Demonstration of Community Asset Management
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Community Asset Management (CAM)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore Community Asset Management (CAM) and discuss how it relates to disaster recovery. CAM focuses on managing physical assets used by communities. Can anyone give an example of such physical assets?

Buildings and infrastructure like schools and hospitals.

Exactly! These assets are crucial during disaster recovery. CAM helps improve the capacity of low-income communities, right?

Yes, it emphasizes not just recovery but maintaining these assets over time.

Correct! Remember, CAM is about lifecycle planning—maintaining assets and planning for their future usability.
The Lifecycle Planning Approach in CAM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve into lifecycle planning. Why do you think it’s important in CAM?

It ensures that assets are not only built but also maintained throughout their lifespan.

Great insight! Lifecycle planning aims to provide continuity in asset management. What processes can enhance community involvement in this?

Involving community members in identifying which assets need repair is essential.

Absolutely! Engaging the community fosters ownership and encourages investment in the upkeep of these assets.
Key Steps in CAM Implementation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What are the critical steps involved in implementing CAM?

Identification of community assets and assessing their condition!

Exactly! After identification, what comes next?

Community surveys to understand the needs.

Yes! These surveys help tailor recovery efforts to actual community needs. Let’s not forget about involving stakeholders. Why is this crucial?

It brings various skills and resources to the effort of recovery.

Well said! Collaboration is key to successfully managing assets in the community.
Barriers to Effective CAM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s discuss barriers to effective CAM. What do you think is a major challenge?

Limited financial resources in low-income communities can hinder efforts.

Absolutely right! But how can communities overcome this?

By collaborating with NGOs and local governments for funding.

Excellent! This teamwork is vital for overcoming obstacles in asset management.
Linking CAM with CBDRM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s integrate CAM with CBDRM. How do these two concepts link?

They both aim to empower communities to manage resources effectively, especially during and after disasters.

Precisely! CAM focuses on asset management, while CBDRM emphasizes broader disaster risk management strategies.

So, effective CAM can improve the resilience of communities to disasters, right?

Exactly! The synergy between CAM and CBDRM enhances overall recovery efforts.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section provides an overview of Community Asset Management (CAM) as a critical aspect of disaster recovery, emphasizing the management of physical assets within communities, particularly in the context of low-income populations. It also touches upon the collaborative engagement needed among stakeholders for effective implementation.
Detailed
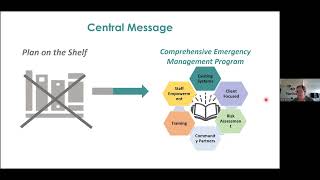
In the context of disaster recovery, Community Asset Management (CAM) focuses on the management of shared physical assets utilized by urban or rural communities. It is particularly vital for low-income communities, where poverty significantly affects resilience and recovery. CAM aims to enhance the capacity of these communities by promoting lifecycle planning of assets, which includes regular maintenance and strategic construction of both new and existing structures. The approach encourages various steps, including asset identification, surveys, stakeholder orientation, and capacity building for technical skills to ensure that communities can manage their recovery effectively. This section also bridges the concepts of CAM with Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM), illustrating their interdependence for successful disaster response and recovery efforts.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Community Asset Management (CAM)
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
CAM is the management of physical assets in collective use by urban or rural populations. It envisages improved capacity of low-income communities.
Detailed Explanation
Community Asset Management (CAM) focuses on how communities manage shared resources, such as buildings, infrastructure, and other physical assets. The goal of CAM is to enhance the capacity of low-income communities, especially in developing regions, by ensuring they can effectively use and maintain these assets. This approach recognizes that people in urban or rural settings often rely on these resources collectively, and improving their management can lead to better outcomes in terms of community resilience and sustainability.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a small village where people rely on a communal water well. CAM would involve the villagers working together to ensure the well is maintained, clean, and accessible to everyone. By managing this communal asset, the villagers can improve their access to clean water, which is vital for their health and daily lives.
Lifecycle Planning in CAM
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
CAM involves lifecycle planning, ensuring continuity in the management and maintenance of community assets.
Detailed Explanation
Lifecycle planning refers to the ongoing process of managing community assets throughout their entire life, from design through construction, use, maintenance, and eventual replacement or decommissioning. CAM emphasizes the importance of not just replacing what is lost, but also planning how to maintain and improve these assets over time. This ensures that community resources remain effective and relevant in meeting the ongoing needs of the community.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a family home. Just as a homeowner must regularly maintain the roof, plumbing, and electrical systems to keep the house livable, a community must plan for the ongoing care and upgrading of shared facilities, such as parks or community centers. If a community neglects these responsibilities, the resources may deteriorate, just like a home would if left unfixed.
Steps in Capacity Building for CAM
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Capacity building involves identifying assets, understanding their condition, and generating awareness about asset management practices.
Detailed Explanation
Capacity building in CAM includes several steps starting with the identification of community assets and assessing their current condition. This assessment helps understand what needs to be repaired or upgraded. It also involves creating awareness and providing training to community members and local authorities about the importance of managing these assets effectively. Engaging both parts of the community helps build a shared responsibility for these resources.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a school community that decides to improve its playground. They start by identifying current equipment and checking for damage. They then hold meetings to educate parents and students on maintaining the playground. In this way, they work together to ensure the playground stays safe and enjoyable for everyone.
Engaging Stakeholders in asset management
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Engagement of various stakeholders like policymakers, engineers, and community members is crucial for successful CAM.
Detailed Explanation
Engaging stakeholders means involving all relevant parties in the process of managing community assets. This can include local government representatives, engineers, community leaders, and everyday citizens. Each group can provide valuable insights and resources, which can enhance the effectiveness of asset management strategies. By working collaboratively, they can create a shared understanding of needs and goals, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility within the community.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine planning a community festival. To make it successful, you would involve local businesses for sponsorship, community leaders for organization, and residents for participation. Similarly, in CAM, getting everyone involved ensures diverse perspectives are considered, making asset management more inclusive and effective.
Demonstration as a Learning Tool in CAM
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Demonstrations of CAM at key sites can equip stakeholders with skills and shared understanding before large-scale rebuilding.
Detailed Explanation
Demonstrating community asset management strategies in real-life settings allows stakeholders to see the practical application of their learning. These demonstrations can highlight effective management practices and serve as a training tool, preparing community members and leaders for future rebuilding efforts. By testing a model on a small scale, stakeholders can work out any issues before attempting to apply the approach on a larger scale, ensuring greater success.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a cooking class where the instructor first demonstrates a recipe before the students try it themselves. This initial demonstration helps the students understand the techniques involved. In the same way, by showing how to manage community assets effectively in a pilot project, stakeholders can learn what works and what doesn't, making them better prepared for future community rebuilding efforts.
Key Concepts
-
Community Asset Management (CAM): Focuses on the management of physical assets within communities.
-
Lifecycle Planning: Involves maintaining and planning for the future of community assets.
-
Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM): Empowers communities to manage disaster risks effectively.
Examples & Applications
A community constructing a new school using local resources after a disaster.
A village implementing a regular maintenance schedule for its water supply system to prevent disruptions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For CAM to be grand, community assets must stand—through lifecycle planned, hand in hand.
Stories
In a small village, the community came together after a flood. They built a school, not just to educate but to unite, discussing how to keep their village strong during any storm.
Memory Tools
CAM - Community Assets Matter; think about Lifecycle and Management, the keys to disaster response.
Acronyms
LAMP
Lifecycle Approach to Manage Assets Properly.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Community Asset Management (CAM)
A strategy focused on the management of physical assets collectively used by communities to ensure their sustainability and usability.
- Lifecycle Planning
An approach that involves managing assets through their entire lifecycle from creation, maintenance to retirement or replacement.
- CommunityBased Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM)
An approach that empowers communities to manage risks and respond effectively to disasters by utilizing local resources and knowledge.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
