Challenges in Mixed-Signal CMOS Circuit Design
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Noise and Interference
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re diving into the challenges of noise and interference in mixed-signal designs. Can anyone tell me why noise is particularly problematic in these systems?

Because digital circuits can create a lot of switching noise?

Exactly! The high-speed switching of digital transistors can lead to electromagnetic interference that affects the performance of analog components. So, what strategies can we employ to mitigate this noise?

We could use shielding and ground planes?

Correct! Shielding helps isolate the analog components from digital noise sources. Plus, we can implement decoupling capacitors to filter out high-frequency noise. Can anyone explain how these capacitors work?

Decoupling capacitors store energy and can quickly discharge when there's a sudden demand, smoothing out voltage fluctuations?

Yes! Remember, we need to keep our analog signals clean for best performance. Let’s summarize: noise due to digital switching can be mitigated with shielding and decoupling strategies.
Power Supply Noise
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss power supply noise. Why do fluctuations in power supply matter for mixed-signal systems?

They can distort the analog signals and lead to errors in the digital circuits.

Exactly! It’s essential to have clean voltage delivered to both analog and digital circuits. What can we do to isolate the power supply for these two sections?

Using separate power rails for analog and digital sections should help.

That's right! This isolation reduces the impact of switching noise from digital circuits on the analog path. Does anyone have an example of a design technique that helps achieve this?

Implementing power domain isolation could work?

Absolutely! This design consideration is crucial for maintaining circuit integrity. Let’s summarize: Keeping power supplies clean is key to a successful mixed-signal design.
Layout and Parasitics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s discuss layout and parasitics. Why is the layout important in mixed-signal circuits?

If the layout is not done carefully, digital signals can interfere with the analog circuits.

That’s crucial! Placement affects performance significantly. What type of issues are we concerned about regarding parasitics?

Parasitic capacitance and inductance can delay signals and affect their integrity.

Exactly! They can change how signals behave, so proper routing and shielding must be part of the design process. Let's remember to keep analog and digital pathways distinct for optimal performance.
Cross-Talk
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s address cross-talk between analog and digital circuits. What does this term mean?

It’s the unwanted interaction between analog and digital signals.

Exactly! Cross-talk can degrade signal quality. What methods can we use to minimize this effect?

We could separate the analog and digital sections on the chip.

Correct! Keeping them physically apart is essential, as is using guard rings and shielding. Who can give a reason why these techniques are effective?

They create a buffer that prevents interference from digital to analog circuits.

Exactly! Summarizing, preventing cross-talk is crucial for the reliability of mixed-signal systems. Good job, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section elaborates on challenges in mixed-signal CMOS circuit design, focusing on noise and interference, power supply noise, layout and parasitics, and the cross-talk that can occur between analog and digital circuits. Strategies for mitigating these challenges are also discussed.
Detailed
Challenges in Mixed-Signal CMOS Circuit Design
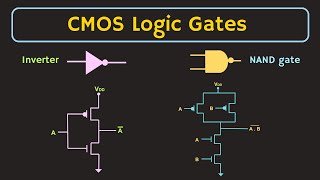
Mixed-signal CMOS circuit design presents unique challenges primarily due to the integration of both analog and digital circuits on a single chip. Key challenges identified include:
- Noise and Interference: Digital circuits are subject to high-speed switching, inducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ground bounce that can adversely affect sensitive analog circuit performance. To address these issues, the use of shielding, ground planes, and isolated power supplies are recommended, as well as the integration of decoupling capacitors to filter out unwanted high-frequency noise.
- Power Supply Noise: Fluctuations in power supply can distort analog signals and lead to digital errors. Implementing low-noise power supplies and utilizing separate power rails can minimize the adverse effects of digital switching noise on analog sections of mixed-signal systems.
- Layout and Parasitics: The physical layout of mixed-signal circuits plays a critical role in performance. Ensuring that analog and digital components are appropriately placed to prevent interference is vital. Parasitic capacitance and inductance effects should also be considered during design, necessitating careful routing and shielding.
- Cross-Talk: Interaction between analog and digital signals within the same chip can lead to degradation in performance. Solutions include keeping the two sections physically distinct and employing isolation techniques like guard rings and effective shielding strategies.
By addressing these challenges through careful design and layout techniques, engineers can develop more robust mixed-signal CMOS circuits that function optimally in various applications.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Noise and Interference
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Digital circuits can generate significant switching noise that may affect analog circuits. This noise is due to the high-speed switching of digital transistors, which can cause electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ground bounce.
● Mitigation Strategies:
○ Use of shielding, ground planes, and isolated analog and digital power supplies to minimize noise coupling.
○ Decoupling capacitors to filter out high-frequency noise from the power supply.
Detailed Explanation
In mixed-signal designs, digital circuits can create noise because they switch on and off rapidly. This noise can disrupt the sensitive analog signals that are crucial for accurate performance. To combat this, engineers can use several techniques: shielding helps block noise, ground planes provide a stable reference point for signals, and isolation of power supplies helps prevent interference from digital circuits reaching the analog parts. Additionally, decoupling capacitors can be implemented to filter out any unwanted high-frequency noise in the power supply, ensuring cleaner power for the circuits.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a quiet concert that is interrupted by loud announcements from the venue. Just like the noise from announcements can disturb the music, digital noise disrupts the clarity of analog signals in circuits. Shielding and proper layout help ensure the music (analog signal) can be heard clearly, without distractions.
Power Supply Noise
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In mixed-signal systems, fluctuations in the power supply can cause both analog circuit distortion and digital errors. It is crucial to design low-noise power supplies that deliver clean voltage to both analog and digital sections of the circuit.
● Power Supply Isolation: Using separate power rails for analog and digital sections, or implementing power domain isolation to reduce the impact of digital switching noise.
Detailed Explanation
Power supply noise can lead to incorrect functioning in mixed-signal designs, as variations in voltage can distort signals. To prevent these disturbances, engineers often design power supplies that produce stable and clean voltage levels. Moreover, separating power supplies for the analog and digital sections can help prevent noise from affecting each part, much like keeping loud machinery away from a quiet workspace to maintain focus and productivity.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to work on a project in a library while construction work is happening next door. The noise from the construction can be distracting. Keeping the construction area separate from the library, just as we use separate power rails in circuits, would create a more peaceful environment for studying.
Layout and Parasitics
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The layout of mixed-signal circuits is a critical factor in determining their performance. The placement of analog and digital blocks on the chip must be carefully considered to prevent digital signals from interfering with analog circuits.
● Parasitic Effects: Parasitic capacitance and inductance due to interconnects can affect the performance of both analog and digital circuits. Proper routing and shielding are essential.
Detailed Explanation
How components are arranged on the chip (the layout) significantly impacts how well the circuit operates. Analog and digital parts need careful placement to minimize interference. Parasitic elements, like unintended capacitance or inductance from circuits’ connections, can introduce noise or signal delays. By effectively routing these signals and using shielding, engineers can ensure better performance of the circuit, similar to arranging furniture in a room to enhance the space's functionality and movement.
Examples & Analogies
Think about setting up a music studio in a room. If the instruments are too close to a noisy air conditioning unit, the quality of the recorded music can suffer. Layout in circuit design functions similarly; optimal arrangement ensures that signals flow smoothly and without unwelcome interference from other 'noisy' components.
Cross-Talk Between Analog and Digital Circuits
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In mixed-signal systems, cross-talk refers to the unwanted interaction between analog and digital signals, which can degrade the performance of both.
● Design Solutions:
○ Keep analog and digital sections physically separated on the chip.
○ Use guard rings and shielding techniques to isolate sensitive analog circuits from noisy digital circuits.
Detailed Explanation
Cross-talk occurs when signals from one part of a circuit interfere with signals from another part, especially between noisy digital signals and sensitive analog signals. To tackle this, designers can physically separate these circuits on the chip. Techniques like guard rings help create a buffer zone between them, much like having soundproof walls between rooms where different activities are happening.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a library where one side is quiet reading rooms and the other side has a loud group playing games. If the rooms are not soundproofed, the noise might disrupt readers. Similarly, cross-talk in circuits can disturb analog signals, hence the need for separation and protection of analog circuits from noisy digital components.
Key Concepts
-
Noise: Unwanted electrical signals that interfere with circuit performance and results from digital switching.
-
Power Supply Noise: Fluctuations in voltage that can lead to distortion in analog circuits and errors in digital circuits.
-
Layout and Parasitics: Effective layout reduces interference, while parasitics can negatively affect circuit performance.
-
Cross-Talk: Unwanted signal coupling between analog and digital parts of a circuit that can degrade performance.
Examples & Applications
In wireless communication chips, shielding is used to protect analog RF signals from digital noise.
In audio processing devices, separate ground planes are effectively used to reduce cross-talk from digital control signals.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When circuits mix, keep noise at bay, with isolation and shields, every day!
Stories
Imagine an orchestra where digital musicians are too loud, causing the analog strings to sound off-key. The conductor's job is to keep them apart, ensuring a beautiful harmony is achieved while playing together.
Memory Tools
N-P-C-C for challenges: Noise, Power supply issues, Cross-talk, and Layout concerns.
Acronyms
PEACE - Place, Eliminate interference, Arrange for efficiency, Control parasitics, Ensure shielding.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Noise
Unwanted electrical signals that interfere with the proper functioning of analog circuits in mixed-signal systems.
- Interference
Disturbances in signal pathways, often due to electromagnetic sources, affecting circuit performance.
- Power Supply Fluctuations
Variations in voltage supplied to circuits which can cause distortion and errors.
- Parasitics
Additional capacitance and inductance introduced by circuit layout which can affect performance.
- CrossTalk
Unwanted coupling of signals between different parts of the circuit, particularly between analog and digital signals.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
