Integrated Optoelectronic Devices
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Integrated Optoelectronic Devices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore integrated optoelectronic devices, which are essential for combining various optical components into single chips. Can anyone tell me why this integration is important?

Is it because it makes things smaller and faster?

Exactly! By miniaturizing components, we can facilitate high-speed data transfer while maintaining performance. Let’s first discuss Photonic Integrated Circuits or PICs.

What exactly is a PIC?

A PIC integrates lasers, modulators, and detectors into a single chip, enhancing functionality. Think of it as putting multiple components into a single package to streamline performance.

How does that affect technology?

This integration is crucial in communication technology. For instance, by using InP or GaAs platforms, we can transfer data at incredibly fast speeds. Remember, PICs allow for miniaturization, which is the 'M' in our mnemonic 'FAST': Functionality, Amalgamated, Small, and Transfer.

Got it! Can we move to the next topic?
LED on Silicon / Heterogeneous Integration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss the integration of LEDs on silicon substrates. Why do you think this method is gaining popularity?

I think it might lower production costs.

Absolutely! This technique allows for scalability and cost-effectiveness. Using Gallium Nitride LEDs on silicon also boosts compatibility with existing technology. Can anyone think of applications for this?

Smart lighting solutions and displays!

Correct! Remember the acronym 'SIMPLE': Scalable, Integrated, Miniaturized, and Performance-oriented Lighting and Electronics. This helps in remembering the benefits of such integration.

Could this technology impact the environment positively as well?

Yes, integrating LEDs effectively can result in energy-efficient systems, contributing to greener technology. Always consider the broader implications of technological advancements.

This is exciting! How do we apply these concepts?
Applications of Integrated Optoelectronic Devices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up our session, let's discuss the significance of integrated optoelectronic devices. What applications come to mind?

Communication networks!

And consumer electronics.

Yes! Integrated devices are critical for developing advanced systems in both sectors. It promotes compact designs while improving performance. Remember, these innovations drive us toward more efficient and smarter technologies.

This information seems quite applicable in our lives!

I’d love to see how they work in real-world scenarios!

Great enthusiasm! Keep researching real-world examples that leverage these technologies, as understanding practical applications solidifies your knowledge!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
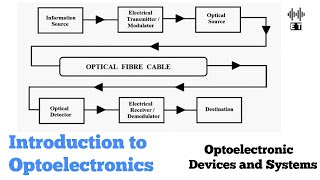
Integrated optoelectronic devices combine various optical components on a single chip, enhancing efficiency and functionality. This section highlights the role of photonic integrated circuits and the integration of LEDs onto silicon platforms, showcasing their applications in modern technology.
Detailed
Integrated Optoelectronic Devices
In this section, we delve into integrated optoelectronic devices, focusing primarily on two major concepts: Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs) and the integration of LEDs on silicon substrates.
Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs)
PICs combine lasers, modulators, and detectors into a single chip, leveraging materials like Indium Phosphide (InP) or Gallium Arsenide (GaAs). This integration is crucial for miniaturizing optical systems and enabling high-speed optical data transfer. The result is a more compact and efficient design that is pivotal for advancing communication technologies.
LED on Silicon / Heterogeneous Integration
The use of Gallium Nitride (GaN) LEDs integrated on silicon substrates presents an innovative approach to manufacturing. This strategy allows for cost-effective, scalable production methods suitable for a range of applications, including smart lighting solutions and advanced display panels. The ability to produce LEDs on silicon not only reduces costs but also enhances the compatibility of optoelectronic devices with existing electronic circuits.
In summary, integrated optoelectronic devices are a crucial step toward realizing more compact, versatile, and efficient systems in various fields, from communication to consumer electronics.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs)
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs)
● Combine lasers, modulators, and detectors on a single chip using InP or GaAs platforms
● Enable miniaturized, high-speed optical data transfer
Detailed Explanation
Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs) are advanced systems that integrate multiple optical components, such as lasers, modulators, and detectors, onto a single semiconductor chip. This integration is typically performed using materials like Indium Phosphide (InP) or Gallium Arsenide (GaAs). By employing PICs, we can achieve highly miniaturized systems that facilitate fast optical data transfer, making them essential for modern communication networks. The miniaturization leads to reduced size and weight of devices, and enhances their performance due to shorter distances for signal transmission.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a PIC like a multi-tool gadget. Just like a multi-tool combines a knife, screwdriver, and scissor into one compact gadget which is easier to carry around and use, a PIC combines several optical components into a single chip, making it more efficient for data transfer in high-speed communication, such as the internet.
LED on Silicon / Heterogeneous Integration
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● LED on Silicon / Heterogeneous Integration
● GaN LEDs integrated on silicon substrate for low-cost, scalable production
● Used in smart lighting and display panels
Detailed Explanation
Heterogeneous integration involves combining different semiconductor materials to develop advanced devices. In this context, Gallium Nitride (GaN) Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are integrated onto a silicon substrate. This approach allows for cost-effective and scalable production of LEDs. The use of silicon, a more common and cheaper material, helps reduce manufacturing costs. This integration is particularly important in the development of smart lighting solutions and modern display panels, making them more accessible and efficient for wider market applications.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine baking a cake. If you use high-quality icing (like GaN) on a regular cake base (like silicon), you can make a stunning and delicious cake that is also affordable. This approach helps create smart lighting systems and flashy LED displays without breaking the bank, making them more popular for everyday use.
Key Concepts
-
Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs): Integrate lasers, modulators, and detectors for compact optical systems.
-
LED on Silicon: Utilizing silicon substrates to produce cost-effective and scalable LEDs.
-
Heterogeneous Integration: Combining different materials to improve device performance.
Examples & Applications
Photonic Integrated Circuits are used in high-speed communication systems to transmit data efficiently.
LEDs on Silicon are commonly found in smart lighting applications and modern display technologies.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In circuits where photons play, integrated chips save the day!
Stories
Imagine a factory where light components work closely together, like best friends in a play to create splendid light displays. They have combined into a single chip, making everything efficient and harmonious. This is how integrated optoelectronic devices work!
Memory Tools
Remember 'PIC as the Superior GIT': Photonic Integrated Circuits lead to Greater Integration Technology.
Acronyms
SIMPLE
Scalable
Integrated
Miniaturized
Performance-oriented Lighting and Electronics.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs)
A technology that integrates multiple optical components like lasers and detectors into a single chip for enhanced functionality.
- LED on Silicon
Integration of Gallium Nitride LEDs on silicon substrates for cost-effective and scalable manufacturing.
- Heterogeneous Integration
The integration of different materials or components in a single device to enhance performance.
- Gallium Nitride (GaN)
A semiconductor material used for LEDs and high-frequency applications.
- Indium Phosphide (InP)
A semiconductor material often used for photonic integrated circuits due to its favorable electronic and optical properties.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
