Real-World Applications
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Communication Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss the role of lasers and photodiodes in communication systems. Can anyone tell me what these devices do in a fiber optic setup?

Are they responsible for sending and receiving signals?

Exactly! Lasers transmit data as light pulses through optical fibers, while photodiodes detect these light pulses at the receiving end. Remember the acronym 'LPS' for Laser-Pulse-Signal}

What makes these connections better than traditional cables?

Great question! Fiber optics can carry much more data at higher speeds and over longer distances compared to copper cables. Can anyone think of real-world examples of this?

I think data centers use them!

Correct! Data centers rely on this technology for high-speed connections. Remember, the efficiency of light is key!

In summary, lasers and photodiodes are essential in fiber optics, enabling high-speed data transmission in communication.
Consumer Electronics Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now shifting focus to consumer electronics, what devices can you think of that use LEDs or laser technology?

Televisions and smartphones?

Absolutely right! LED displays are now prevalent in TVs and smartphones. Can anyone explain how they contribute to improved visuals?

They provide brighter images and more energy-efficient lighting?

That's correct! Brighter and more efficient indeed. Let's remember 'LED' not just as a term but as 'Light Emitting Display' for better recall.

What about IR sensors? Where do they fit?

Great point! Infrared sensors in devices enhance user interaction through features like touchless controls. Summarizing, LEDs and lasers are pivotal in enhancing consumer technology.
Automotive Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Transitioning to automotive applications, what role do you think optoelectronic devices play in cars?

I think they help with visibility in headlights?

Right! GaN LEDs are now used in modern car headlights. Has anyone noticed how they perform differently from traditional bulbs?

They seem to shine brighter and last longer!

Exactly! They have longer lifespans and provide better illumination. Remember the phrase 'Safety through Light' as it sums up their function well.

What about sensors for parking?

Great insight! Infrared photodetectors in parking sensors enhance safety. To summarize, optoelectronic devices improve visibility and safety in the automotive sector significantly.
Healthcare Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Shifting focus to healthcare, how do you think lasers are used in medical settings?

For surgeries and procedures?

Correct! Lasers aid in precision surgeries. Can anyone tell me about another medical application like pulse oximeters?

They measure blood oxygen levels using light!

Exactly! Lasers help get a precise reading of oxygen levels in the blood. Remember 'POP' for Pulse Oximeter Precision!

What about imaging?

Great question! Medical imaging techniques also utilize lasers for clear imaging. Summarizing, lasers and photodetectors significantly enhance healthcare technology.
Industrial Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

For our last discussion, let’s examine the industrial applications. How are lasers utilized in industries?

In welding and cutting materials?

Correct! Lasers provide precise cutting and welding. What about photodiodes?

They are used in barcode scanners, right?

Exactly! They read barcodes quickly and accurately. Remember 'PQR' - Precision, Quick, Reliable for industrial applications!

Do they also help in gas detection?

Yes! Photodetectors help improve safety through efficient gas detection in industrial environments. To summarize, lasers and photodiodes are integral to industrial advancements.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section highlights the practical applications of optoelectronic devices made from compound semiconductors, detailing how lasers, photodiodes, LEDs, and other devices are implemented across different industries, including communication systems, consumer technology, automotive features, healthcare innovations, and industrial processes.
Detailed
Real-World Applications of Optoelectronic Devices
Optoelectronic devices, such as LEDs, lasers, and photodetectors, have numerous real-world applications that significantly enhance technology across various sectors. The use of compound semiconductors allows these devices to perform efficiently and effectively in tasks requiring the interaction of light and electronics.
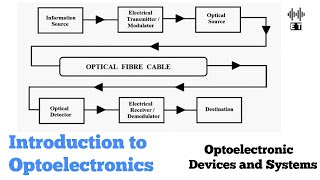
- Communication: In the communication sector, lasers and photodiodes are primarily used in fiber optics and data centers. They facilitate high-speed data transfer and long-distance communication, leveraging the efficiency of guided light.
- Consumer Electronics: Consumer electronics heavily rely on LEDs and Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers (VCSELs). This includes applications in televisions, smartphones, and infrared sensors, which contribute to modern visual and interactive technology.
- Automotive: In the automotive field, GaN (Gallium Nitride) LEDs and infrared photodetectors are utilized in headlights and parking sensors, enhancing safety and visibility in vehicles.
- Healthcare: Healthcare applications employ lasers and infrared detectors for diagnostic tools such as pulse oximeters and medical imaging systems, where precise light interaction is crucial for accurate readings and procedures.
- Industrial: In industrial settings, lasers and photodiodes find usage in welding, barcode scanning, and gas detection, improving productivity and safety through reliable and fast technology.
Through these applications, optoelectronic devices demonstrate their significance in integrating light and electronic functionalities, further driving advancements in technology.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Applications in Communication
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Devices Used: Lasers, Photodiodes
- Application Example: Fiber optics, datacenters
Detailed Explanation
In the communication sector, devices like lasers and photodiodes play a crucial role. Lasers are used to transmit data over long distances through fiber optic cables, which can carry significant amounts of information swiftly and efficiently. Photodiodes, on the other hand, are responsible for converting the received light signals back into electrical signals, allowing the information to be processed by electronic devices. This combination facilitates high-speed internet and data transfer services.
Examples & Analogies
Think of fiber optics like a busy highway system. Just as cars (data) travel quickly along clear roads (fiber cables), lasers transmit data swiftly through these cables. When the cars reach their destination, photodiodes are like receptionists converting the car arrivals back into instructions for the office (electronic devices), ensuring everything runs smoothly.
Consumer Electronics
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Devices Used: LEDs, VCSELs
- Application Example: TVs, smartphones, IR sensors
Detailed Explanation
In consumer electronics, Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) and Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers (VCSELs) are widely used. LEDs provide backlighting for televisions and displays, as well as illumination in various household products. VCSELs are used in sensors for smartphones, enabling features like face detection and gesture recognition. This technology enhances user experience and improves the functionality of devices we use daily.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a theater stage where LEDs are the colorful lights that create vibrant scenes for the audience (users) to enjoy. Similarly, VCSELs act like theater ushers, guiding the 'audience' (smartphone's software) to recognize and respond to the audience's presence and actions, making the interaction more engaging and intuitive.
Automotive Applications
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Devices Used: GaN LEDs, IR Photodetectors
- Application Example: Headlights, parking sensors
Detailed Explanation
In the automotive industry, Gallium Nitride (GaN) LEDs provide powerful and efficient lighting for headlights, improving visibility for drivers and enhancing safety. Infrared photodetectors are used in parking sensors, which help drivers by detecting obstacles and alerting them to their surroundings. Together, these technologies contribute significantly to safety and convenience in modern vehicles.
Examples & Analogies
Think of GaN LEDs as the bright searchlights used by modern explorers (cars) navigating through dark terrains (roads) at night. Meanwhile, the IR photodetectors act like a trusty guide dog, alerting the explorer to any hidden obstacles nearby, ensuring a smoother and safer journey.
Healthcare Innovations
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Devices Used: Lasers, IR Detectors
- Application Example: Pulse oximeters, imaging, phototherapy
Detailed Explanation
In healthcare, lasers and infrared detectors are crucial. Lasers are used in various medical procedures, including surgeries, where precision is necessary. Infrared detectors like those found in pulse oximeters measure the oxygen levels in blood and are vital for monitoring patient health. Phototherapy using lasers treats skin conditions and promotes healing, showcasing the versatility and importance of optoelectronics in medicine.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a surgeon using a laser like a scalpel, allowing for meticulous cuts without damaging surrounding tissue. In contrast, the pulse oximeter works like a flashlight in a dark room, shining light on the blood to reveal how much oxygen it carries, essential for determining a patient's health condition.
Industrial Applications
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Devices Used: Lasers, Photodiodes
- Application Example: Welding, barcode scanning, gas detection
Detailed Explanation
In industrial settings, lasers and photodiodes are integral components. Lasers help in welding materials with precision and speed, which is essential for manufacturing. Photodiodes are used in barcode scanners, enabling efficient product identification and inventory management. Additionally, laser-based gas detection systems are employed to monitor safety in environments that may contain hazardous gases.
Examples & Analogies
Think of industrial lasers as the high-tech paintbrushes used by artists (workers) who need to create strong bonds between materials (welding). Meanwhile, photodiodes in barcode scanners act like keen detectives, quickly recognizing products and ensuring that everything is accounted for in a bustling store, making operations smooth and efficient.
Key Concepts
-
Communication Sector: Lasers and photodiodes enhance data transfer in fiber optics.
-
Consumer Electronics: LEDs and VCSELs are pivotal for modern displays and sensors.
-
Automotive Applications: Optoelectronic devices improve visibility and safety in cars.
-
Healthcare Innovations: Lasers and photodetectors are key tools in diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
-
Industrial Uses: Enhancements in welding, scanning, and detection through lasers and photodiodes.
Examples & Applications
Fiber optic communication systems that utilize lasers and photodiodes to transfer data.
LED-based displays in TVs and smartphones for high-quality visuals.
Infrared photodetectors in parking sensors that improve vehicle safety.
Medical lasers used in surgical procedures and pulse oximeters for health monitoring.
Lasers in industrial settings for precision tasks like cutting steel and gas detection.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Light in a fiber, fast it flows, lasers, and sensors, that’s how data goes.
Stories
Imagine a world where light beams carry messages and images through fibers, connecting people instantly—this is the story of modern communication driven by lasers and photodiodes.
Memory Tools
'LED' for 'Light Emitting Device' makes remembering its display function quite easy.
Acronyms
PQR for Precision, Quick, Reliable in industrial applications of lasers and photodiodes.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Optoelectronic Devices
Devices that involve the interaction of light and electronics, such as LEDs, laser diodes, and photodetectors.
- Lasers
Devices that emit coherent light through stimulated emission, commonly used in communication and healthcare.
- Photodiode
A semiconductor device that converts light into an electrical current, used for detecting light in various applications.
- LED (Light Emitting Diode)
A semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it, extensively used in displays and lighting.
- GaN (Gallium Nitride)
A semiconductor material used for high-efficiency LEDs and lasers in various applications.
- VCSEL (Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser)
A type of laser diode that emits light vertically from the surface, used in optical communication.
- Infrared Detectors
Devices that detect infrared light, commonly utilized in applications such as safety sensors and imaging.
- Data Centers
Facilities used for housing computer systems and associated components, crucial for data communication.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
