Introduction
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
What is Optoelectronics?
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome class! Today we dive into optoelectronics. Can anyone tell me what they think optoelectronics refers to?

Is it about how light interacts with electrical devices?

Exactly! Optoelectronics combines the physics of light and electronics. It's fascinating because it allows devices to emit or detect light.

So, what are some devices that use optoelectronics?

Great question! Devices like LEDs, laser diodes, and photodetectors rely on these principles. Remember—LEDs provide light, lasers produce focused beams, and photodetectors sense light. To remember this, think of 'LLP' for Light-LED, Laser, and Photo-detectors!
Importance of Compound Semiconductors
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss compound semiconductors. Why do you think they are preferred over silicon for light-based applications?

Do they have better light-emitting capabilities?

Yes! They have a direct bandgap that allows for efficient light emission. Can anyone explain the difference between direct and indirect bandgap?

Direct bandgap materials can emit light more effectively compared to indirect bandgap materials like silicon!

Spot on! This property is crucial for applications such as LEDs, making compound semiconductors essential in modern optoelectronic technology.
Applications of Optoelectronic Devices
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s wrap up our discussion by exploring where we find these devices. What are some applications of LEDs, lasers, and photodetectors?

LEDs are used in lighting and displays, right?

Correct! They revolutionized lighting with energy-efficient solutions. And what about lasers?

Lasers are used in communications and medical applications!

Exactly! As for photodetectors, any ideas?

They are crucial in sensing applications, like in cameras or optical receivers.

Well done! The integration of these devices across various sectors showcases the depth of optoelectronic applications in our daily lives.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section introduces optoelectronics, the vital role of compound semiconductors in creating devices like LEDs, laser diodes, and photodetectors, and emphasizes their importance in various applications, including communication and sensing.
Detailed
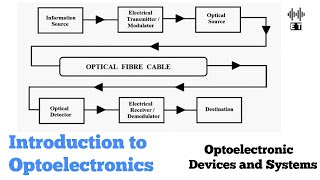
Introduction to Optoelectronics
Optoelectronics is a field that explores the interaction of light (photons) and electronics (electrons). This integration has led to the development of several high-tech devices that are crucial in modern technology. Compound semiconductors, which have direct bandgaps and tunable optical properties, play a significant role in this domain, making them particularly suitable for producing essential optoelectronic devices. Some of these devices include light-emitting diodes (LEDs), laser diodes, and photodetectors.
These devices are not just laboratory curiosities; they are integral to a myriad of real-world applications, enhancing aspects such as communications, decorative and functional lighting, display technologies, as well as advanced sensing mechanisms. The subsequent sections will delve deeper into the principles governing these optoelectronic devices and their significant roles in our daily lives.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Optoelectronics
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Optoelectronics involves the interaction of light and electronics.
Detailed Explanation
Optoelectronics is a field of technology that combines the principles of optics (the study of light) and electronics (the study of electrical circuits). This means it deals with devices that use light to perform electronic functions. For instance, devices like LEDs and laser diodes convert electrical energy into light.
Examples & Analogies
Think of optoelectronics like a bridge between two worlds: the world of light, which we can see and use, and the world of electronics, which controls how our devices operate. Just like how bridges connect two pieces of land, optoelectronic devices connect light to technology.
Compound Semiconductors
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Compound semiconductors, with their direct bandgap and tunable optical properties, are ideally suited for developing optoelectronic devices such as LEDs, laser diodes, and photodetectors.
Detailed Explanation
Compound semiconductors are materials made from two or more elements that exhibit specific electronic properties ideal for optoelectronic applications. Their direct bandgap allows them to emit and detect light efficiently when an electrical current passes through them. This means they can be used to make devices like LEDs, which emit light, or photodetectors, which detect light.
Examples & Analogies
Consider compound semiconductors like a special recipe used to cook a delicious dish. Just as a unique combination of ingredients can create a flavorful meal, combining different elements in these semiconductors creates materials that perform specific functions related to light.
Importance of Optoelectronic Devices
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These devices are integral to applications in communication, lighting, displays, and sensing.
Detailed Explanation
Optoelectronic devices play crucial roles in various applications. For instance, they are used in communication systems to transmit data through light signals, in lighting technology such as LEDs for illuminating spaces, in display technology for screens, and in sensors that detect environmental changes. Their versatility ensures that they are a key component of modern technology.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine how a Swiss Army knife has multiple tools for different tasks. Similarly, optoelectronic devices serve various purposes across different fields, making them essential in our technology-driven world.
Scope of the Chapter
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This chapter explores the working principles and real-world applications of major optoelectronic devices made using compound semiconductors.
Detailed Explanation
The chapter will delve into how various optoelectronic devices function and provide examples of their applications in real life. This will include an exploration of devices like LEDs, laser diodes, and photodetectors, discussing the science behind them and how they are used in everyday technology.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this chapter as a journey through an optoelectronics museum, where each exhibit showcases a different device. As you walk through, you’ll learn about how each device works and see real-world examples of how they're used in society.
Key Concepts
-
Optoelectronics: Integration of light and electronics.
-
Compound Semiconductors: Materials with favorable light-emission properties.
-
Direct Bandgap: Efficient photon emission property in materials.
-
LEDs: A type of light-emitting device.
-
Laser Diodes: Devices for producing coherent light.
-
Photodetectors: Sensors for detecting light intensity.
Examples & Applications
LEDs are widely used in general lighting and electronic displays, enhancing energy efficiency.
Laser diodes find application in fiber-optic communications, enabling high-speed data transfer.
Photodetectors are integral to camera systems and bar code scanners by measuring light levels efficiently.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Light in a diode, what a great sight! / Electronics work, shining so bright.
Stories
Once upon a time in a tech kingdom, light and electronics decided to team up, creating amazing devices that lit up the world.
Memory Tools
They Light up, Emit light, and Diode they are.
Acronyms
Use 'CLEVER' to recall Compound Semiconductors, Light, Emission, Very Efficient, and - it's Really essential!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Optoelectronics
The branch of technology that deals with the interaction of light and electronics.
- Compound Semiconductors
Materials made of two or more elements that have unique electronic and optical properties.
- Direct Bandgap
A property of semiconductors which allows electrons to recombine and emit photons efficiently.
- LED (Light Emitting Diode)
A semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it.
- Laser Diode
A semiconductor device that produces coherent light through stimulated emission.
- Photodetector
A device that detects and measures light intensity through photocurrent generation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
