Layout and Parasitics
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Importance of Layout in Mixed-Signal Circuits
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about why layout is critical in mixed-signal circuits. The arrangement of analog and digital blocks directly affects how well they function together. Can anyone tell me why their placement matters?

I think it’s because the digital parts can generate noise that may interfere with the analog parts.

Exactly! This noise coupling can degrade performance. So, a good layout minimizes interference. Can anyone think of a way to achieve this?

By physically separating the blocks?

Right! Separation helps, along with employing shielding techniques. Remember, 'LAYOUT' stands for Layout And Yield Optimal Techniques—use this mnemonic to remember our focus!

That’s helpful! What about the effects of parasitics?

Great question! Parasitic capacitance and inductance can delay signals or create unwanted interactions. Let's explore how we can mitigate that.

Is routing part of that solution?

Yes! Proper routing is key. To summarize, effective layout and routing reduce interference and improve performance in mixed-signal circuits.
Understanding Parasitics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into parasitics. Parasitic capacitance occurs because of the physical proximity of conductors. Why is this an issue?

It can cause delays in the signals, right?

Correct! Also, parasitic inductance can create voltage spikes. What's a method we can use to reduce these parasitic effects?

We can use shielding and proper layout techniques.

Exactly! You can also think of 'SHIELD' as an acronym to remember that shielding, especially for sensitive circuits, is crucial for protecting against interference.

Are there design metrics to consider for this layout?

Yes, measuring propagation delay and ensuring signal integrity are important metrics. In summary, understanding parasitics allows us to design better circuits.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the importance of layout in mixed-signal circuit design, highlighting how the placement of analog and digital blocks affects circuit performance. Parasitic capacitance and inductance resulting from interconnects are also addressed as critical factors requiring effective routing and shielding.
Detailed
Layout and Parasitics in Mixed-Signal Design
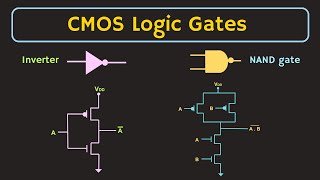
In mixed-signal CMOS circuit design, the physical layout of components significantly influences circuit performance. Proper placement of analog and digital blocks is vital to ensure minimal interference between them. Parasitic effects, such as parasitic capacitance and inductance generated by interconnects, can introduce delays and distortions in signal transmission. These challenges make careful routing and shielding techniques essential for maintaining the integrity of both the analog and digital systems within a chip.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Importance of Circuit Layout
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The layout of mixed-signal circuits is a critical factor in determining their performance. The placement of analog and digital blocks on the chip must be carefully considered to prevent digital signals from interfering with analog circuits.
Detailed Explanation
The layout of mixed-signal circuits refers to how the various components (both analog and digital) are positioned on an integrated circuit (IC). This arrangement is very important because if the digital components generate noise, it can disturb the sensitive analog parts. Therefore, careful planning is necessary to ensure that analog and digital blocks are placed in a manner that minimizes this interference.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a busy restaurant where some tables are next to the kitchen (which is noisy) and some are away from it. If patrons want a quiet dining experience, they should avoid the tables near the kitchen. Similarly, in circuit design, we want to keep sensitive sections (like analog circuits) far from noisy sections (like digital circuits) to ensure optimal performance.
Parasitic Effects
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Parasitic effects: Parasitic capacitance and inductance due to interconnects can affect the performance of both analog and digital circuits. Proper routing and shielding are essential.
Detailed Explanation
Parasitic effects refer to unintended capacitance and inductance that occur within the interconnections of a circuit. These effects can significantly impact circuit performance by introducing delays and degrading signal integrity. To mitigate these effects, engineers must implement effective routing strategies and use shielding techniques to isolate sensitive signals from noise and interference.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a game of telephone where the message gets distorted depending on how intertwined the strings connecting each participant are. If the strings overlap too much, it becomes hard for each person to hear the message clearly. In the same way, in circuit design, if the paths for electrical signals are not well organized (or if they're tangled up with other signals), it can lead to distorted signals, making the performance of the circuit suffer.
Key Concepts
-
Layout: The strategic arrangement of circuit components to minimize interference.
-
Parasitics: Unintended capacitance and inductance arising from circuit design that can distort signals.
-
Shielding: Protective measures taken to reduce noise impacts on sensitive circuits.
Examples & Applications
A mixed-signal chip where the digital section is isolated from the analog section using guard rings.
Using a ground plane in a circuit layout to shield against external electromagnetic interferences.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In layout we trust, to keep signals just, without noise and fuss!
Stories
Imagine two friends, Analog and Digital, living in a house. They stay in separate rooms to avoid constant bickering. Their layout keeps the peace, allowing them to function harmoniously.
Memory Tools
'LAYOUT': Layout Aids in Yielding Optimal Utility.
Acronyms
'SHIELD'
Securing High Integrity in Encoder and Layout Design.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Layout
The arrangement of components in a circuit that influences performance and interference.
- Parasitics
Unwanted capacitance and inductance effects that arise from the physical layout of circuit components.
- Shielding
Techniques used to prevent interference from external noise sources, often involving surrounding sensitive circuits with conductive material.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
