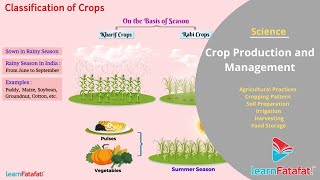
Sowing
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Seed Selection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Before we dive into sowing, can anyone tell me why it’s important to select good quality seeds?

I think it’s because they help ensure we get a good harvest!

Exactly! Good seeds lead to strong plants and higher yield. We often say, 'Healthy seeds equal healthy crops.' Remember this phrase; it's a helpful reminder!

What happens if we don’t use healthy seeds?

Using unhealthy seeds can lead to poor growth, disease, and low yields. It’s like trying to build a house on weak foundations!
Methods of Sowing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s look at the methods of sowing. Who can name a traditional method?

Isn't there a method with a funnel tool that drops seeds into the soil?

Yes, great recall! Now, can anyone compare that with a more modern method?

We have seed drills now that plant seeds automatically, right?

Exactly! Seed drills sow seeds at consistent depths and distances, which saves time and labor. Every system has its advantages!
Importance of Spacing in Sowing
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s talk about spacing. Why do you think we need to keep a certain distance between seeds?

So they don’t compete for nutrients?

Exactly! Proper spacing reduces competition for water and sunlight, which is essential for strong plant growth. Think of it as giving each plant its own personal space!

What if we plant them too close?

Close planting leads to overcrowding, which can result in weak plants and lower yields. Remember the rule of thumb: 'Space gives grace!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Sowing is a crucial step in crop production that involves selecting healthy seeds and using appropriate methods for planting them in the field. The section highlights various tools and techniques used in sowing, including traditional and modern methods, and emphasizes the significance of proper spacing to ensure healthy plant growth.
Detailed
Sowing: An In-Depth Summary
Sowing is an essential step in agriculture, marking the transition from preparation to planting. Before sowing, farmers carefully select high-quality seeds, ensuring they are clean, healthy, and of a variety known for high yields. Understanding the process of seed selection is vital, as good seeds form the foundation of a successful crop.
Types of Sowing Methods
- Traditional Sowing: Traditionally, a funnel-shaped tool was used, allowing seeds to be manually filled and dropped into the soil at desired depths.
- Modern Sowing: The advent of technology has introduced seed drills, which automate the sowing process. This equipment sows seeds uniformly at specified depths and spacings, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor.
- Spacing Considerations: Correct spacing between seeds is crucial to avoid overcrowding, which can lead to competition for nutrients, sunlight, and water. Proper spacing enables optimal growth conditions for plants.
Use of Nurseries
Certain plants, particularly paddy, require a nursery for initial growth before they are transplanted into the field. Growing seedlings in nurseries allows for better control over plant health and growth factors.
In summary, careful seed selection, appropriate sowing techniques, and considerations for plant spacing are vital for ensuring successful crop production.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Sowing
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Sowing is an important part of crop production. Before sowing, good quality, clean and healthy seeds of a good variety—are selected. Farmers prefer to use seeds which give high yield.
Detailed Explanation
Sowing refers to the process of planting seeds in the soil to grow crops. It's crucial because the choice of seeds directly impacts the overall yield of the crop. Farmers make careful selections of seeds, ensuring they are clean, healthy, and of a known variety that is expected to produce high yields. This means they choose seeds that are less likely to have diseases and are more suited to the local climate and soil conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of sowing seeds like planting flowers in a garden—choosing the right seeds ensures that your garden will bloom beautifully. Just like you wouldn’t want to plant seeds from a wilting flower, farmers select seeds that are strong and healthy to ensure a fruitful harvest.
Methods of Sowing
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Traditional tool: The tool used traditionally for sowing seeds is shaped like a funnel. The seeds are filled into the funnel, passed down through two or three pipes having sharp ends. These ends pierce into the soil and place seeds there. Seed drill: Nowadays the seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. This sows the seeds uniformly at equal distance and depth.
Detailed Explanation
There are two primary methods for sowing seeds: the traditional method and the modern seed drill. The traditional method involves using a funnel-shaped tool that allows seeds to be dropped through pipes into the soil. This method requires manual labor and is less precise in terms of seed placement. In contrast, the modern seed drill connects to a tractor and can precisely sow seeds at regular intervals and depths, helping to ensure that each seed has the best chance to germinate and grow without competition from neighboring seeds.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine using a simple scoop to sprinkle seeds into a garden compared to using a machine that drops seeds perfectly at equal distances. The machine helps ensure all the seeds grow in the best way possible, just like how a chef uses a precise measuring tool for perfect ingredient portions.
Sowing Seedlings
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Seeds of a few plants such as paddy are first grown in a nursery. When they grow into seedlings, they are transplanted to the field manually.
Detailed Explanation
Some seeds, like those of paddy, are first sown in a controlled environment known as a nursery. In the nursery, the seeds are nurtured until they sprout into seedlings—young plants that are ready for transplantation. Once the seedlings are robust enough, they are carefully uprooted and planted into the main field. This method allows farmers to maximize growth potential and ensures that they use strong plants that can withstand environmental factors.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like starting a toddler in a daycare where they get food and care before going off to school. The nursery helps the seeds grow strong before they face the challenges of growing in the vast open field.
Spacing and Growth Considerations
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Appropriate distance between the seeds is necessary to avoid overcrowding of plants. This allows plants to get sufficient sunlight, nutrients, and water from the soil.
Detailed Explanation
When sowing seeds, it's essential to space them properly. Overcrowding can lead to competition for resources like sunlight, water, and nutrients in the soil, which can stunt the growth of plants. Proper spacing allows each plant to thrive, absorbing the necessary resources effectively without overshadowing or hindering one another.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how people stand in a crowded elevator versus a spacious one. In a crowded elevator, it’s hard to move and breathe, but in a spacious one, everyone has room to stand comfortably and enjoy the ride.
Key Concepts
-
Seed Selection: The practice of choosing high-quality seeds for planting to ensure healthy crop growth.
-
Sowing Techniques: The methods employed to plant seeds, including traditional and modern approaches.
-
Spacing: The distance maintained between seeds during planting to optimize growth conditions.
Examples & Applications
Using a seed drill, farmers can ensure seeds are planted at the correct depth and spacing, which promotes better water absorption and nutrient uptake.
In paddy cultivation, seedlings are first grown in nurseries to allow for healthy early growth before transplanting them to the fields.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To sow the seeds is our goal, quality seeds make crops whole.
Stories
Once a farmer planted seeds in rows, he watched as every plant arose. By choosing wisely from the start, his farm thrived with all its heart.
Memory Tools
Remember: S-Selection, O-Organization, W-Watering, I-Irrigation, N-Nurturing, G-Growth for successful sowing.
Acronyms
SOIL
Seeds
Open space
Irrigation
Light - all crucial for healthy sowing.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Sowing
The process of planting seeds in the soil to grow crops.
- Seed Drill
A mechanical device that sows seeds at proper depth and spacing.
- Nursery
A place where young plants are grown until they are ready for transplanting.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
