Basic Practices of Crop Production
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Soil Preparation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll learn about the first step in crop production: soil preparation. Why is this important, Student_1?

Isn't it to make the soil ready for planting?

Exactly! Loosening the soil helps roots to penetrate and breathe better. It's like giving them space to grow—what do you think helps the soil stay rich in nutrients?

The microbes and earthworms help with that!

Fantastic! This process of loosening is called tilling or ploughing. Do you remember what tools are used for this?

We use a plough and a hoe, right?

Correct! So, what's the first step before we start sowing seeds?

Preparation of soil!

Great! Let’s remember this with the acronym PS: 'Prepare the Soil.'
Sowing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that the soil is ready, let's discuss sowing. Student_4, why do you think we need quality seeds?

Quality seeds grow better and can give us more crops.

Exactly! Healthy seeds lead to healthy plants. When we sow, we have to consider the depth and distance between seeds. What happens if they are too close?

They might compete for sunlight and nutrients!

Correct! Overcrowding can lead to weak plants. What are some tools we might use for sowing?

We can use a seed drill or just sow by hand.

Good points! Lastly, remember that proper sowing technique is crucial to ensure even growth. Let's use the mnemonic S.E.E.D: 'Sow Evenly, Effectively, and Deeply.'
Irrigation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's move to irrigation. Why do plants need water, Student_3?

Plants need water to stay alive and grow!

Right! Water helps absorb nutrients from the soil. How do we supply this water?

We can use wells, canals, or modern tools like sprinkler systems.

Exactly! Each method has its advantages. Drip irrigation, for instance, uses water efficiently. Can anyone think of the benefits of keeping the soil moist?

It helps in germination and protects against frost!

Very good! Remember, irrigation is key to healthy crops. Use the memory aid W.A.T.E.R: 'Water Availability To Ensure Roots.'
Weeding and Protection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about weeds. What are they, Student_2?

Weeds are unwanted plants that grow with crops.

Exactly! Weeds compete for light, water, and nutrients, which can hurt our crops. How can we manage weeds?

We can remove them manually or spray chemicals called weedicides.

Yes! It’s important to control weeds before they flower. Let’s remember the phrase 'Wipe Out Weeds!' to keep it in mind.
Harvesting and Storage
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We’ve covered a lot! Now we reach the end of crop production: harvesting. What does this involve, Student_4?

Cutting the crops when they are mature.

Exactly! And after harvesting, what’s the next step?

We need to store the crops properly.

Yes, to keep them safe from moisture and pests! Let's summarize with 'Harvest, Dry, Store' as our key phrases for the end process.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section elaborates on the key practices of crop production, highlighting the importance of soil preparation, sowing quality seeds, managing water through irrigation, and the need for protection against weeds, ultimately leading to successful harvesting and storage of crops.
Detailed
Basic Practices of Crop Production
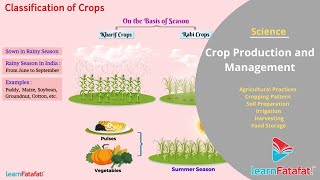
Crop production is crucial for ensuring food security for the growing population. This involves a series of agricultural practices categorized into various steps:
- Preparation of Soil: The first step in crop production where soil is turned and loosened to promote root penetration and aeration. Tilling enhances microbial activity and brings nutrient-rich soil to the surface.
- Sowing: Involves selecting quality seeds and planting them with appropriate spacing and depth. Traditional methods and modern tools, like seed drills, are employed for effective sowing.
- Adding Manure and Fertilizers: To replenish nutrients in the soil, farmers add organic manure and chemical fertilizers. Manure enhances soil texture and moisture retention, whereas fertilizers provide essential nutrients.
- Irrigation: A necessary practice for maintaining soil moisture, crucial for plant growth. Different methods, such as traditional systems and modern techniques like drip irrigation, are utilized based on water availability and crop needs.
- Protecting from Weeds: Weeding is essential to eliminate competition for nutrients and water. This can be achieved using manual methods or chemical weedicides.
- Harvesting: The process of cutting crops when mature. It can be done manually or with machines.
- Storage: After harvesting, crops must be stored properly to prevent spoilage from pests and moisture.
Understanding these fundamental practices is vital for successful crop management and agricultural sustainability.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Agricultural Practices
Chapter 1 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Preparation of soil
- Sowing
- Adding manure and fertilisers
- Irrigation
- Protecting from weeds
- Harvesting
- Storage
Detailed Explanation
This chunk lists the basic practices involved in crop production. Each practice serves a specific purpose in the overall process of farming. These steps are crucial for successful agricultural production.
Examples & Analogies
Think of crop production like baking a cake. Preparation of soil is like preparing the cake batter, sowing seeds is like pouring the batter into a cake pan, adding manure and fertilisers is like adding flavor or raised ingredients, irrigation is like baking the cake to perfection, protecting from weeds is preventing other flavors from overpowering the cake, harvesting is taking the cake out of the oven, and storage is keeping the cake fresh for later.
Preparation of Soil
Chapter 2 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The preparation of soil is the first step before growing a crop. One of the most important tasks in agriculture is to turn the soil and loosen it. This allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil. The loosened soil helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes present in the soil.
Detailed Explanation
Preparation of soil involves tilling or ploughing to aerate the soil and mix in organic matter. Loosening the soil helps plant roots spread and absorb necessary nutrients and water more effectively. It also creates a conducive environment for beneficial organisms like earthworms, which further aerate and enrich the soil.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to dig a hole in hard clay versus soft, fluffy sand. You will find it easier to plant something in the soft sand because it is already loose and allows for more airflow. Just like in gardening, better soil preparation leads to healthier plants.
Sowing
Chapter 3 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Sowing is an important part of crop production. Before sowing, good quality, clean and healthy seeds of a good variety are selected. Appropriate distance between the seeds is necessary to avoid overcrowding of plants.
Detailed Explanation
Selecting high-quality seeds is essential for a good crop yield. Sowing involves planting the seeds at appropriate distances to allow each plant enough space to grow without competing too much with each other for nutrients and sunlight.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a crowd at a concert. If everyone is packed tightly together, they won’t be able to move properly, and some might miss out on the music. However, if they maintain some space between each other, they can enjoy the concert better, just like properly spaced seeds grow healthier.
Using Manure and Fertilisers
Chapter 4 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The substances which are added to the soil in the form of nutrients for the healthy growth of plants are called manure and fertilisers.
Detailed Explanation
Manure is an organic substance from decomposed plant or animal remains, while fertilisers are chemical compounds that provide specific nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Adding these substances is crucial for replenishing nutrients in the soil, especially after multiple cycles of cropping.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how you need to fuel your body with nutritious food to stay healthy. Similarly, plants require nutritious soil to thrive. Manure and fertilisers act as the food that helps them grow strong.
Irrigation
Chapter 5 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The supply of water to crops at regular intervals is called irrigation. The time and frequency of irrigation varies from crop to crop, soil to soil and season to season.
Detailed Explanation
Irrigation is vital for ensuring that plants receive adequate water, especially in dry seasons or regions. Crop requirements for water depend on numerous factors, including the type of crop, soil characteristics, and local climate conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Just like how you need to drink water regularly to stay hydrated and healthy, crops need a consistent water supply to grow well. Imagine if you only watered a plant once a month – it wouldn’t survive very long.
Protection from Weeds
Chapter 6 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In a field, many other undesirable plants may grow naturally along with the crop. These undesirable plants are called weeds. The removal of weeds is called weeding.
Detailed Explanation
Weeds compete with crops for vital resources such as water, nutrients, and sunlight. Removing these unwanted plants is essential to ensure that crops can grow strong without competing for these resources.
Examples & Analogies
If you plant flowers in your garden but let wild grass grow free, the grass will likely take all the nutrients and block sunlight. Regularly removing the grass ensures the flowers thrive, just as weeding in crops allows the crops to flourish.
Harvesting
Chapter 7 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Harvesting of a crop is an important task. The cutting of crop after it is mature is called harvesting. In harvesting, crops are pulled out or cut close to the ground.
Detailed Explanation
Once crops have matured, they are harvested to collect the yield. This can be done manually using tools like sickles or mechanically with harvesters. After harvesting, crops often need to be processed to separate the useful parts from inedible parts.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine waiting for your home-baked cookies to cool down before you eat them. You wouldn't want to eat them raw from the oven! Similarly, after crops are harvested, they must be prepared for storage and consumption.
Storage of Produce
Chapter 8 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Storage of produce is an important task. If the harvested grains are to be kept for longer time, they should be safe from moisture, insects, rats and microorganisms.
Detailed Explanation
Proper storage of grains is essential to prevent spoilage and infestations. After harvesting, grains need to be dried and stored in a way that protects them from pests, moisture, and decay, ensuring they remain viable for consumption or planting.
Examples & Analogies
Think about how you store leftover food in airtight containers to keep them fresh. The same principle applies to storing grains – protecting them from air and pests ensures they don't go bad.
Key Concepts
-
Soil Preparation: The process of turning soil to facilitate growth.
-
Sowing: Planting seeds at the right depth and distance for optimal growth.
-
Irrigation: Watering crops at needed intervals.
-
Weeding: Removal of undesirable plants to protect crops.
-
Harvesting: Cutting crops when they are mature for collection.
-
Storage: Keeping harvested crops safe from damage and spoilage.
Examples & Applications
Using a plough to turn the soil before planting.
Employing drip irrigation in a fruit garden to conserve water.
Harvesting wheat with a sickle or using a combine harvester for efficiency.
Adding organic manure to replenish soil nutrients after a crop season.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To grow crops so rich and fine, preparation is the first sign.
Stories
Imagine a farmer named Joe who carefully tilled his soil before planting seeds, ensuring they grew strong and healthy, yielding a bountiful harvest.
Memory Tools
P.S.I.W.H.S: Prepare Soil, Irrigate, Weeding, Harvest, Store.
Acronyms
C.R.O.P
Cultivation
Replenishment
Observation
Preservation.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Agricultural Practices
Methods and techniques employed in farming to grow crops.
- Tilling/Ploughing
The process of turning and loosening the soil.
- Irrigation
The supply of water to crops at regular intervals for healthy growth.
- Manure
Organic substance added to soil to enrich it.
- Fertilizer
Chemical substances added to soil to enhance nutrient content.
- Weeds
Unwanted plants that compete with crop plants for resources.
- Harvesting
The process of gathering mature crops from the fields.
- Storage
Proper techniques for keeping harvested crops safe from spoilage.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
