DFID's Resilience Framework and Livelihood Framework
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Essentials of the Resilience Framework
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today's discussion revolves around the DFID's Resilience Framework and its relationship to the Livelihood Framework. The shift from livelihoods to resilience emphasizes building communities that can withstand disasters. Can anyone explain what resilience means in this context?

Does it mean being prepared for future risks and being able to bounce back from disasters?

That's correct! Resilience is about both preparedness and recovery. Can anyone think of frameworks that support this idea?

What about the disasters risk management framework?

Exactly! There are various frameworks like the Sundae Framework and the Hugo Framework for Action. Remember these acronyms: SH (Sundae Framework) and HF (Hugo Framework) as they highlight priorities for action in resilience.

What happens if a local community lacks these frameworks?

Great question! Without these frameworks, communities are left vulnerable, which leads to greater risks during disasters.

So it's crucial to involve local communities in this framework?

Absolutely! Community involvement through CAM and CBDRM is vital for effective disaster risk management. Remember the acronym CAM for Community Asset Management.

In summary, the transition towards resilience frameworks focuses on empowering communities and building stronger networks.
Legal and Institutional Challenges
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's look at the role of legal structures in disaster risk management, especially in Nepal. Who can tell me about the challenges faced by legislation in this area?

Are there laws in place that aren't being enforced?

Precisely! Bills can remain just that—bills—without being converted into effective acts. This gap creates issues in local disaster management.

How do these legal gaps impact community disaster planning?

They hinder proper integration of disaster risk reduction into development plans. The lack of legal framework leads to insufficient local planning and community preparedness. Remember the term 'integration'—it’s key!

What could be done to bridge this gap?

Engaging local authorities in drafting and implementing disaster management plans with legal backing can help. It's all about connecting the dots between legislation and community action.

To summarize, the legal framework is essential for effective disaster management. Legal recognition strengthens community planning efforts.
Case Studies and Practical Examples
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive into some case studies such as the Pitalkhora caves and how geotechnical assessments are conducted. What makes these assessments significant?

They help understand the risks specific to that location?

Right! They guide interventions and preserve heritage. Can anyone name other cities facing similar risks?

Ayutthaya and Kiruna?

Exactly! Each has unique risks related to historical preservation and development pressures. Kiruna, for instance, must deal with mining impacts.

What lessons can we learn from these cases?

One key lesson is the importance of strategic planning—how power dynamics influence choices in disaster management and community rebuilding. Remember the acronym LAMP: Lessons from Assessment and Management Planning.

To summarize, these case studies highlight the necessity of assessing risks and developing strategic interventions to safeguard communities and heritage.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
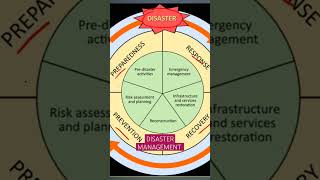
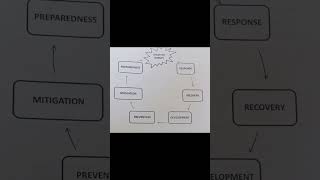
The section highlights the evolution from livelihood frameworks to resilience frameworks within the context of disaster risk and poverty. It also discusses the importance of community-based disaster risk management and legal aspects of disaster management in places like Nepal, with examples drawn from various case studies.
Detailed
DFID's Resilience Framework and Livelihood Framework
This section outlines the development of the Department for International Development's (DFID) Resilience Framework and its connection to Livelihood frameworks. Emphasizing the relationship between disaster risk and poverty, the discussion covers various global frameworks for action, including the Sundae and Hugo frameworks. The importance of institutional and community-based networks, such as community asset management (CAM) and community-based disaster risk management (CBDRM), is highlighted as essential for reducing disaster risks. Additionally, legal challenges within disaster risk management planning are discussed, particularly focusing on Nepal’s frameworks and the disconnect between disaster response and development planning.
Significant examples include the assessment of heritage sites like the Pitalkhora caves and how these have been approached from a geotechnical perspective. Comparative analysis of cities like Ayutthaya and Kiruna, along with case studies like Gibellina and Cappadocia, illustrate the challenges and interventions required for effective disaster management. Theoretical aspects of reconstruction and power dynamics are also explored, providing insights into how such frameworks can be strategically theorized and applied in practice.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Resilience Frameworks
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
And I have referred with the good practice reviews work on John Twigs work of disaster risk reduction and that is where he compiled everything all these frameworks into one segment. So, this is a very recent edition.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces us to the concept of resilience frameworks as discussed in the context of disaster risk reduction. John Twigs compiled various frameworks into a single segment, highlighting the evolution of thought in this area. The mention of 'good practice reviews' signifies an effort to gather and assess effective strategies for managing disaster risks, indicating that the information is up-to-date and relevant for current applications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a recipe book where different cooking techniques are compiled into one guide. Just as chefs combine various methods to create delicious dishes, disaster management experts gather different frameworks to effectively reduce risks associated with disasters.
Disaster Risk and Poverty Nexus
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
And where we talked about the disaster risk and poverty nexus.
Detailed Explanation
Here, the discussion shifts to a crucial connection between disaster risk and poverty. This 'nexus' refers to how vulnerable populations, often living in poverty, are disproportionately affected by disasters. Understanding this relationship is essential for creating effective policies and frameworks that address both poverty and disaster resilience simultaneously.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a community living in a flood-prone area with limited resources. When a flood occurs, those who are already struggling financially may suffer more, as they lack the means to prepare, respond, or recover. Recognizing this connection helps in designing targeted assistance for those most at risk.
Global Resilience Frameworks
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
So, when we talk about the resilience frameworks and that at a global level, how the Sundae framework, how the Hugo framework for action, what are these priorities for action.
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, the conversation expands to cover global initiatives such as the Sundae Framework and the Hugo Framework for Action. These frameworks set international priorities for action, guiding how organizations and governments should address disaster risks and build resilience. They serve as key references for developing local strategies in alignment with global standards.
Examples & Analogies
It's like following a map when traveling to an unfamiliar destination. Global frameworks act as roads on this map, showing the best routes and strategies to reach safety and resilience in disaster-prone areas.
Community-Based Networks
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
And we did also discuss about the community-based networks. That is where the CAM and CBDRM. So, this is where the community asset management and the community-based disaster risk management.
Detailed Explanation
This section highlights the importance of community-based networks in disaster management, specifically mentioning Community Asset Management (CAM) and Community-Based Disaster Risk Management (CBDRM). These approaches emphasize empowering local communities to manage their own resources and risks effectively, which can lead to more sustainable outcomes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a neighborhood that comes together to create a community garden. Not only does this provide food security, but it also helps residents learn about environmental stewardship and resilience. Similarly, when communities manage their resources and risks together, they can build stronger defenses against disasters.
Legal and Planning Challenges
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
So that is where the local disaster risk management planning guidelines know how it is not properly able to connect the disasters and development.
Detailed Explanation
The emphasis here is on the challenges faced in integrating disaster risk management with local development planning. It highlights that often, legal frameworks and guidelines are not sufficiently aligned, which can hinder effective responses to disasters. Creating coherent policies that link development and disaster risk management is crucial.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to build a bridge without a solid foundation. Just like the bridge needs good engineering principles to connect two sides effectively, disaster management needs well-thought-out policies that link development to create a resilient infrastructure.
Key Concepts
-
Disaster Risk Reduction: Strategies aimed at minimizing vulnerabilities and disaster impacts within communities.
-
Institutional Networks: Organizations such as the UN, that work together to support disaster management efforts.
-
Community Resilience: The capacity of a community to respond to and recover from disasters through shared resources and cooperation.
-
Legal Frameworks: Laws and policies that guide disaster risk management and support community preparedness.
Examples & Applications
Pitalkhora caves were assessed for risks using geotechnical perspectives.
The city of Ayutthaya illustrates heritage preservation amidst disaster risks.
Kiruna, a mining town, faces challenges due to subsidence from mining activities, prompting strategic planning.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To be safe from despair, build resilience with care, prepare and repair, so communities can fare.
Stories
Once in a town plagued by floods, residents huddled together. They knew that through collaboration and resource management, they would build back stronger than before – this is the essence of resilience.
Memory Tools
For disaster readiness, think of R.E.A.C.T: Resources, Engagement, Assessment, Collaboration, and Training.
Acronyms
D.R.M. stands for Disaster Reduction Management, a framework for minimizing disaster impacts.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Resilience Framework
A structured plan that outlines methods to enhance community preparedness and recovery in face of disasters.
- Livelihood Framework
A model focusing on the resources and livelihoods of communities, often in relation to poverty alleviation.
- CAM (Community Asset Management)
A community-driven approach to managing resources and assets for sustainable development.
- CBDRM (CommunityBased Disaster Risk Management)
A participatory method that involves communities in the development and implementation of risk reduction measures.
- Geotechnical Assessment
Evaluation of soil, rock, and groundwater conditions to inform construction and land use decisions.
- Integration
The process of bringing together various elements to work cohesively towards a common goal.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
