Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs)
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about Photonic Integrated Circuits, or PICs. Can anyone tell me what they think a PIC might be?

Are they like electronic circuits but for light?

Exactly! PICs harness the power of light by integrating optical components such as lasers and modulators on a single chip, improving efficiency. Why do you think this is significant in technology?

It must help in making devices smaller and faster!

Correct! And this miniaturization allows for high-speed optical data transfer, which is essential in communication systems.
Materials used in PICs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What materials do you think are commonly used for making PICs?

I've heard of Gallium Arsenide; is that used?

Absolutely! GaAs and Indium Phosphide (InP) are widely used due to their excellent optical properties. Can anyone think of the advantages of using these materials?

They probably have good efficiency for light and electricity?

Right again! Their direct bandgap enables efficient light emission, which is crucial for devices designed for optical communications.
Applications of PICs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss applications. Where do you think we could see the impact of PICs?

In smart lights and displays!

Exactly! PICs are crucial in developing energy-efficient smart lighting systems and advanced display technologies. Why do you think that matters?

Because they save energy and allow for better designs?

Precisely! They lower power consumption and reduce the size of the devices, making technology more sustainable.
Heterogeneous Integration in PICs
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about heterogeneous integration. What do you think it means?

It sounds like combining different materials for better performance.

That's correct! Heterogeneous integration allows us to mix materials like GaN LEDs with silicon for low-cost production. Why is that beneficial?

It makes production cheaper and allows for more options?

Exactly! This process opens doors for scalable optoelectronic systems, driving innovation forward.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs), which integrate various optoelectronic components onto a single chip, facilitating high-speed optical data transmission. The section highlights advancements in using InP and GaAs platforms for miniaturization and integration in applications such as smart lighting and display technologies.
Detailed
Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs)
Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs) represent a significant advancement in optoelectronic device fabrication. By integrating multiple components like lasers, modulators, and detectors on a single chip, PICs enable miniaturization and enhance the speed and efficiency of optical data transfer. The primary materials used for these circuits are Indium Phosphide (InP) and Gallium Arsenide (GaAs), both known for their exceptional optical and electronic properties.
PICs stand as a cornerstone in modern communication systems due to their capability to significantly reduce the form factor while maintaining performance levels. This is crucial in applications such as smart lighting, display panels, and high-speed data networks, where space and efficiency are paramount. Innovations in heterogeneous integration techniques allow for combining different materials, which opens new avenues for developing cost-effective and scalable optoelectronic systems. As the demand for fast and reliable optical networks continues to grow, PICs are poised to play an increasingly vital role in the evolution of integrated photonics.
Youtube Videos


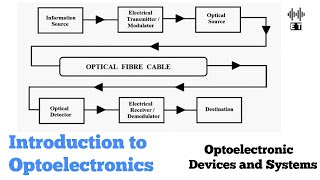

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Photonic Integrated Circuits
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs) combine lasers, modulators, and detectors on a single chip using InP or GaAs platforms.
Detailed Explanation
Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs) are advanced technology that integrates multiple optoelectronic devices such as lasers, modulators, and detectors onto one chip. This integration is possible using suitable semiconductor materials like Indium Phosphide (InP) or Gallium Arsenide (GaAs). By placing these components together, PICs can perform complex functions while being compact and efficient.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a PIC as a smartphone that combines different functions like a camera, GPS, and music player into one device. Just as a smartphone allows you to do many things without needing separate gadgets, PICs allow multiple functionalities to happen on a single chip, which saves space and energy.
Advantages of PICs
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
PICs enable miniaturized, high-speed optical data transfer.
Detailed Explanation
One of the main advantages of Photonic Integrated Circuits is their ability to miniaturize the components needed for optical data transfer. By integrating all the necessary parts on a single chip, not only is the size reduced, but it also allows for faster data transmission. This high-speed performance is crucial in applications like telecommunications where quick data exchange is essential.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a busy highway where multiple lanes are merged into a single lane. If all the traffic is managed efficiently, cars can move faster even in a smaller space. Similarly, PICs streamline the optical communication process, allowing high-speed data transfer within a compact form factor.
Key Concepts
-
Integration: Multiple optical components combined on a single chip for efficiency.
-
Materials: Use of InP and GaAs due to their optical properties.
-
Applications: Importance in smart lighting and displays.
Examples & Applications
Example of PICs: The integration of a laser, modulator, and photodetector on a single chip for fiber optic communication.
An application of GaN LEDs integrated into smart lighting systems for efficient energy use.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
PICs fit a mix on a chip, for lasers and detectors to zip!
Stories
Imagine a tiny garden where different plants coexist. Each plant represents a different optical component, and together they create a beautiful, efficient environment — that's how PICs work with lasers, modulators, and detectors on a single chip!
Memory Tools
When thinking about PICs, remember: 'LMD' (Laser, Modulator, Detector) - these are the key elements integrated together.
Acronyms
PICS means
for Photonic
for Integrated
for Circuit
for System!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs)
Devices that integrate multiple optical components like lasers, modulators, and detectors on a single chip.
- Indium Phosphide (InP)
A semiconductor material known for its efficiency in optoelectronic applications.
- Gallium Arsenide (GaAs)
A direct bandgap semiconductor used for lasers and high-efficiency optoelectronic devices.
- Heterogeneous Integration
The process of combining different materials to enhance device performance.
- Modulator
A device that encodes information onto a light wave.
- Optical Data Transfer
The transmission of data using light signals through optical fibers or other mediums.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
