Wheelchair-Friendly Toilets & Public Facilities
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Principles of Accessibility
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the principles of accessibility in designing public facilities. Who can tell me why equitable use is important?

Equitable use ensures that everyone, regardless of their ability, can use the facilities.

Exactly! Equitable use promotes that inclusivity aspect. Let's talk about other principles too. What do you think 'tolerance for error' means?

It must mean ensuring the design minimizes hazards to the users?

Good point! This principle helps in creating safe spaces. Let’s remember the acronym 'E-F-S-P-L-T', which stands for Equitable, Flexible, Simple, Perceptible, Low Effort and Tolerance for Error to sum up these principles. Can anyone repeat that?

E-F-S-P-L-T!

Great! Always remember this to connect back to our discussion on accessibility principles.
Dimensions and Clearances in Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In the design of accessible toilets, can anyone mention a critical minimum space requirement?

The turning radius should be 1500 mm diameter!

That's right! Why do you think this measurement is important?

It allows wheelchair users to navigate without obstacles.

Exactly! Another key is the door width; what is the minimum requirement?

900 mm clear opening.

Yes, and remembering such specifics is vital, as they directly impact usability!
Features of Wheelchair-Accessible Toilets
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve into the crucial features of wheelchair-accessible toilets. What are some features you think are necessary?

Grab bars should be included for support.

Good! How about the height of the W.C. seat?

It should be between 450 and 500 mm.

Exactly! Also, providing lever-type faucets or sensor-operated ones makes it easier. Can you all recall the types of designs we discussed?

Western-style toilets are the preferred design.

Absolutely! Understanding these features is key to designing truly accessible environments.
Importance of Signage and Safety Features
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Signage plays a vital role in ensuring accessibility. What features should signage have?

It should include Braille and be highly visible.

Correct! High contrast is vital. Now, what about safety features?

Slip-resistant floors and emergency alarms are essential.

Yes! These safety features help prevent accidents and provide users with a sense of security. Can anyone remember how we ensure installations are compliant?

By following the ADA and ISO standards.

Exactly! Compliance ensures that the accessibility requirements are met.
Retrofitting and Urban Planning
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Retrofitting existing toilets for accessibility is crucial. What is one modification needed?

Widening doorways to meet the 900 mm requirement.

Excellent! Retrofitting must be cost-effective. What techniques could be used?

Surface-mounted rails require no chiseling.

Right! Now, as we integrate this into urban planning, what should be considered?

Creating barrier-free paths in public spaces.

Exactly! These considerations promote inclusivity across the board.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section emphasizes creating inclusive environments through wheelchair-accessible toilets and public facilities. It outlines essential design principles, dimensions, features, and compliance standards necessary for ensuring functionality and dignity for users, highlighting the importance of flexibility and user-centered planning.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
This section focuses on the principles and guidelines necessary for creating wheelchair-friendly toilets and public facilities, reinforcing the concept of Universal Design. Key principles, such as equitable use and flexibility, illustrate the necessity of accommodating diverse needs among users. Detailed measurements for essential components including turning radiuses, door widths, and fixture heights ensure that facilities support independence and dignity.
Key Design Considerations
- Accessibility Principles: The section outlines critical design values including simple and intuitive use, perceptible information, and safe, low-effort physical requirements to enhance usability for individuals with disabilities.
- Dimensional Standards: It provides precise dimensions, such as door widths of 900 mm and a height of W.C. seats between 450-500 mm, to facilitate comfortable access.
- Facility Features: The design must incorporate accessible features like grab bars, anti-skid flooring, and user-friendly fixtures to ensure safety and usability.
- Signage and Communication: The importance of clear signage, including Braille and high-contrast indicators, is emphasized to facilitate navigation for differently-abled individuals.
- Gender-Neutral and Family-Friendly Considerations: Facilities should also cater to caregivers and families, ensuring privacy and adequate space are maintained.
- Compliant Construction Practices: Engineers are instructed to adhere to various codes and standards (like ADA, ISO) for effective implementation.
- Retrofitting Practices: Suggestions are made to modify existing structures to improve accessibility sustainably.
In conclusion, this section provides a comprehensive view on best practices in designing wheelchair-accessible toilets and public facilities, underlining the role of civil engineers in fostering inclusivity.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Wheelchair-Friendly Design
Chapter 1 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Creating an inclusive built environment is a key aspect of Universal Design, especially in the context of persons with disabilities (PwDs). Among the most critical components of such environments are wheelchair-friendly toilets and public facilities, which promote dignity, independence, and equal access for all.
Detailed Explanation
This introduction emphasizes the importance of designing spaces that are accessible to individuals with disabilities, specifically those who use wheelchairs. An inclusive environment ensures that all individuals can navigate public spaces without barriers, supporting their dignity and independence.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine visiting a park where all paths and facilities are designed so everyone, regardless of their mobility, can enjoy. Accessible toilets allow for families with diverse needs to feel welcome and comfortable.
Principles of Accessibility
Chapter 2 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Equitable Use – Design should be useful to people with diverse abilities.
- Flexibility in Use–Accommodate a wider range of individual preferences and abilities.
- Simple and Intuitive–Easy to understand regardless of user’s experience or cognitive ability.
- Perceptible Information – Communicate necessary information effectively.
- Tolerance for Error – Minimize hazards.
- Low Physical Effort–Use should be comfortable without causing fatigue.
- Size and Space for Approach and Use – Adequate clearance for wheelchair approach, reach, and manipulation.
Detailed Explanation
These principles guide the design of toilet facilities and public spaces to ensure they are accessible for everyone. Each principle highlights a key aspect of the design process, ensuring spaces are not only usable but also welcoming for people with varying abilities.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a public restroom where the doors open automatically (Equitable Use), the heights of the fixtures are friendly for all users (Flexibility in Use), and signs are large and clear. This makes the experience easier and safer for everyone.
Dimensions and Clearances
Chapter 3 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Toilets and public facilities must be designed in accordance with ergonomic dimensions for wheelchair users:
- Minimum Space Requirements
- Turning radius: 1500 mm diameter
- Approach space: 900 mm width (minimum)
- Door width: 900 mm clear opening
- Height of W.C. seat: 450–500 mm from floor
- Grab rail height: 800–850 mm from floor
- Washbasin height: 800–850 mm from floor with knee clearance.
Detailed Explanation
This section outlines the essential measurements that must be incorporated when designing wheelchair-accessible toilets. These dimensions ensure that a user can easily approach, enter, and use the facilities without physical strain.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a kitchen. The counter height is important for both sitting and standing cooks. Similarly, the height of toilet fixtures must accommodate those in wheelchairs so they can use the products comfortably.
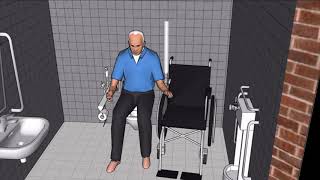
Design Features of Wheelchair-Accessible Toilets
Chapter 4 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
13.3.1 Location and Orientation
- Toilets must be located near public entryways, elevators, and other key services.
- Must be accessible via barrier-free routes.
- Entrance orientation should allow privacy while providing easy navigation.
Detailed Explanation
The location and design of wheelchair-accessible toilets are crucial for usability. If they're positioned near main access points and designed to ensure privacy while being accessible, they serve users much better.
Examples & Analogies
Think about finding a restroom in a busy mall. The closer it is to the main area and the easier it is to find, the better experience for everyone, especially someone who might need extra time navigating.
Safety and Comfort Considerations
Chapter 5 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
13.3.4 Toilet Commode (W.C.)
- Western-style (seat-type) preferred for ease of transfer.
- Rear wall and adjacent side wall must have grab bars.
- Space beside the W.C. must be at least 900 mm wide for side transfer.
Detailed Explanation
This section highlights the specific design elements that enhance safety and comfort for wheelchair users when using toilets. These include the type of toilet seat, the presence of grab bars, and ensuring appropriate space for maneuverability.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to get into a car seat from your wheelchair. A wide and supportive structure, like a grab bar, makes this easier and safer, just like how these design principles aid users in toilets.
Final Thoughts on Wheelchair-Friendly Facilities
Chapter 6 of 6
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Accessibility is not a one-time achievement — it requires constant upkeep. Civil engineers must ensure that facilities remain compliant with standards and continue to meet the needs of users.
Detailed Explanation
Ensuring accessibility in public facilities is an ongoing process, requiring regular maintenance and monitoring to adapt to the needs of users and comply with updated standards.
Examples & Analogies
Just like how a restaurant regularly checks its facilities to ensure they are clean and working, public facilities must continually assess their accessibility to provide the best experience for everyone.
Key Concepts
-
Universal Design: Principles aimed at creating accessible environments for everyone.
-
Accessibility Standards: Guidelines that must be followed to ensure facilities are accessible.
-
Ergonomic Dimensions: Measurements that consider the comfort and usability for individuals with mobility impairments.
Examples & Applications
The installation of grab bars in restrooms assists individuals in transitioning to and from wheelchairs safely.
Public transport stations are incorporating elevators and wide doors to accommodate wheelchair users.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In toilets for all, grab bars stand tall, keep them near and safe from a fall.
Stories
Imagine designing a public bathroom where everyone, including Alan in his wheelchair, can wash his hands easily and independently because the sink is low, and grab bars are there for him to hold on.
Memory Tools
To remember the key principles, think 'E-F-S-P-L-T' - Equitable, Flexible, Simple, Perceptible, Low Effort, Tolerance.
Acronyms
RAMP - Ramps Accessible, Minimum slope of 1
12
Pathway clear
Safety features included.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Equitable Use
Designs that are useful and accessible to people of diverse abilities.
- Flexibility in Use
Design accommodates a wide range of individual preferences and abilities.
- Minimum Space Requirement
The least amount of area needed for safe use and navigation.
- Grab Bar
A supportive bar installed in toilets to aid mobility.
- Universal Design
Design principles aimed at making environments accessible to all.
- ADA
Americans with Disabilities Act, which sets standards for accessibility.
- ISO
International Organization for Standardization; develops and publishes international standards.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
