Cross-Talk Between Analog and Digital Circuits
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Cross-Talk
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about cross-talk in mixed-signal circuits. Can anyone tell me what cross-talk means in this context?

Isn't it when signals from one circuit affect another circuit?

That's correct, Student_1! Cross-talk occurs when interference from digital signals negatively impacts analog circuit performance. Why do you think this is an important issue in circuit design?

Because it can make the analog part less accurate, right?

Exactly! Cross-talk can degrade the reliability and accuracy of mixed-signal systems, which is critical in applications like ADCs and IoT devices.
Effects of Cross-Talk
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand what cross-talk is, can anyone describe some potential effects it might have on a circuit?

It could cause noise, right? Making the signals less clear?

Absolutely! Noise can mask the desired signals, leading to errors in signal interpretation and processing. Any other effects?

Maybe it would cause the whole system to malfunction?

Exactly, Student_4! Severe cross-talk can lead to system failures, especially in real-time processing applications.
Design Solutions for Mitigating Cross-Talk
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss how we can mitigate cross-talk. What’s one strategy designers can use?

I think keeping the analog and digital sections separate would help.

Right! Physical separation helps reduce the coupling of noise. What’s another method?

Building guard rings around the analog circuits?

Exactly! Guard rings help minimize interference from digital circuits. Can anyone think of a third approach?

What about using shielding?

Great point, Student_3! Shielding can block electromagnetic interference, further protecting sensitive sections of the circuit.
Recap and Clarification
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's recap what we learned about cross-talk. Who can summarize the main points?

Cross-talk is the unwanted interaction between signals that can affect performance, and we can reduce it through separation, guard rings, and shielding.

Great summary, Student_4! Does anyone have questions about cross-talk or the techniques we've discussed?

How do we decide the right amount of separation?

Excellent question! It often depends on the frequencies involved and the specific design requirements. Balancing layout and functionality is key.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Cross-talk refers to the undesired interactions between analog and digital signals in mixed-signal circuits. The section details design solutions to mitigate these impacts, such as physical separation and shielding techniques, ensuring optimal performance in integrated systems.
Detailed
Cross-Talk Between Analog and Digital Circuits
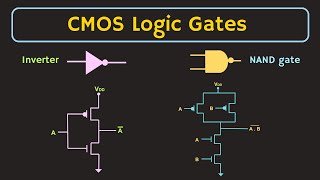
In mixed-signal systems, cross-talk refers to the unwanted interaction between analog and digital signals which can negatively impact their performance. As analog circuits are sensitive to noise, any interference from digital circuits can lead to functional degradation, affecting the overall system reliability and accuracy.
Design Solutions for Cross-Talk Issues
- Separation: Keeping analog and digital sections physically apart on the chip is a primary strategy to reduce cross-talk. This minimizes the path through which noise can couple from one domain to another.
- Guard Rings: Implementing guard rings around sensitive analog circuitry helps to absorb and divert noise from digital circuits, acting as a buffer against interference.
- Shielding Techniques: Effective shielding can significantly reduce the impact of noise from digital circuits by enclosing sensitive analog paths in conductive materials that block electromagnetic interference.
Significance: Understanding and addressing cross-talk is crucial in mixed-signal design, particularly for high-performance applications such as data converters and wireless communication systems.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Cross-Talk
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In mixed-signal systems, cross-talk refers to the unwanted interaction between analog and digital signals, which can degrade the performance of both.
Detailed Explanation
Cross-talk occurs when signals from one circuit (analog or digital) begin to interfere with signals from another circuit. This can happen due to physical proximity on a chip, where the electric fields or electromagnetic waves from one circuit inadvertently couple into another. As a consequence, the performance of either the analog or the digital circuit can suffer, leading to possible errors or degraded signal integrity.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to listen to a conversation while other conversations are happening loudly around you. The noise from other conversations can distract you or make it hard for you to understand what is being said in your conversation. Similarly, in electronic circuits, if the digital signals create noise, it can interfere with the analog signals, making the desired information difficult to extract.
Design Solutions for Cross-Talk
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Design Solutions:
- Keep analog and digital sections physically separated on the chip.
- Use guard rings and shielding techniques to isolate sensitive analog circuits from noisy digital circuits.
Detailed Explanation
To mitigate cross-talk, designers implement several strategies. Keeping analog and digital components physically separated on the same chip reduces the chances of signals interfering with each other. Additionally, guard rings, which are conductive structures surrounding sensitive analog circuits, help create barriers against unwanted interference. Shielding techniques involve placing barriers or using materials that block electromagnetic interference between circuits, thereby protecting weak analog signals from the noise generated by stronger digital signals.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a library where quiet areas are separated from the noisy sections. If people are talking loudly near the bookshelves, those areas should have soundproof walls or barriers to allow readers to concentrate better. Likewise, in circuits, keeping digital components away and using guard rings is like putting up sound barriers to ensure that the delicate analog signals can function without disturbance.
Key Concepts
-
Cross-Talk: Unwanted interference between analog and digital signals.
-
Guard Rings: Structures to minimize interference in circuits.
-
Shielding: Using conductive materials to block noise.
Examples & Applications
An example of cross-talk could be when a digital signal fluctuates, causing errors in an analog voltage measurement within the same chip.
Implementing guard rings in an analog section of a mixed-signal chip can improve performance by reducing noise from nearby digital circuitry.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When signals clash and inputs stray, cross-talk leads our paths astray.
Stories
Imagine a quiet library (analog circuit), where loud students (digital signals) disturb the peace. To keep the library serene, barriers and rules (guard rings and shielding) are established to keep distractions at bay.
Memory Tools
Remember 'SPG' - Shielding, Physical separation, Guard Rings - techniques to combat cross-talk.
Acronyms
CROSSTALK
'Circuits Reducing Overlap Signals Through Accurate Layout Knowledge.'
Flash Cards
Glossary
- CrossTalk
Unwanted interaction between analog and digital signals in mixed-signal circuits.
- Guard Ring
A protective circuit or area designed to minimize interference from surrounding noise.
- Shielding
The use of conductive materials to block electromagnetic interference.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
