Influence of Damping on Seismic Response
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Seismic Response and Damping
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss how damping influences the seismic response of structures. Can anyone explain what we mean by 'seismic response'?

'Seismic response' refers to how a structure behaves during an earthquake, such as how much it moves or shakes.

That's correct! Now, how do you think damping plays a role in this response?

I think higher damping would reduce how much a building moves during an earthquake?

Exactly! Higher damping leads to lower displacements and accelerations, making structures more resilient. Remember, damping modifies the Response Spectrum, a key tool in seismic design.

What is the Response Spectrum, though?

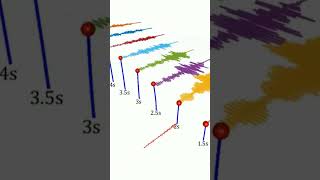
Great question! The Response Spectrum is a plot showing the peak response (displacement, velocity, or acceleration) of a structure for varying frequencies of ground motion.

So, if damping changes that spectrum, it must be important for designing buildings!

Absolutely! In our designs, we need to include damping correction factors to ensure structures can handle seismic forces efficiently.

To recap, damping is crucial for reducing seismic response and must be factored into design spectra for safety in earthquake-prone areas.
Damping Correction Factors in Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dig deeper into damping correction factors. How do they help us in seismic design?

They adjust the design spectra to account for different damping levels?

Correct! These factors are crucial because standard assumptions often only consider a typical damping ratio of around 5%. What happens when structures have higher or lower damping?

Higher damping would mean we need less force in our calculations, right?

Exactly. It’s essential to use accurate damping values to ensure our designs are both efficient and safe. Can anyone think of an example of an engineering application where this might be critical?

Maybe buildings in highly seismic regions need tailored damping for their design spectra?

Exactly! Locations like California frequently update their codes to include these factors based on recent earthquake data. This helps ensure buildings can withstand seismic forces effectively.

As we conclude, remember that damping significantly alters the seismic response. Always ensure to incorporate the correct damping factors when designing for different structures!
Practical Applications and Implications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let's consider the broader implications of our discussion. Why is effective damping critically important in earthquake engineering?

It reduces the risk of collapse during an earthquake, protecting lives.

Right! Damping also helps lower the forces exerted on structural members, enhancing safety and serviceability. Can anyone think of additional benefits?

It might also reduce repair costs after minor quakes, since structures face less damage?

Absolutely! Efficient damping can improve the lifespan of a structure. Additionally, implementing devices like tuned mass dampers can further enhance damping effects. What structures can benefit from such devices?

Tall buildings and bridges might use them, right?

Spot on! In tall buildings, these devices can significantly reduce sway and vibrations, ensuring a safer environment. Always consider the influence of damping in seismic response to optimize your designs.

In summary, effective damping reduces seismic response, impacts design spectra, and ultimately protects lives and property. Keep these principles in mind as you progress in earthquake engineering!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Damping plays a crucial role in seismic design, as it modifies the response spectrum and helps engineers account for effective damping through correction factors. Increased damping results in a lower seismic response, making structures more resilient against seismic forces.
Detailed
Influence of Damping on Seismic Response
Damping significantly influences how structures respond to seismic events. Higher levels of damping lead to a substantial reduction in seismic response, meaning that both displacements and accelerations within a building are lower, thus minimizing potential damage.
This section discusses how damping alters the Response Spectrum, a fundamental tool used in seismic design. Engineers integrate effective damping into design spectra through damping correction factors, ensuring that structures can adequately withstand seismic forces. By understanding the relationship between damping and seismic response, engineers can design safer and more effective earthquake-resistant structures.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Impact of Damping on Seismic Response
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Higher damping leads to lower seismic response (lower displacements and accelerations)
Detailed Explanation
Damping in structures plays a crucial role during seismic events, affecting how much they move (deflection or displacement) and how much force (acceleration) is experienced. When a structure has higher damping, it's better at absorbing and dissipating energy from seismic waves, resulting in a reduction in both the amount of displacement and acceleration that the structure experiences during an earthquake.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a basketball player jumping to block a shot. If the player has a strategy that allows them to absorb the force of the jump—like bending their knees and rolling with the momentum—they are less jostled when they land, compared to a player who lands stiffly. Similarly, a structure with high damping is able to 'bend' with the seismic forces, which helps it avoid serious damage.
Modification of Response Spectrum
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Damping modifies the Response Spectrum, which is used in seismic design
Detailed Explanation
The Response Spectrum is a tool used by engineers to understand how structures will respond to different frequencies of seismic activities. Damping modifies this spectrum by adjusting its shape, which helps in predicting how structures can withstand seismic forces. The effects of damping are factored in so that designs can accommodate these changes and improve safety against earthquakes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Response Spectrum as a music playlist that lists how different types of music (or frequencies) affect a listener's mood. If you play soothing music (high damping), the listener feels relaxed and less affected by any disturbances (like loud noises). Wouldn't you want to select the right playlist for a calm environment? Similarly, engineers adjust the Response Spectrum using damping to create safer structures.
Damping Correction Factors
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Effective damping is accounted for in design spectra by introducing damping correction factors
Detailed Explanation
In seismic design, correction factors are added to account for the level of damping in the structure. These factors help engineers modify their calculations to ensure that the design will perform well under various conditions, especially during an earthquake. By incorporating these factors, the designs become more reliable and tailored to specific conditions.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine baking a cake; depending on your oven's temperature accuracy, you might need to adjust the time you bake the cake. If the oven runs hot, you’ll reduce baking time. Likewise, damping correction factors adjust the design calculations, ensuring that structures take into account how their specific damping will affect their performance during seismic events.
Key Concepts
-
Higher Damping: Results in lower seismic response, reducing displacements and accelerations.
-
Response Spectrum: Essential tool in seismic design modified by damping.
-
Damping Correction Factors: Adjustments made in design spectra to account for varying damping levels.
-
Seismic Resilience: Structures with effective damping perform better under seismic stress.
Examples & Applications
In a tall building, implementing a tuned mass damper can significantly lower the vibration response during an earthquake.
Reinforced concrete structures typically have higher inherent damping, aiding in the management of seismic forces.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Damping's a friend, not a foe, it helps structures sway slow.
Stories
Imagine a tall tower swaying during an earthquake. With strong winds, it might topple over, but with dampers like a friendly guide, it gently sways, keeping safe inside.
Memory Tools
Remember DSR: Damping Saves Response! Higher damping means less response during quakes.
Acronyms
DRS
Damping Reduces Seismic effects.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Damping
The mechanism that dissipates energy in a vibrating system, reducing motion.
- Seismic Response
The behavior of a structure during an earthquake, including displacements and accelerations.
- Response Spectrum
A graphical representation of the peak response of a structure to varying frequencies of ground motion.
- Damping Correction Factors
Adjustments made to design spectra to account for varying levels of damping.
- Earthquakeresistant Structures
Buildings designed to withstand seismic forces effectively.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
