Inclusion and Participation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
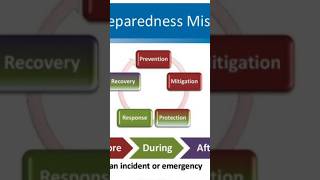
Gerando Process Overview
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're exploring the Gerando process, which is crucial for managing disaster risks in communities. Can anyone tell me why local involvement is important in disaster management?

Local people know their community best and can identify the hazards they face.

Exactly! The Gerando process begins with establishing local DRM committees. Why do we need such committees?

To coordinate efforts and ensure everyone has a voice in the process.

Great point! These committees are vital to understanding significant shocks and stresses in the community.

What kind of shocks could they identify?

Good question! They could identify droughts, floods, or even conflicts. This understanding leads us to conduct vulnerability assessments, which are essential for planning.

How do they conduct those assessments?

They analyze the vulnerabilities and capacities of the community participants. It helps them to create effective disaster preparedness plans. Remember, it's all interconnected!

To summarize, local committees initiate the Gerando process by identifying hazards and conducting assessments, which is crucial for building effective disaster management strategies.
The Importance of Social Capital
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on, let’s talk about social capital. Can anyone explain what it means in the context of community disaster management?

It includes the networks and relationships within the community that can help during disasters.

Exactly! Social capital helps strengthen community responses. How does a crisis influence social connections?

It brings people closer together and makes them collaborate more.

Right! During crises, communities often unite, enhancing cooperation. How does this relate to the effective implementation of the Gerando process?

Stronger connections mean better communication and more effective implementation of disaster plans.

Well expressed! A community's social capital not only facilitates better responses but also nurtures a culture of trust and support.

To sum up, social capital is essential in fostering collaboration and improving community resilience in disaster situations.
Transparency, Time, and Trust in Participation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss the three T’s: Transparency, Time, and Trust. Who can explain why transparency is vital?

Transparency ensures everyone understands the processes and decisions involved.

Well put! Transparency builds trust, which is essential for successful participation. Why is time significant in building relationships?

It allows community members to get to know each other and feel invested in the outcome.

Exactly! Trust creates a sense of shared responsibility. Can you think of examples of how these concepts work together in a community response?

If a community is transparent about decisions and takes time to build relations, they’re more likely to work effectively together.

Absolutely! Transparency, time, and trust reinforce one another, leading to stronger community ties and outcomes.

In summary, these three T’s are vital in ensuring meaningful community participation and collaboration in disaster risk management.
Challenges of Community Involvement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's discuss the challenges of including everyone in CBDRM activities. Why do you think inclusion can be difficult?

Not everyone may be aware of the programs or feel empowered to participate.

Great observation! There can also be power dynamics in communities that challenge equal participation. What role does empowering vulnerable groups play?

It ensures their needs and perspectives are included in the disaster management processes.

Exactly! Recognizing and incorporating the most vulnerable populations is key to successful community involvement. How can organizations improve transparency in their processes?

By sharing information about decision-making and strategies openly with the whole community.

Exactly right! Transparency about procedures empowers communities, reducing the challenges of participation. To sum it up, addressing inclusion challenges is essential for effective CBDRM.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section highlights Gerando, a process aimed at strengthening community capacities in disaster risk management through local committees and participatory methods. It stresses the significance of transparency, time, and trust in fostering meaningful community involvement, while identifying challenges such as the undervaluation of informal social networks during crises.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Inclusion and Participation
Inclusion and participation in disaster risk management (DRM) are pivotal to successful community-based disaster risk management (CBDRM). This section elaborates on the Gerando process, which supports local communities in assessing and managing hazard impacts through collaboration and local capacities.
Key Stages in the Gerando Process
The Gerando methodology consists of six integral stages: 1. Establishing local DRM committees; 2. Identifying significant shocks and stresses faced by the community; 3. Conducting vulnerability and capacity assessments; 4. Identifying early warning indicators; 5. Developing and implementing mitigation plans; and 6. Drawing up community disaster preparedness plans. A trained community coordinator facilitates this process to ensure effective participation.
Importance of Community Inclusion
The text discusses the challenges faced in recognizing the role of informal social networks and the actions taken by communities during disasters, such as search and rescue operations. Official disaster management organizations often undervalue these community responses, deeming them irrelevant due to the lack of formal direction.
The Role of Social Capital
Inclusion hinges on understanding social capital, which encompasses the networks, trust, and relationships among community members. Moments of crisis often strengthen these bonds, presenting opportunities for enhanced cooperation and unity.
Three T's of Participation
The participation process requires: 1. Transparency - clarity in communication about the benefits and drawbacks of interventions; 2. Time - necessary for building meaningful relationships and ensuring community ownership; 3. Trust - outcomes of transparency and time spent together, fostering a sense of shared goals.
Balancing Participation
The section raises the practical question of how feasible it is to involve everyone in CBDRM activities, acknowledging potential challenges. It emphasizes the need to incorporate the most vulnerable populations, enhancing efficacy through open information sharing about decision-making processes and addressing power relations within communities.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
The Importance of Participation in CBDRM
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Inclusion and expectations and that is where the participation, whom to include, how to include and because they have all different expectations and this is where the participatory methods play an important role if you are talking about participation that there is also a note of successful 3 T’s.
Detailed Explanation
Participation is crucial for the success of Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM). It involves determining whom to include in the process and how to include them effectively. Different community members have varying expectations, and addressing these is essential for successful engagement. This is where participatory methods become important, as they help facilitate inclusion and ensure that everyone’s voice is heard during the planning and implementation stages.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine organizing a community picnic. To make it successful, you need to involve everyone—families, individuals, volunteers—to gather their ideas on food, games, and location. Each person has different interests, and by discussing these together, you create a plan that satisfies most attendees. Likewise, in CBDRM, participation ensures every community member contributes to disaster management strategies.
The 3 T's of Effective Participation
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The first T talks about the transparency which requires clarity, openness, accountability and it respects a need for communities to be informed about the drawbacks of interventions as well as their benefits. Time; the second aspect is time, it is needed to build meaningful relationships between communities, outsiders and the intermediate; the in-between, to implement activities and to enable communities to take ownership of the process. The trust; it is a result of transparency and the time in the participatory process creating a sense of shared effort, goals and responsibility.
Detailed Explanation
Effective participation in CBDRM can be understood through the 3 T's: Transparency, Time, and Trust. Transparency means being clear and open about decision-making processes, allowing community members to understand both the pros and cons of proposed interventions. Time is necessary for building relationships between different stakeholders, allowing communities to take ownership of their disaster management strategies. Trust develops as a result of transparency and time, encouraging a collaborative atmosphere where everyone feels responsible for the outcomes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a school project where students form groups. If the teacher clearly explains the project goals (transparency), allows time for collaboration (time), and encourages friendship and communication (trust), the students are likely to work better together. In CBDRM, a similar dynamic occurs, where transparency, time, and trust lead to effective disaster management planning.
Engaging Vulnerable Groups
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Some of the key tools, involving the most vulnerable so, who are all affected, who are frequently targeted or who are under threat, try to involve them as much as possible that is one of the important step.
Detailed Explanation
An important strategy in CBDRM is actively involving the most vulnerable groups within the community. These groups are often the ones who face the most severe impacts from disasters, and their insights and experiences are critical for effective disaster management. Engaging these individuals ensures that their needs and concerns are addressed in the planning process, making the disaster management strategies more robust and inclusive.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a town planning a new park. If they only ask families with children for input, they might overlook the needs of elderly residents who may want benches or shaded areas. In disaster management, involving vulnerable groups means actively seeking their input to ensure that preparedness measures are supportive and effective for everyone, especially those most at risk.
Challenges of Comprehensive Participation
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
But the question is; is it practical to involve everyone all the time in CBDRM activities? This is very difficult question; this is very difficult task for any NGO to address it.
Detailed Explanation
While it’s critical to include a wide range of voices in CBDRM activities, the practicalities of doing so can be quite challenging. Not all communities may have the resources or capabilities to include everyone in every discussion or decision-making process. Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and facilitators must navigate these challenges while striving to engage a diverse group of participants as much as possible.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to create a community newsletter. If you invite everyone to contribute but don’t have the time or space to include all their ideas, it can lead to frustration and feelings of exclusion. In CBDRM, finding a balance between inclusion and practicality is essential to ensure that participation remains meaningful without overwhelming the processes.
Key Concepts
-
Gerando Process: A systematic approach to involve local communities in disaster risk management.
-
Community Involvement: The importance of including local perspectives in disaster preparedness and response.
-
Social Capital: The role of networks and relationships in enhancing community resilience.
-
Three T's of Participation: Transparency, Time, and Trust as essential elements of effective participation.
-
Challenges of Inclusion: The difficulties faced in including all community members in participatory processes.
Examples & Applications
Example of a local DRM committee successfully identifying drought as a significant shock in their community and developing a preparedness plan.
A case where transparency in the decision-making process improved the community's trust and participation rates.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When disaster strikes, community’s might, Our bonds grow strong, in dark and light.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a village, people faced a flood. They came together, sharing stories and resources, and created a plan, demonstrating the power of unity and trust.
Memory Tools
T.C.T. - Trust, Communication, Time to remember the three key aspects of participation.
Acronyms
S.C.A.R. - Social Capital, Assessments, Relationships (to remember the importance of social capital in assessing community needs).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Gerando
A process designed to support local community capacities for disaster risk management through organized committees.
- Disaster Risk Management (DRM)
Strategies and processes aimed at minimizing the risks associated with disasters.
- Social Capital
The networks, relationships, and trust among individuals within a community that can be mobilized during crises.
- Participatory Methods
Techniques that engage community members in decision-making and planning processes.
- Transparency
Openness and clarity in communication regarding decisions and processes involved in community planning.
- Vulnerability Assessment
An evaluation of the risks and weaknesses within a community that could exacerbate the impact of disasters.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
