Three T's of Successful Participation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Transparency
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're delving into the first 'T': Transparency. Can anyone tell me what transparency means in the context of community participation?

I think it means being open and honest about what’s happening.

Exactly! Transparency involves clarity and openness. It’s essential for communities to understand both the benefits and drawbacks of interventions. Remember the mnemonic 'CLO': Clarity, Listening, Openness. Let’s discuss why it’s essential for building trust.

If people are informed, they’re more likely to participate, right?

Absolutely! Transparency boosts accountability and encourages community involvement. What might happen if there’s a lack of transparency?

People might distrust the process or the facilitators.

Exactly. Trust issues can derail a whole project. In summary, transparency sets the stage for successful community engagement.
The Role of Time in Building Relationships
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's move on to the second 'T': Time. Why do you think time is important in building relationships in CBDRM?

Because without enough time, you can’t really get to know each other well.

Exactly! Time allows for stronger relationships and better collaboration. The phrase 'Time creates trust' sums it up well. Let's think about the impact if we rushed the processes.

We might miss important details and people's concerns.

Yes! The rushed approaches could lead to misunderstandings and dissatisfaction. It’s crucial to take the necessary time to build a sense of ownership. In conclusion, adequate time fosters long-lasting and productive relationships.
Cultivating Trust within Communities
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we will explore the final 'T': Trust. After discussing Transparency and Time, how do you think they contribute to building Trust?

I think if you're transparent and you take your time, people will feel more secure.

Exactly! Trust is the outcome of transparency and time spent together. It reflects a community's confidence in the participatory process and its stakeholders. How can we ensure that trust is maintained during these initiatives?

By consistently being open and delivering on promises.

Spot on! It’s all about accountability and shared responsibility. To sum up, establishing trust can significantly enhance the effectiveness of community participation.
Practical Involvement in CBDRM
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We’ve learned about the Three T's; now let’s discuss involvement in CBDRM. Is it practical to involve everybody all the time?

That sounds really challenging! Not everyone can participate in every meeting.

Right! It’s a complex issue. We need to focus on involving most vulnerable individuals as often as possible. What approaches can help with this?

Maybe using alternative communication methods or involving community leaders to gather input?

Great suggestions! Using various methods and engaging trusted figures can help amplify community voices. In summary, always strive for inclusion while navigating participation challenges.
The Intersection of Power Relations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s address power dynamics. How do you think power relations impact the participation of marginalized groups?

They might feel intimidated or ignored if the powerful people dominate the conversations.

Exactly. Unequal power dynamics can prevent effective engagement. We should strive to empower the marginalized. What can be done to change these dynamics?

Ensuring that everyone has a voice and actively encouraging contributions from all levels.

Absolutely! Promoting equal participation is crucial for a successful CBDRM process. To conclude, understanding power dynamics is foundational to fostering genuine community engagement.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
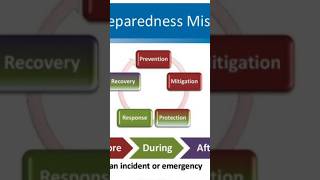
The section outlines the 'Three T's' — Transparency, Time, and Trust — which are crucial for successful participation in disaster risk management. These elements facilitate community engagement, help build relationships, and enable effective collective action. Challenges, including power dynamics and the involvement of vulnerable groups, are also discussed.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
This section highlights the 'Three T's' — Transparency, Time, and Trust — as essential elements for successful participation in community-based disaster risk management (CBDRM) initiatives.
- Transparency involves maintaining clarity and openness, ensuring that communities are well-informed about both the benefits and potential drawbacks of interventions. It is crucial for building accountability and credibility among stakeholders.
- Time plays a vital role in developing meaningful relationships. Adequate time allows community members, external facilitators, and intermediaries to collaborate effectively, leading to a shared sense of ownership over the processes involved.
- Trust emerges from the foundations of Transparency and Time; it reflects the community's confidence in the participatory processes and the efforts of involved stakeholders.
The section also raises essential questions about the practicality of involving everyone in CBDRM, emphasizing the importance of engaging vulnerable populations in decision-making. By fostering an environment of transparency and inclusion, communities can strengthen their social capital, enabling them to better prepare for and respond to disasters.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to the Three T's
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Inclusion and expectations and that is where the participation, whom to include, how to include and because they have all different expectations and this is where the participatory methods play an important role if you are talking about participation that there is also a note of successful 3 T’s.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the concept of the 'Three T's' which are key components for successful participation in community-based disaster risk management (CBDRM). It emphasizes the importance of understanding who should participate and how to involve them, considering that different individuals and groups have varying expectations. The 'Three T's' - transparency, time, and trust - will be elaborated further in the subsequent chunks, but for now, it sets the stage for why these elements are crucial in participatory methods.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine organizing a community event. Before you can plan, you need to know who wants to attend and what they expect from the event. Similarly, in disaster management, knowing who to involve and how to cater to their needs is vital. By understanding these three elements (Three T's), you can foster a stronger, more engaged community.
Transparency
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The first T talks about the transparency which requires clarity, openness, accountability and it respects a need for communities to be informed about the drawbacks of interventions as well as their benefits.
Detailed Explanation
Transparency in this context means being open and honest with the community about the processes involved in disaster risk management. It involves providing clear information regarding both the advantages and potential downsides of any interventions. When communities understand what to expect, they can make informed decisions and are more likely to participate actively in the processes. Transparency fosters a sense of ownership and involvement, as stakeholders are more willing to engage when they know that their voices are heard and considered.
Examples & Analogies
Think of transparency like being in a relationship where both partners share their thoughts and feelings openly. If one partner hides important information, trust can break down. In disaster management, openly discussing plans and potential risks is akin to maintaining that open communication, allowing the community to feel secure and supportive of the initiatives being taken.
Time
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Time; the second aspect is time, it is needed to build meaningful relationships between communities, outsiders and the intermediate; the in-between, to implement activities and to enable communities to take ownership of the process.
Detailed Explanation
The second T, time, emphasizes the importance of patience and sustained effort in building strong relationships among various stakeholders, including community members, outside organizations, and intermediaries. Establishing trust and collaboration requires time; it's not something that happens instantaneously. By dedicating time to communicate and engage with the community, all parties can develop a deeper understanding of each other, leading to more effective collaboration and ultimately, empowered communities who take ownership of disaster management processes.
Examples & Analogies
Building a friendship takes time and effort. Similarly, think of time as the glue that holds relationships together in disaster management. Just like with friends, you need shared experiences and discussions to build trust. Community engagement is the same; spending time together leads to stronger ties and a shared commitment to tackling challenges.
Trust
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The trust; it is a result of transparency and the time in the participatory process creating a sense of shared effort, goals and responsibility.
Detailed Explanation
The final T, trust, is built from the foundations of transparency and time. When communities see that outsiders are being open about processes and that efforts are being made over time to engage them, they develop trust in those involved. Trust is essential for cooperation and for fostering a collaborative environment where all stakeholders feel responsible for, and committed to, disaster management efforts. It is this shared sense of responsibility that enables a community to work together effectively during crises.
Examples & Analogies
Think of trust as the confidence you have in a team during a group project. If each member is transparent about their contributions and invests time in collaboration, the trust within the team grows. Similarly, in disaster management, when communities feel confident that everyone is working toward the same goals and that their contributions are valued, they are more likely to engage positively and actively.
Practical Considerations in Participation
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
But the question is; is it practical to involve everyone all the time in CBDRM activities? This is very difficult question; this is very difficult task for any NGO to address it.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk raises an important question about the practicality of involving every community member in all disaster risk management activities. While inclusivity is ideal, it can be particularly challenging for organizations to facilitate full participation, especially in larger communities or when resources are limited. It suggests that while participatory approaches are vital, it is important to recognize practical constraints and seek out effective ways to engage the most relevant stakeholders.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to get every student involved in planning a school event. You might face challenges due to time constraints or differing levels of interest and availability. Similarly, in disaster management, while aiming for full participation is great, finding workable solutions to involve key individuals or groups effectively can be more realistic and beneficial for achieving meaningful outcomes.
Key Concepts
-
Transparency in CBDRM: Essential for accountability and trust.
-
The significance of Time: Vital in building strong relationships.
-
Trust as a result: Emerges from transparency and time.
Examples & Applications
An example of transparency could be a community meeting where the project goals, timelines, and potential risks are clearly communicated.
An instance of the need for time would be organizing multiple community forums to discuss a disaster management plan thoroughly.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Transparency’s the key, Trust is the bond, Time helps us connect, Together respond.
Stories
Imagine a village that faced a flood. They gathered in a circle, sharing fears and hopes. Days passed, and time turned strangers into friends. With clarity, they planned together, ensuring everyone felt trusted and included.
Memory Tools
To remember the Three T's, think of TTT: Transparency, Time, Trust. Keep it simple!
Acronyms
Use 'T3' to recall the Three T's of successful participation.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Transparency
The quality of being open and clear about processes and decisions, which helps build trust.
- Time
The duration needed to cultivate meaningful relationships and ownership in community processes.
- Trust
The confidence the community has in the processes based on transparency and time.
- Social Capital
The networks and relationships that individuals or communities draw upon to achieve their goals, which can enhance collective action.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
