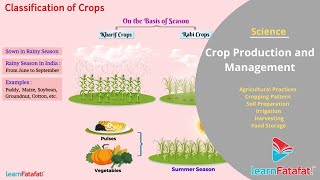
Preparation of Soil
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Soil Preparation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today, we are discussing the preparation of soil, which is crucial before we begin growing any crops. Can anyone tell me why we need to prepare the soil?

Um, to make it easier for plants to grow?

Exactly! Loosening the soil allows roots to penetrate deeper and breathe properly. It also helps in holding nutrients and water. What do you think happens if the soil is too compact?

The roots can’t grow well, and the plants will struggle.

That's right! Remember, more oxygen for roots equals healthier plants. Let’s remember it with the phrase 'Loosen Up for Roots'.
Tilling or Ploughing Techniques
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's look into tilling or ploughing. Can anyone define what ploughing is?

It's when we use a plough to break up the soil.

Good job! Tilling helps mix nutrients back into the soil and is essential for crop growth. Does anyone know what tools are used for this?

I think they use ploughs and also hoes!

Absolutely! Hoes are great for weeding and loosening soil, while modern tractors use cultivators for larger farms. Let’s remember 'Plough, Hoe, and Grow'!
Importance of Nutrients in Soil
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, why do you think we should add nutrients like manure or fertilizers before we plant?

Because plants need food to grow!

Exactly! Nutrients enhance plant growth and soil fertility. Remember, healthy soil leads to healthy crops. Can anyone recall the difference between organic manure and chemical fertilizers?

Organic manure is natural, like from animal waste, and fertilizers are chemicals?

Correct! Keep in mind that 'Natural is Better for Soil'.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Soil preparation involves loosening and turning the soil to promote root penetration and nutrient absorption. Various tools such as ploughs and hoes are used, and the importance of healthy soil enriched with organic matter and nutrients is emphasized for effective crop production.
Detailed
Preparation of Soil
Soil preparation is the foundational step in crop production. It involves loosening and turning soil to allow roots to grow deep and access necessary nutrients. The loosened soil promotes the growth of beneficial organisms like earthworms and microbes which further aerate and enrich the soil, ensuring that nutrients from decomposed matter are available to plants. This process is vital as only the top few centimeters of soil supports plant growth. By turning the soil, nutrient-rich layers come to the surface, making them accessible to crops.
Importance of Tilling or Ploughing
Tilling, also known as ploughing, helps mix organic matter into the soil and prepares it for sowing seeds. Traditional wooden or modern iron ploughs are employed for this task, while specific tools are used to break up soil clumps and level the field, beneficial for irrigation and sowing. The addition of manure before tilling enhances the soil's nutrient content.
Agricultural Implements
Before sowing, tools like ploughs, hoes, and cultivators are crucial. Farmers often use ploughs pulled by animals or tractors, while hoes help in weed removal and soil aeration. In contemporary farming, seed drills are popular for their efficiency in sowing seeds at consistent depths.
This section outlines not just the techniques used for soil preparation but also highlights the symbiotic relationship between healthy soil and crop yield, pivotal for supporting food production.
Youtube Videos




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Soil Preparation
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The preparation of soil is the first step before growing a crop. One of the most important tasks in agriculture is to turn the soil and loosen it. This allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil. The loose soil allows the roots to breathe easily even when they go deep into the soil.
Detailed Explanation
Soil preparation is essential because it impacts the growth and health of plants. When soil is turned and loosened, it becomes easy for roots to grow deep into it. This deep growth ensures that plants can access more nutrients and moisture. Additionally, loose soil allows for better air circulation around the roots, which is critical for respiration.
Examples & Analogies
Think of soil like a sponge. When it's compacted, it's hard for water to get through, and it doesn't expand much. When you loosen it, just like squeezing a sponge, it becomes more absorbent and allows water and nutrients to flow through much easier.
Beneficial Organisms in Soil
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The loosened soil helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes present in the soil. These organisms are friends of the farmer since they further turn and loosen the soil and add humus to it.
Detailed Explanation
Earthworms and microbes play a vital role in maintaining soil health. When the soil is loose, these organisms can thrive and do their work. Earthworms break down organic material and enhance soil texture, which promotes better drainage and aeration. Microbes help decompose dead plants and animals, returning valuable nutrients back to the soil. These processes make the soil richer and more suitable for planting.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a compost pile in your garden. As food shrinks away, earthworms and microbes break it down into nutrient-rich compost. In farming, these same creatures help convert your soil into a fertile ground for growing crops.
Nutrient Cycling in Soil
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Soil contains minerals, water, air and some living organisms. In addition, dead plants and animals get decomposed by soil organisms. In this way, various nutrients in the dead organisms are released back into the soil. These nutrients are again absorbed by plants.
Detailed Explanation
The soil is a dynamic ecosystem. When plants and animals die, their bodies break down through decomposition. This process, aided by soil organisms, releases nutrients back into the soil. These nutrients are essential for the growth of new plants. Therefore, keeping soil healthy and well-prepared helps in sustaining plant growth over time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of nutrient cycling like a recycling bin. When you put items into a recycling bin (dead matter), they get processed and turned into new materials (nutrients). The healthier your bin (soil), the more resources you’ll have for new growth (new plants).
Tilling and Ploughing Techniques
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing. This is done by using a plough. Ploughs are made of wood or iron. If the soil is very dry, it may need watering before ploughing.
Detailed Explanation
Tilling or ploughing is crucial to preparing the soil for planting. Ploughs can be either manual or machine-driven. If the soil is too dry, it must be moistened first; otherwise, it could become too hard to break up effectively. The act of ploughing not only loosens the soil but can also incorporate any applied fertilizers or manure, making them more effective for plants.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how chefs prepare vegetables before cooking. They chop, slice, and mix them together before they go in the pot. Similarly, tilling mixes nutrients and prepares the soil so plants can grow better, much like preparing ingredients for a meal enhances its flavor.
Leveling the Field
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Levelling the field is beneficial for sowing as well as for irrigation. Levelling of soil is done with the help of a leveller.
Detailed Explanation
Leveling the field creates an even surface, which is important for two main reasons: sowing seeds uniformly and ensuring even distribution of water during irrigation. If the soil is uneven, some areas might receive too much water while others may get too little, leading to poor crop growth.
Examples & Analogies
Think of leveling like preparing a canvas for painting. If the canvas is not even, your artwork won't turn out well. Likewise, an even field ensures that when seeds are sown, they have an equal chance to grow.
Use of Manure Before Tilling
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Sometimes, manure is added to the soil before tilling. This helps in proper mixing of manure with soil. The soil is moistened before sowing.
Detailed Explanation
Adding manure before tilling helps to mix organic matter into the soil, enriching it with nutrients. It also aids in improving the soil structure, which enhances its ability to retain moisture. Proper moisture levels are essential for plant seed germination and overall health.
Examples & Analogies
Just like mixing batter for a cake, combining manure with soil ensures that nutrients are evenly distributed throughout the soil, which leads to consistent and healthy plant growth when seeds are planted.
Key Concepts
-
Tilling: The process of loosening and turning the soil to prepare it for planting.
-
Soil Nutrients: Essential elements that promote healthy plant growth.
-
Ploughing: The act of using a plough to break up and turn the soil.
-
Beneficial Microorganisms: Soil organisms like earthworms that enhance soil fertility.
Examples & Applications
Using a plough to prepare a field for wheat planting.
Adding cow dung manure to enrich the soil before sowing.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Before we plant, we must prepare, loosen the soil, show we care.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a fertile land, farmers prepared their soil with a steady hand. They ploughed and tilled, added manure, and soon their crops grew tall and pure.
Memory Tools
Remember 'LAMP' for soil prep: Loosen, Add nutrients, Mix, Plant seeds.
Acronyms
Soil Prep
'FARM' - Fertile
Aerate
Rich
Moist.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Tilling
The agricultural preparation of soil by mechanical agitation, including digging, overturning, and breaking up soil.
- Plough
A tool used for tilling soil, typically pulled by animals or tractors, to prepare the land for planting.
- Manure
Organic matter used as fertilizer for soil, derived from animal dung or decomposed plant matter.
- Soil Erosion
The removal of the topsoil layer, which is essential for crop growth, often due to water or wind.
- Nutrients
Substances that provide nourishment essential for the growth and maintenance of plants.
- Aeration
The process of introducing air into the soil, which helps in root respiration.
- Earthworms
Beneficial soil organisms that help in aeration, decomposition, and nutrient cycling in soil.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
