaland?

Does it mean that some states have different rules or powers compared to others?

Exactly! Article 371 allows for local laws to be valid and protects cultural identities. Can you think of why this might be important?

It helps preserve their traditions and rights, right?

Yes! It ensures that diverse cultural identities can thrive. That’s a key aim of our Constitution.

So, it gives power to those regions to set their laws based on their needs?

Correct! It enables them to govern more effectively while still being part of the national framework.

In summary, asymmetric federalism recognizes that different regions may require specific governance to ensure harmony.
Unity in Diversity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s connect federalism back to our national identity. How does recognizing regional needs contribute to our unity?

If we accept diverse identities, maybe people feel more respected.

Exactly! When people feel included, it fosters a sense of belonging to the nation as a whole.

What about religious communities? Are they included in this respect?

Great question! Our Constitution emphasizes equal respect among communities and encourages them to co-exist peacefully.

So, everyone has a voice in this federal system.

Absolutely! Remember, the phrase 'Unity in Diversity' reflects our approach to governance.

To summarize, federalism promotes both regional identity and national integrity by allowing diverse voices to be heard.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explores the structure of federalism in India, focusing on the central government's authority in relation to individual states, specifically addressing the asymmetric nature of Indian federalism as outlined in provisions such as Article 371. It emphasizes the necessity of adaptable governance in a diverse nation, underscoring the importance of recognizing regional and cultural identities.
Detailed
Detailed Overview of Federalism in the Indian Constitution
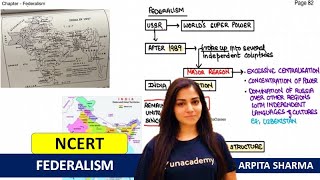
Federalism in India is characterized by the division of powers between the central government and various states, aiming to balance the authority between a strong central government and the diverse needs of regional states. The Indian Constitution creates a predominately unitary structure but also incorporates elements of asymmetry, particularly through provisions that cater to specific regional requirements.
- Central vs. State Authority: The Constitution ensures a strong central authority, allowing it to maintain unity in governance. However, this is complemented by special provisions for certain states, such as those found in Article 371, which recognize the unique cultural and administrative needs of regions like Nagaland.
- Asymmetric Federalism: Unlike symmetrical federalism seen in other countries like the USA, Indian federalism accounts for regional disparities through asymmetric arrangements, allowing certain states to enjoy privileges that others do not. This is critical in accommodating linguistic and cultural differences within a diverse population.
- The Role of National Identity: The Constitution seeks to nurture a unified national identity while respecting regional identities. It rejects separate electorates based on religion, aiming to ensure inclusion and fraternity among various communities.
The framework laid out by the Indian Constitution regarding federalism not only enables the recognition of regional identities but also seeks to promote harmony, underscoring the importance of equitable rights and representation in a multi-lingual state.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Asymmetric Federalism in India
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Second, by introducing the article concerning North-East (Art. 371), the Indian Constitution anticipates the very important concept of asymmetric federalism. We have seen in the chapter on federalism that the Constitution has created a strong central government. But despite this unitary bias of the Indian Constitution, there are important constitutionally embedded differences between the legal status and prerogatives of different sub-units within the same federation.
Detailed Explanation
The Indian Constitution, while establishing a strong central government, acknowledges the diverse needs of different regions, particularly in the North-East, by allowing for special provisions under Article 371. This means that not all states have the same powers; some regions are granted more autonomy to protect their unique cultures and identities. This approach is termed asymmetric federalism because some states have different rights compared to others.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a school where some classes have different rules compared to others based on their specific needs, such as extra time for exams for younger students or specific subjects tailored for a gifted group. This allows each class to thrive based on its unique aspects while still being part of the same school.
Special Provisions for the North-East
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Under Article 371A, the privilege of special status was also accorded to the North-Eastern State of Nagaland. This Article not only confers validity on pre-existing laws within Nagaland, but also protects local identity through restrictions on immigration.
Detailed Explanation
Article 371A provides Nagaland with unique rights that uphold its cultural identity by allowing existing laws to remain valid and imposing rules to control immigration. This means that people can't just move into Nagaland freely without restrictions, preserving the local culture and ensuring that it doesn't change drastically due to outside influences.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a family’s house rules that protect the family traditions—like allowing only family members to host events—while opening their doors to friends during special occasions. This way, family traditions are respected, while still allowing for outside relationships.
Linguistic Federalism and Political Recognition
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Although the Constitution did not originally envisage this, India is now a multi-lingual federation. Each major linguistic group is politically recognised and all are treated as equals.
Detailed Explanation
The Indian Constitution acknowledges that India is home to many languages, and it politically recognizes various linguistic groups. This means that each language group has its rights and representation, ensuring that no single language or culture dominates the political landscape. Equal treatment of languages helps maintain unity while respecting diversity.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a community potluck where everyone is encouraged to bring a dish from their culture. Each dish represents different traditions (languages), and acknowledging each dish helps everyone feel included, fostering a greater sense of community while celebrating diversity.
Balancing National and Regional Identities
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Thus, the Constitution constantly reinforces a common national identity. In the chapter on federalism, you have studied how India strives to retain regional identities along with the national identity.
Detailed Explanation
The Constitution works to create a strong, unified national identity while also respecting individual regional identities. It recognizes that people can be proud of their regional backgrounds (like language or culture) while still belonging to the broader identity of India. This balance is crucial for promoting harmony among diverse communities.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a sports team where players wear the same jersey but represent different local clubs. They train and play together as one team, but each player brings their unique skills and local pride, which enriches the overall performance of the team.
Avoidance of Separate Electorates
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Indian Constitution tried to balance these various identities. Yet, preference was given to common identity under certain conditions. This is clarified in the debate over separate electorates based on religious identity which the Constitution rejects.
Detailed Explanation
The Constitution decided against creating separate electorates, which would allow different religious communities to vote separately, as this could lead to division and weaken national unity. Instead, it promotes a single electoral system that encourages all groups to participate together, enhancing the sense of fraternity and shared identity among diverse populations.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine if students in a school were allowed to vote only within their classroom groups instead of as a whole school. This could create divisions among classes. Instead, voting school-wide allows everyone to bond over common goals while respecting individual class identities.
Key Concepts
-
Federalism: The division of powers between different levels of government in a state.
-
Asymmetric Federalism: A system where states have different powers and responsibilities.
-
Article 371: Special provisions that grant particular privileges to certain Indian states.
-
Unitary Bias: The tendency of a federal system to favor a central authority over regional autonomy.
-
National Identity: The collective identity of a nation, incorporating diverse cultural and regional identities.
-
Unity in Diversity: A principle that highlights the coexistence of various identities and cultures within a single nation.
Examples & Applications
Article 371 provides Nagaland with unique powers to preserve its cultural identity.
The central government maintains authority over critical national matters while allowing states various powers.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
'Federalism's the way we share, Powers are split with thoughtful care.'
Stories
Imagine a family where each sibling has a different room and set of rules, reflecting their unique personalities, yet they all gather for family meals, symbolizing how India can respect regional identities while maintaining national unity.
Memory Tools
Remember 'F.A.U.R' - Federalism, Asymmetric, Unity, Regional identity.
Acronyms
FEDERAL - Federation's Equality, Division of power, Regional Admin Laws.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Federalism
A system of government in which power is divided between a central authority and constituent political units.
- Asymmetric Federalism
A form of federalism where the constituent states have unequal powers and responsibilities.
- Article 371
A constitutional provision that grants special status to certain states in India, allowing for unique governance arrangements.
- Unitary Bias
A characteristic of a federal system that favors a strong central government over regional authorities.
- National Identity
A sense of a nation as a cohesive whole, represented by distinctive symbols, cultures, and values.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
