Zener Diode Voltage Reference
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Zener Diodes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're going to delve into Zener diodes, specifically how they serve as voltage references. Can anyone tell me what happens when a Zener diode is reverse-biased?

It conducts current only in reverse breakdown, right?

Exactly! In reverse breakdown, it maintains a constant voltage. This is key for use in voltage reference circuits. Now, why do you think we might choose a Zener diode over other options?

Because it's simple to implement!

Right, the simplicity of design makes it appealing. But what about its limitations?

I know it has a large temperature coefficient, which affects stability.

Exactly! A high temperature coefficient can lead to variability in the output voltage with temperature changes. Let's remember that with the acronym *STABLE* — Simplicity, Temperature coefficient, And Limited effectiveness.

That helps! So we need to be cautious when using them in sensitive applications?

Precisely! Let’s summarize: Zener diodes provide a simple solution for voltage references but require careful handling due to temperature sensitivity.
Operation of Zener Diodes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss how Zener diodes actually maintain their voltage. Can anyone remind us about the operational region they function in?

The reverse breakdown region!

Exactly! In this region, the Zener voltage remains relatively constant regardless of changes in current. Can anyone explain why that’s important?

Because it keeps the reference voltage stable, even if the circuit conditions change!

Good observation. Now, let’s apply this knowledge. If a circuit requires a reference voltage of 5V, how would a Zener diode be utilized?

We would select a Zener diode rated for 5V and connect it in reverse bias!

Great! And what do we remember regarding load current?

The Zener operates best under a stable current range, right?

Exactly! Now, in summary, a Zener diode provides stable voltage in reverse breakdown, which is crucial for reliable voltage reference applications.
Limitations of Zener Diodes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What are some limitations we might encounter when using Zener diodes?

Temperature stability is a big issue.

That's right! Their large temperature coefficient makes them less stable than alternatives. What applications might struggle with this?

I think applications that require high precision, like ADCs?

Correct! High-precision applications often need tighter voltage regulation. What alternatives might we consider?

Bandgap references might be better for temperature stability!

Great suggestion! Let's remember the *STABLE* acronym again to evaluate our options. Finally, let’s summarize: Zener diodes offer simplicity but require caution in precision applications because of their temperature sensitivity.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Zener diodes are utilized in voltage reference applications due to their stable voltage drop across a variety of current conditions. While they offer a simple solution, their large temperature coefficient leads to stability issues, necessitating careful consideration in circuit design.
Detailed
Zener Diode Voltage Reference
The Zener diode operates effectively in voltage reference circuits primarily due to its characteristic of producing a stable voltage drop when reverse-biased, particularly in the breakdown region. This stability is quite advantageous across varying current and voltage conditions. However, despite its simplicity in implementation, the Zener diode exhibits substantial temperature coefficients which can result in poor temperature stability. In practical applications, the temperature sensitivity of the Zener diode necessitates careful design measures to ensure it operates reliably, particularly in precision circuits where accurate voltage levels are critical.
Youtube Videos
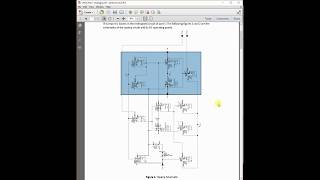

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Operation of the Zener Diode
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Zener diode operates in the reverse breakdown region, where the voltage across the diode remains nearly constant despite variations in current.
Detailed Explanation
A Zener diode is designed to allow current to flow in the reverse direction once the voltage reaches a specified breakdown threshold. Unlike regular diodes, which are designed to block reverse current, Zener diodes are used to regulate voltage. In this reverse breakdown region, despite changes in current flowing through it, the voltage across the Zener diode remains stable and almost constant, which is crucial for providing a reliable voltage reference in circuits.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Zener diode like a water dam. Once the water level (voltage) reaches a certain point (the Zener voltage), the dam can let water (current) flow over it without significantly changing the height of the water behind it. This allows the system to maintain a consistent level of water (voltage), no matter how much rain (current) falls.
Advantages of Zener Diode
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Zener diodes are easy to implement and offer a simple voltage reference solution.
Detailed Explanation
One of the main advantages of using Zener diodes in voltage reference circuits is their simplicity. They can be added to a circuit with minimal components, making them a cost-effective solution for providing a stable reference voltage. Additionally, because they are common components in electronics, they are readily available and easy to work with, making them ideal for many applications.
Examples & Analogies
Using a Zener diode is like choosing a simple tool for a job; a basic screwdriver can do the job effectively without needing the complexity of a power drill. Similarly, Zener diodes perform their function well without adding extra complications to the circuit.
Limitations of Zener Diode
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The temperature coefficient of the Zener diode is usually quite large, which leads to poor temperature stability.
Detailed Explanation
One significant limitation of Zener diodes as voltage references is their temperature coefficient, which describes how the voltage across the diode changes with temperature. As temperature increases, the Zener voltage may vary, resulting in a less stable reference voltage. This sensitivity to temperature can be problematic in applications where voltage stability is critical, making it necessary to consider additional compensation techniques to mitigate this issue.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a rubber band that expands and contracts with temperature; just as the rubber band does not hold its shape in the heat, a Zener diode may not maintain its voltage reference across different temperatures. This behavior makes designers think carefully about where and how to use Zener diodes.
Key Concepts
-
Zener Diode: A semiconductor device used as a voltage reference which maintains a stable voltage in reverse bias.
-
Reverse Breakdown: The region in which a Zener diode conducts with a nearly constant voltage, essential for voltage reference applications.
-
Temperature Coefficient: An important consideration that indicates how much the Zener diode's output voltage varies with temperature.
Examples & Applications
In a temperature-sensitive application like an ADC, a Zener diode may not be appropriate due to its poor temperature stability.
To implement a 5V reference in a circuit, a Zener diode rated for 5V can be placed across the power supply in reverse bias.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Zener diodes are quite nifty, they hold their voltage when currents shift-y.
Stories
Imagine a Zener diode as a floor guard at a party, keeping the voltage at a steady level even as guests (current) come and go. Just like at a party, too many guests (too much current) might cause problems!
Memory Tools
Think of ZENT for Zener's key traits: Z = Zero feedback needed, E = Easy implementation, N = Needs careful temperature consideration, T = Tolerates specific ratings.
Acronyms
Remember *VCT* for Zener
= Voltage stability
= Current stability
= Temperature coefficient.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Zener Diode
A type of diode that allows current to flow in the reverse direction when a specific reverse voltage is reached, maintaining a stable voltage drop.
- Reverse Breakdown Region
The operational region where a Zener diode conducts in the reverse direction, characterized by a constant voltage output.
- Temperature Coefficient
A measure of how much a component's output changes with temperature; significant in determining stability.
- Voltage Reference
A stable voltage signal used as a benchmark for the voltage levels in an electric circuit.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
