Requirements for Voltage References
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Stability in Voltage References
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about stability in voltage references. Why do you think a stable output voltage is crucial?

Is it because fluctuations could affect circuit performance?

Exactly! A stable voltage reference ensures that other circuits operate reliably. Can someone explain what can affect this stability?

I think temperature changes and power supply variations can cause instability.

Correct! Thus, devices designed to provide voltage references must maintain stability in these conditions. Key concepts to remember are *stability* and its role in circuit accuracy.
Accuracy Measurement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's move on to accuracy in voltage references. How would you define accuracy in this context?

Isn't it the closeness of the output voltage to the specified target voltage?

Great definition! Accuracy is critical because any deviation can lead to errors in applications like ADCs. What factors can influence the accuracy of a voltage reference?

I believe it can depend on the components used in the circuit.

Absolutely! Component tolerances can significantly affect accuracy. Remember, *accuracy* ensures our systems function within designed tolerances.
Power Consumption
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s discuss power consumption. Why is low power consumption particularly important in voltage references?

Because many devices are battery-powered, and high power consumption can drain batteries too quickly.

Exactly! Devices use voltage references in many applications, so high power consumption is undesirable. What practices can help reduce power consumption in these designs?

Using low-current designs or optimizing biases?

Spot on! Lowering power use without sacrificing performance is key to effective designs.
Noise Reduction
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's talk about noise. Why do you think it’s important for voltage references to have low noise levels?

Low noise is essential to prevent distortion in sensitive circuits, right?

Absolutely! Noise can corrupt the accuracy of signals processed by circuits. What solutions can we use to achieve low noise in our designs?

I think using proper filtering techniques could help with that.

Correct! Valid filtering mechanisms can greatly enhance performance. Remember, having a *low noise output* helps maintain purity in other circuit signals.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
A voltage reference must exhibit stability over time and temperature changes, provide accurate output, consume low power, and generate minimal noise. These characteristics make them critical for reliable performance in various analog applications.
Detailed
Requirements for Voltage References
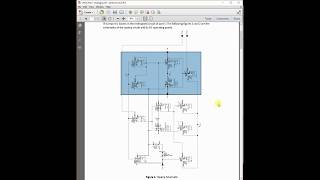
Voltage references are crucial in CMOS analog circuits, ensuring stable voltage outputs regardless of supply variations or temperature changes. A good voltage reference should possess several key characteristics:
- Stability: The output voltage remains consistent over time, unaffected by temperature or supply voltage variations.
- Accuracy: It offers a precise output voltage, with minimal deviation from the desired value.
- Low Power Consumption: Particularly important for battery-operated devices, it should consume minimal power.
- Low Noise: A low noise output is necessary to prevent distortion in sensitive circuitry.
These attributes are vital for applications in ADCs, DACs, and other systems requiring precise voltage levels.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Stability
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Stability: The output voltage should be stable over time and not drift with temperature or supply voltage changes.
Detailed Explanation
Stability in a voltage reference means that the output voltage remains consistent regardless of external factors such as temperature fluctuations or variations in the supply voltage. For example, if the supply voltage changes due to battery drain, a stable voltage reference will still provide the same output voltage. This is essential in circuits where precision is key, as any drift could lead to significant errors in the overall operation.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a stable reference voltage like a trustworthy clock. Just as a reliable clock keeps consistent time despite changes in its environment (like temperature or humidity), a stable voltage reference maintains a constant output voltage even when the input conditions change.
Accuracy
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Accuracy: The voltage reference should provide a precise output voltage with minimal deviation from the desired value.
Detailed Explanation
Accuracy refers to how close the output voltage of the reference is to its specified value. A highly accurate voltage reference will have very little deviation from the set voltage, meaning if we want a reference voltage of, say, 1.2 Volts, an accurate reference will produce output very close to this value. In applications where precise voltage levels are critical, such as ADCs and DACs, accuracy is paramount.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're trying to hit a target with a dart. If your throws land close to the bullseye every time (high accuracy), you're more likely to hit your mark. In contrast, if your darts scatter randomly around the board, your accuracy is low and you may miss the target entirely.
Low Power Consumption
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Low Power Consumption: The reference should consume minimal power, especially in battery-powered applications.
Detailed Explanation
Low power consumption is especially crucial in devices powered by batteries, where maximizing battery life is a priority. A voltage reference should be designed to use as little power as possible to prolong the usability of battery-operated devices. This means that when designing or choosing a voltage reference, one must consider how much current it draws and the total power it consumes during operation.
Examples & Analogies
Consider low-power devices like modern smartphones, which use energy-efficient components to ensure that the battery lasts longer. Just as these devices optimize energy consumption, a good voltage reference should minimize power usage to avoid draining the battery quickly.
Low Noise
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Low Noise: The output voltage should be noise-free to avoid distortion in other sensitive circuits.
Detailed Explanation
Low noise in a voltage reference ensures that the output remains clear and stable, without fluctuations that can interfere with other parts of a circuit. Noise can come from various sources, including thermal effects and external electromagnetic interference. In sensitive applications, such as audio processing or precision analog computations, high noise levels can distort signals, leading to inaccurate outputs. Therefore, it's vital for voltage references to provide a clean, noise-free voltage.
Examples & Analogies
Think of low noise in a voltage reference like a quiet library. Just as a quiet environment helps you concentrate better on your book, a low-noise voltage reference helps other circuits function accurately without interference from unwanted signals.
Key Concepts
-
Stability: Essential for consistent performance in voltage references.
-
Accuracy: Determines reliability in voltage output.
-
Low Power Consumption: Critical for devices reliant on battery power.
-
Low Noise: Important for maintaining signal integrity in sensitive applications.
Examples & Applications
In an ADC, a voltage reference ensures the accuracy of the conversion process by providing a stable input level.
Low dropout voltage reference circuits are commonly used in portable electronic devices to maintain battery life.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Voltage reference, steady and bright, keeps my circuits running just right.
Stories
Imagine a data center where voltage references maintain smooth operations, ensuring servers run correctly without interruptions.
Memory Tools
A memory aid to remember voltage reference requirements: 'S-A-N-N' stands for Stability, Accuracy, Low Power, and Low Noise.
Acronyms
Use the acronym S.A.L.N. to recall Stability, Accuracy, Low power consumption, and Low noise features.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Voltage Reference
A component in analog circuits that provides a stable and accurate output voltage.
- Stability
The ability of a voltage reference to maintain its output over time and under varying conditions.
- Accuracy
The degree to which the output voltage corresponds to the intended value.
- Power Consumption
The amount of power a voltage reference utilizes, which is crucial in battery-powered applications.
- Noise
Unwanted electrical signals that can distort the intended output signal in a circuit.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
