Power Supply Noise
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Power Supply Noise
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’ll discuss power supply noise, an important factor in mixed-signal systems. Can anyone tell me what they think power supply noise is?

Is it just any fluctuations in the voltage?

Exactly! Power supply noise refers to any variation in voltage from the power source that can adversely impact the performance of circuits.

How does that affect analog signals, though?

Great question! Noise can distort analog signals, leading to inaccuracies in output. This is crucial for applications like audio processing.

And what about digital systems?

Digital circuits can also suffer, as noise may cause errors in computation. This highlights the need for low-noise power supplies.

So, how do we design low-noise power supplies?

We’ll cover that shortly. Remember, isolation methods like separate rails can significantly help. Let's summarize: power supply noise can affect both analog and digital circuits, and understanding this is vital for effective circuit design.
Isolation Techniques for Power Supplies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we've introduced power supply noise, let's explore isolation techniques. Why do you think we need to isolate power supplies?

To prevent noise from one area affecting another?

Exactly! By isolating the power supplies for analog and digital sections, we can reduce the interference caused by digital switching noise.

Can you give us some examples of isolation methods?

Common methods include using separate power rails, guard rings to shield sensitive areas, and ground planes that provide a stable reference.

How does using separate power rails really help?

Using separate rails ensures that fluctuations in the digital power supply do not directly interfere with the analog section. This is crucial for maintaining signal integrity.

Can we measure the impact of this isolation?

Definitely! We can test circuit performance before and after implementing isolation to see improvements in signal clarity. To wrap up, power supply noise isolation is key to reliable mixed-signal circuit design.
Practical Applications and Challenges
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's now talk about how power supply noise affects practical applications. How do you think this issue manifests in consumer electronics?

Maybe in audio devices?

Absolutely! In devices like smartphones, power supply noise can lead to poor audio quality. We've seen several instances where engineers have to address these issues.

What strategies do companies use to tackle this?

They often use sophisticated power management ICs that filter out noise, combined with layout strategies to ensure separation of sensitive components.

Should there be a balance between performance and noise suppression?

Yes! Different applications require different balances. High-performance applications may necessitate more stringent noise control measures.

So, designing circuits is about trade-offs?

Correct! Engineers must weigh noise implications against performance needs. In summary, understanding and mitigating power supply noise is crucial in modern mixed-signal designs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Power supply noise is a significant challenge in mixed-signal systems as fluctuations in power can distort analog signals and cause errors in digital applications. The design of low-noise power supplies and isolation techniques is crucial to maintain system integrity and ensure noise-free operation of both analog and digital circuits.
Detailed
Power Supply Noise
Power supply noise refers to the fluctuations in the voltage supplied to electronic circuits, which can lead to distortion in analog signals and errors in digital computations. In mixed-signal systems, where both analog and digital circuits coexist, the interference caused by power supply noise is particularly detrimental.
Key Points:
- Impact on Performance: Variations in the power supply can introduce noise that adversely affects the performance of analog circuits, leading to distortion, and can cause digital circuits to malfunction or produce incorrect data.
- Design Considerations: It's essential to design low-noise power supplies that can provide stability and cleanliness to both analog and digital sections of a circuit. This may involve using separate power rails or implementing isolation strategies to shield sensitive components from digital switching noise.
- Power Supply Isolation: Employing distinct power supply domains helps mitigate the influence of digital noise on analog functions, preserving the integrity of both types of circuits and improving overall system reliability.
Creating effective mixed-signal systems demands careful attention to power supply design to ensure high fidelity and performance across all operational requirements.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Effects of Power Supply Fluctuations
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In mixed-signal systems, fluctuations in the power supply can cause both analog circuit distortion and digital errors.
Detailed Explanation
Power supply fluctuations can lead to unwanted changes in the voltage levels supplied to the circuits. In analog circuits, this may manifest as distortion in the output signal, meaning the signal does not accurately represent the input. Conversely, in digital circuits, these fluctuations can produce errors, where the circuit fails to read or interpret the digital signals correctly. Thus, maintaining a stable power supply is vital for the proper operation of both types of circuits.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to listen to music on a radio while someone is continuously turning the volume knob up and down erratically. Just like the random changes in volume make it hard to follow the song, fluctuations in voltage make it challenging for analog circuits to maintain clear signals and can disrupt digital circuits' ability to function correctly.
Importance of Low-Noise Power Supplies
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It is crucial to design low-noise power supplies that deliver clean voltage to both analog and digital sections of the circuit.
Detailed Explanation
A clean power supply ensures that the voltage levels remain steady and free from noise or disturbance as they feed into the circuits. Low-noise supplies prevent external disturbances from coupling noise into sensitive components, thus preserving the integrity of the signal. This design consideration is critical in mixed-signal systems, where both analog and digital components need stable voltage to operate correctly without interference.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a power supply like the water supply to a house. If the pipes are dirty or too narrow, the water may come in spurts or with sediments, making it impossible to fill a glass smoothly. Similarly, a clean and steady power supply allows circuits to operate effectively, just like clean water allows your home to function properly.
Power Supply Isolation Techniques
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
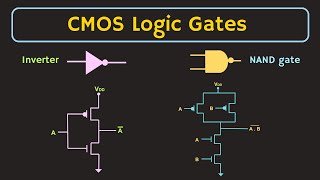
Power Supply Isolation: Using separate power rails for analog and digital sections, or implementing power domain isolation to reduce the impact of digital switching noise.
Detailed Explanation
To minimize the interference caused by power supply noise in mixed-signal systems, designers often create separate power rails for analog and digital circuits. This means that the analog section receives its own dedicated power supply, separate from the digital section, minimizing the noise created by digital signals during switching. Additionally, implementing power domain isolation further enhances performance by ensuring that the noisy operations of digital parts do not affect the sensitive analog components.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a busy highway where two lanes are going in opposite directions. If the lanes are well separated, the traffic in one lane doesn’t interfere with the other. Similarly, using separate power rails for analog and digital circuits prevents digital noise from spilling over and affecting the analog performance.
Key Concepts
-
Power Supply Noise: Refers to voltage fluctuations affecting circuit performance.
-
Power Supply Isolation: Techniques used to minimize interference between analog and digital circuits.
-
Ground Plane: A design feature that helps stabilize voltage and reduce noise.
-
Guard Ring: A method for shielding sensitive circuit areas from noise.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: In audio applications, power supply noise can produce unwanted hiss or distortion, impacting user experience.
Example 2: In wireless communication devices, fluctuations in supply voltage can disrupt signal processing, leading to data errors.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Keep your power supply clean, and signals stay pristine.
Stories
Imagine a musician on stage. If the speakers buzz due to faulty power supply noise, the music is distorted, ruining the show. Just as a musician needs a clear sound, circuits need clean power.
Memory Tools
I-S-G (Isolation, Shielding, Guard Rings) – remember these methods to minimize noise.
Acronyms
PIN (Power Isolation Needed) - Use this to remember that power supply isolation is crucial.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Power Supply Noise
Fluctuations in voltage supplied to circuitry that can distort analog signals and create errors in digital circuits.
- Isolation Techniques
Methods used to prevent noise caused by one circuit section from affecting another, such as separate power rails.
- Ground Plane
A conductive plane in a circuit design that helps provide a stable reference voltage and reduces noise.
- Guard Ring
A physical barrier used in layout design to prevent noise coupling between circuit sections.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
